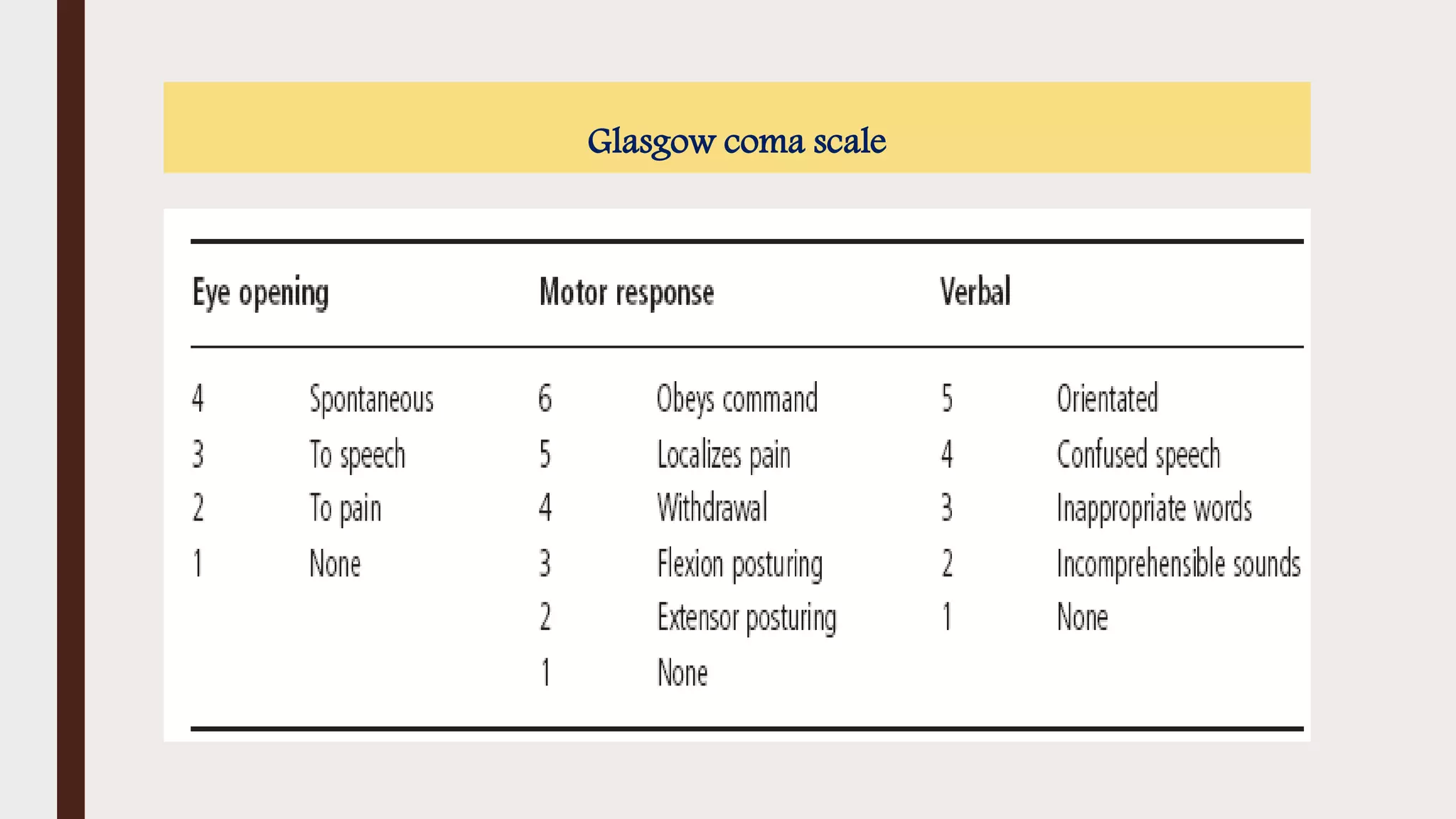
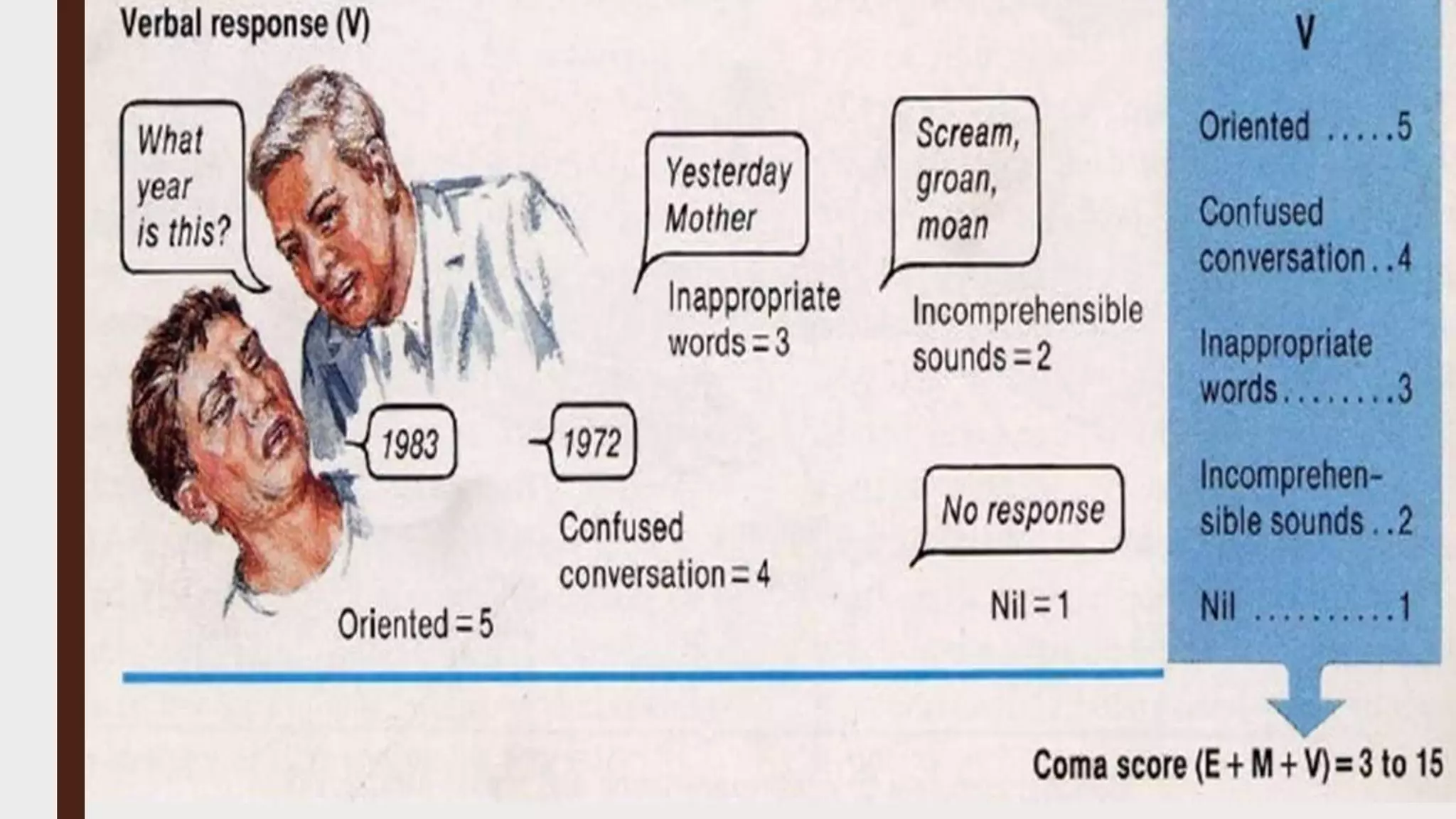
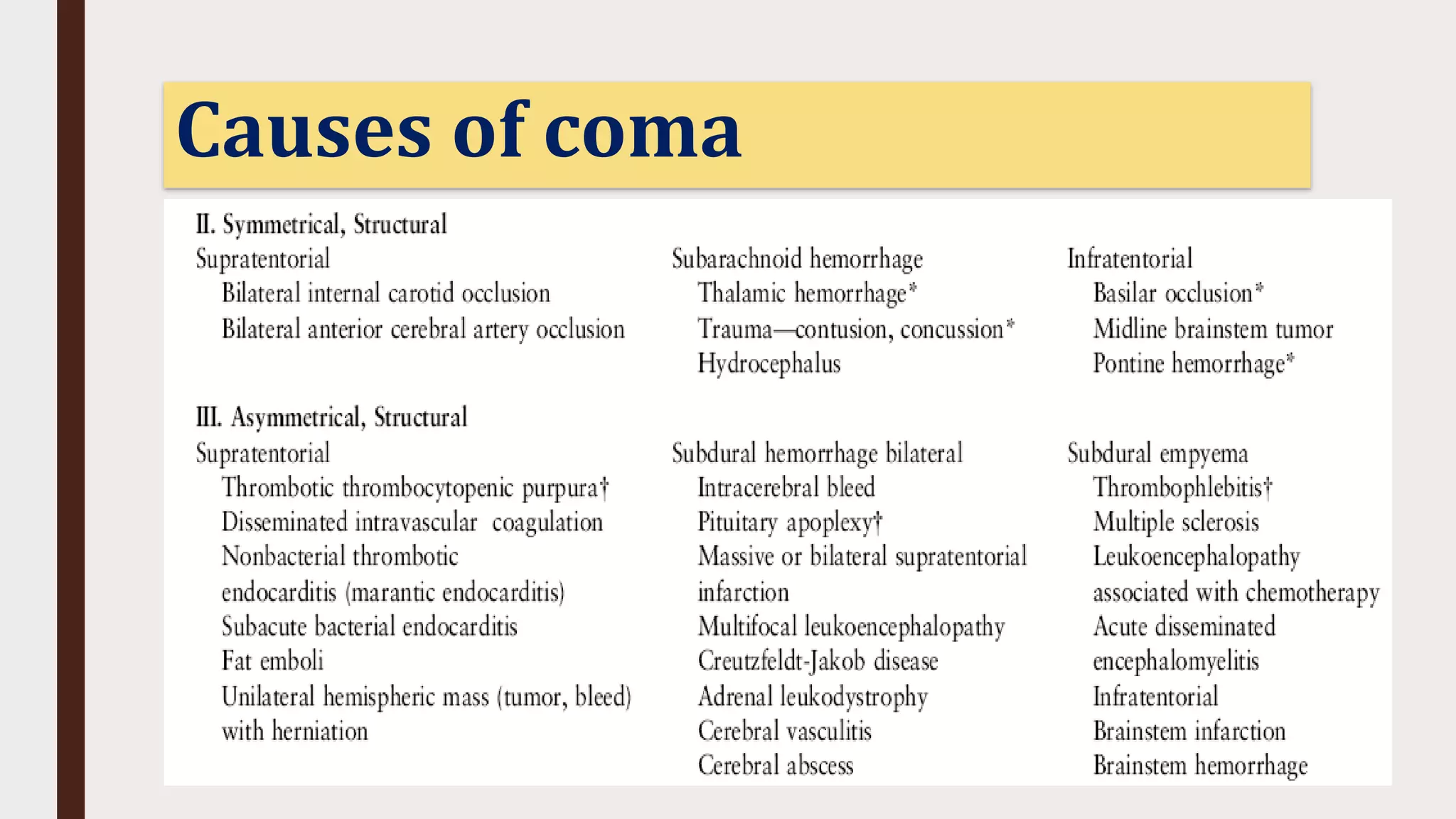
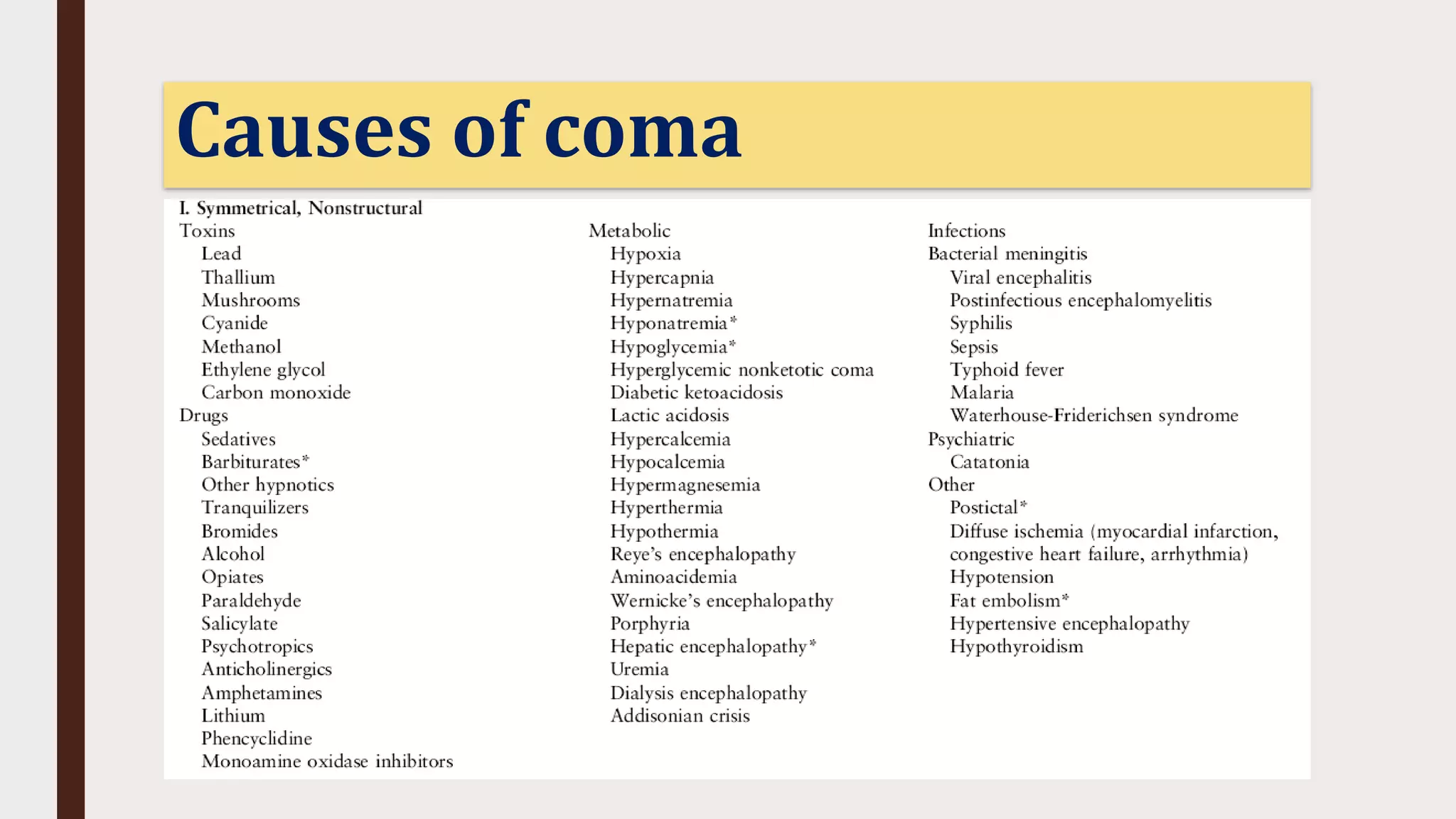
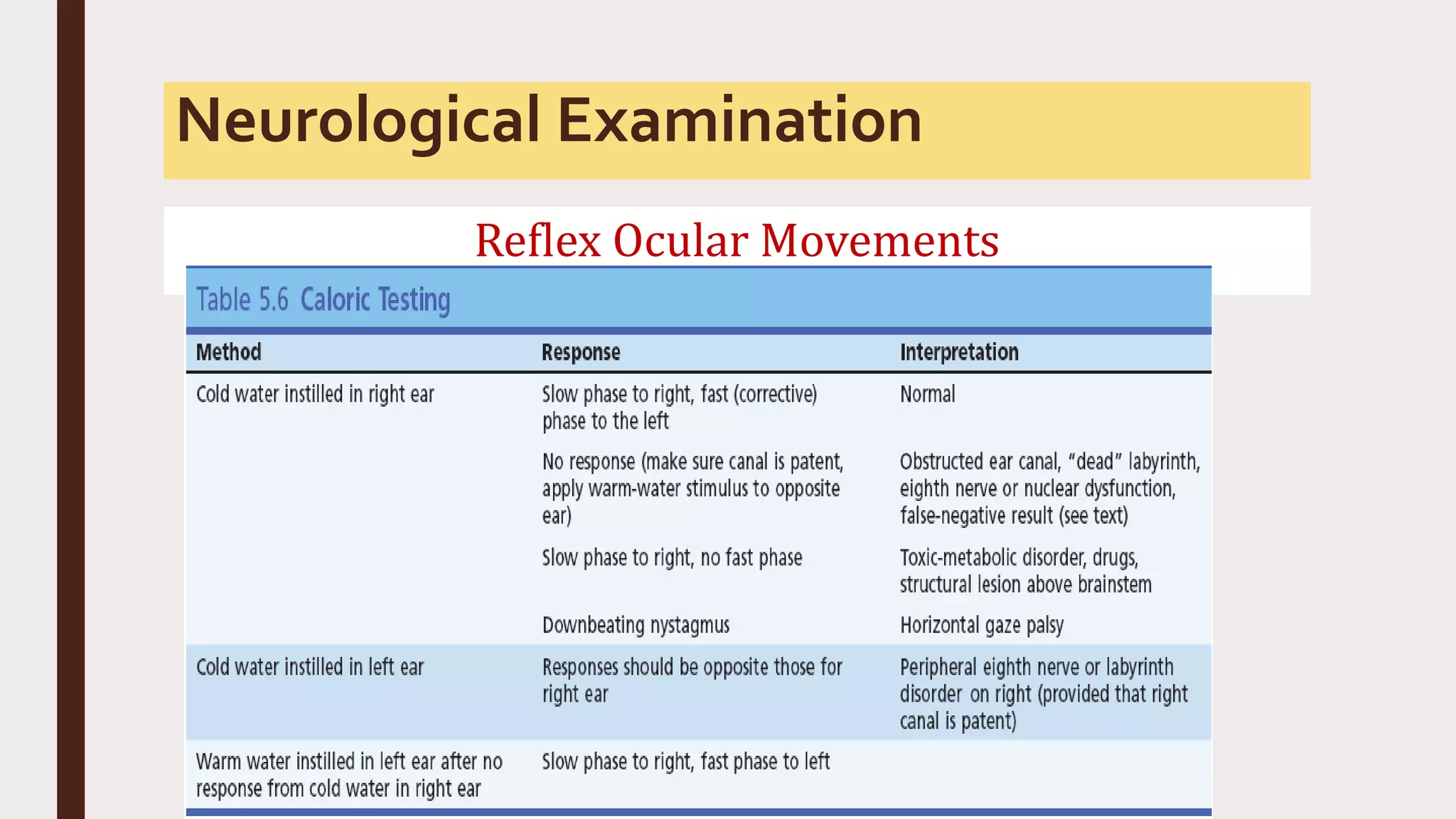
This document provides an overview of consciousness and approaches to disturbances of consciousness such as coma. It defines key terms like coma, stupor, and delirium. Coma can be caused by structural brain insults, metabolic derangements, infections, drugs or toxins. The clinical approach involves stabilizing vital functions, assessing severity using scales like Glasgow Coma Scale, and evaluating for immediate life-threatening causes through diagnostic tests and empirical treatment when needed to prevent further brain damage. A thorough neurological exam evaluates factors like consciousness level, pupil size and reactivity, ocular motility, motor responses and more to localize the cause. Distinguishing features between toxic/metabolic vs. structural comas are discussed.