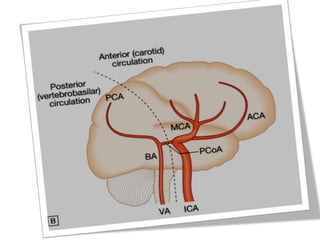
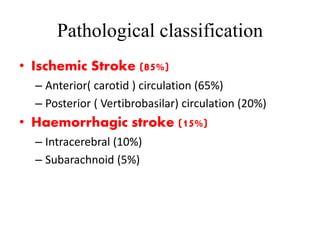
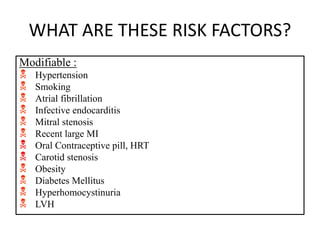
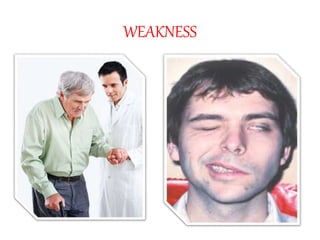
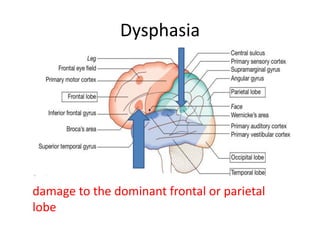
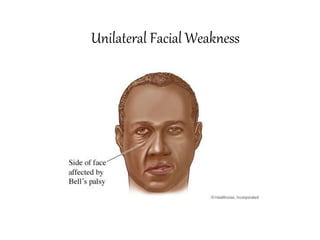
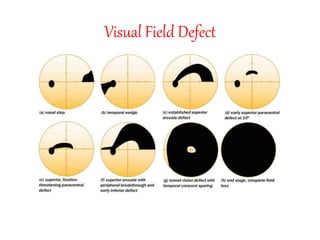
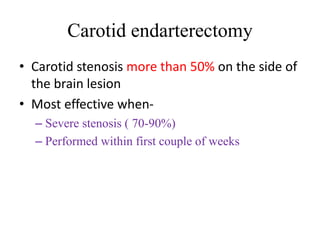
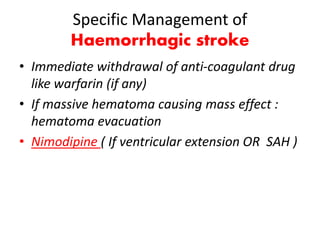
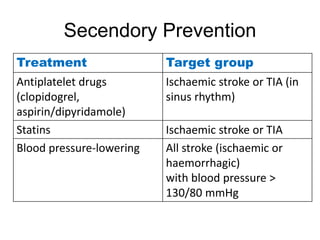
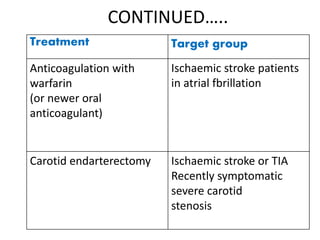
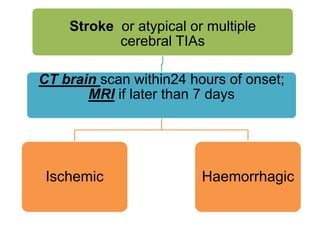
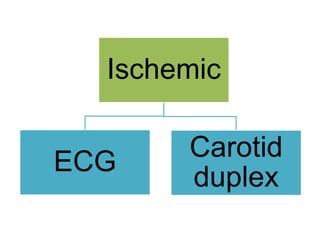
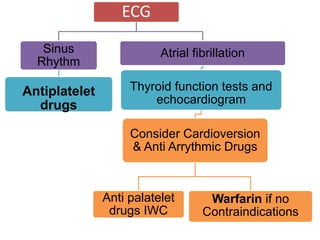
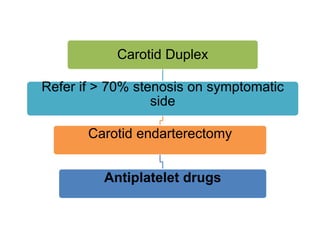
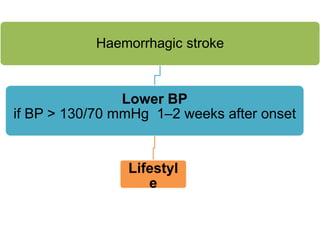
This document defines stroke as a focal brain dysfunction lasting over 24 hours caused by a non-traumatic vascular issue. It then classifies strokes as ischemic (85%) or hemorrhagic (15%) and discusses their risk factors like hypertension, smoking, atrial fibrillation, diabetes, and age. The diagnosis involves examining for weakness, speech issues, vision problems, and performing a CT or MRI scan. Investigations help identify the cause and rule out mimics. Treatment focuses on stabilizing the patient, controlling risk factors, and using thrombolysis, aspirin, or anticoagulants depending on the type of stroke. Lifestyle changes and secondary prevention aims to modify risk and prevent future strokes.