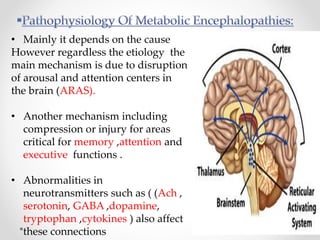
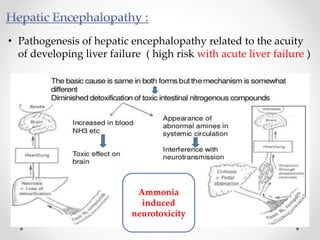
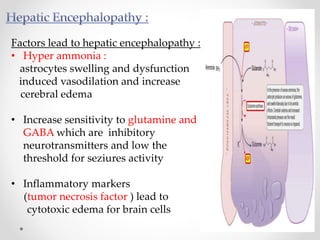
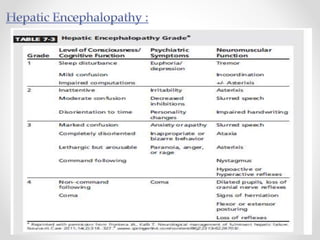
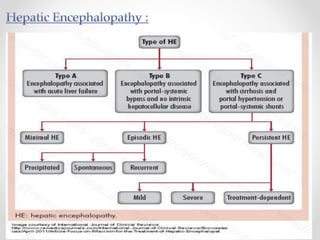
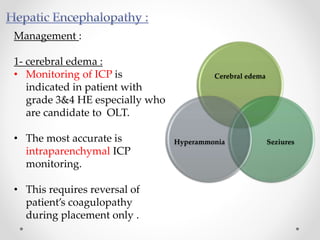
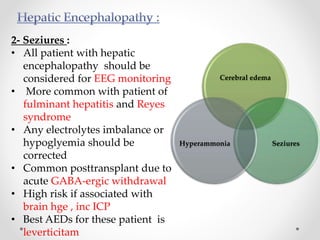
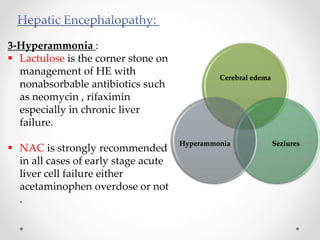
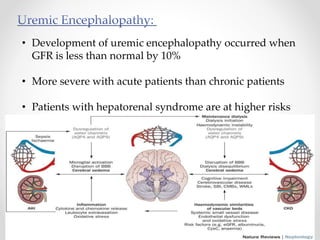
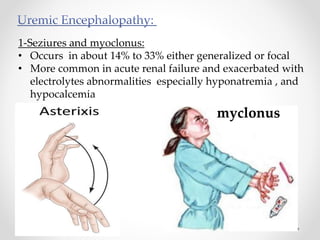
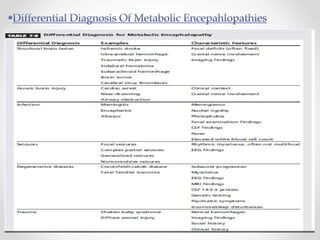
This document discusses metabolic encephalopathies, including their definition, pathophysiology, common types, diagnosis, and management. It focuses on hepatic encephalopathy caused by liver failure and uremic encephalopathy caused by kidney failure. The main mechanisms involve disruption of brain arousal centers and neurotransmitter abnormalities. Management involves treating the underlying condition, controlling seizures, reducing ammonia levels, and managing cerebral edema. Metabolic encephalopathies in critically ill patients can lead to long-term neurocognitive deficits even if the initial brain dysfunction was reversible.