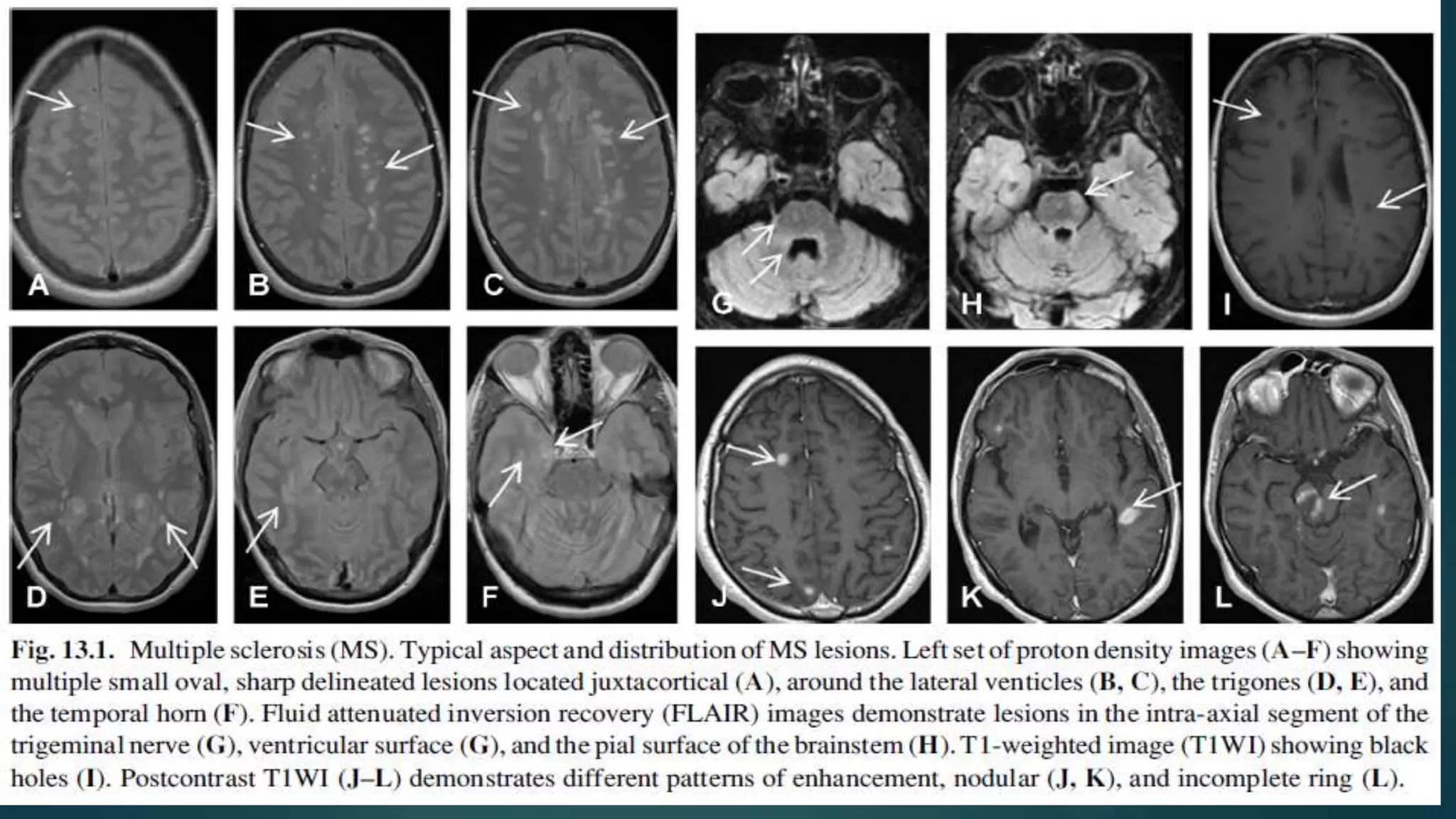
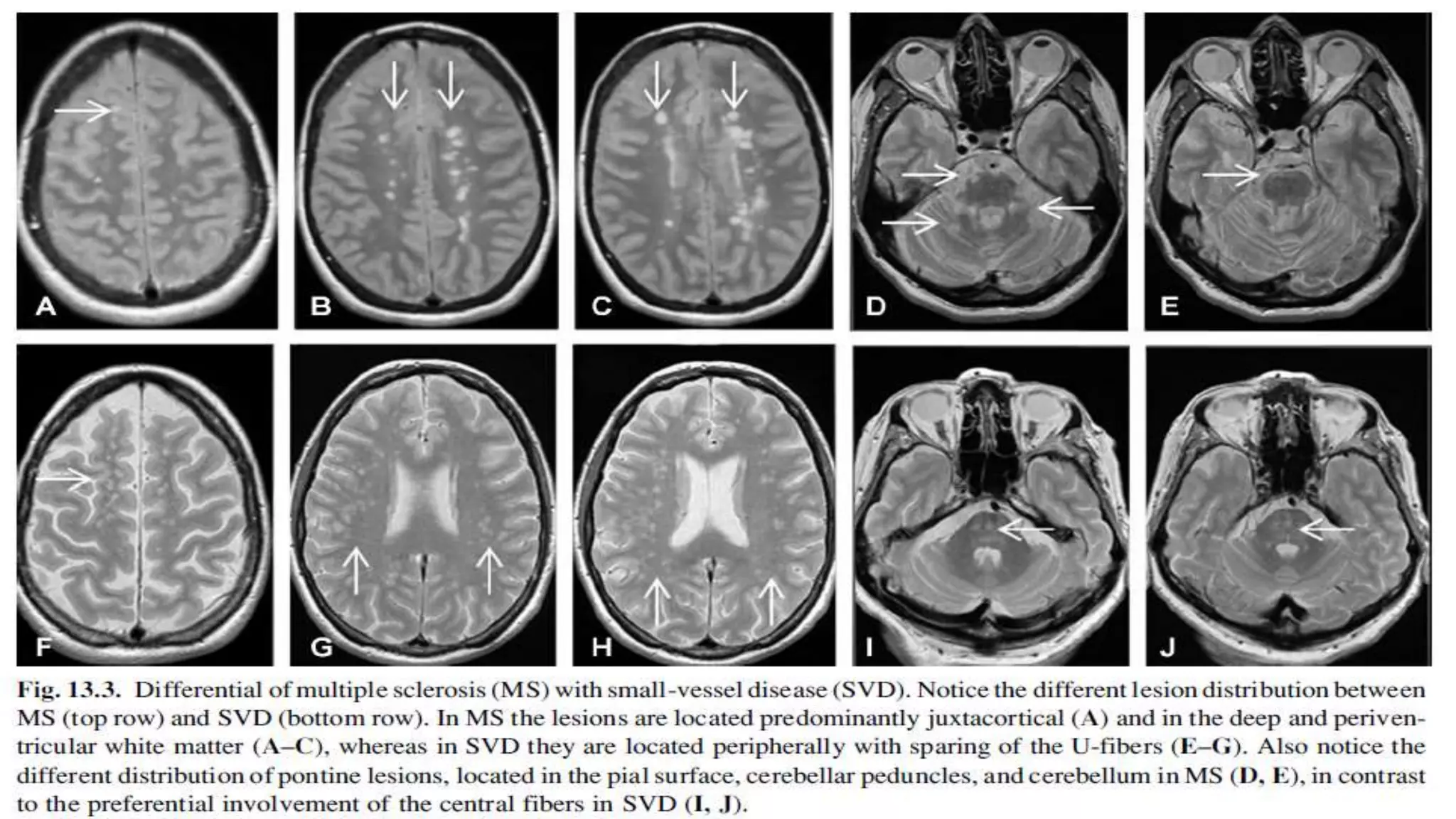
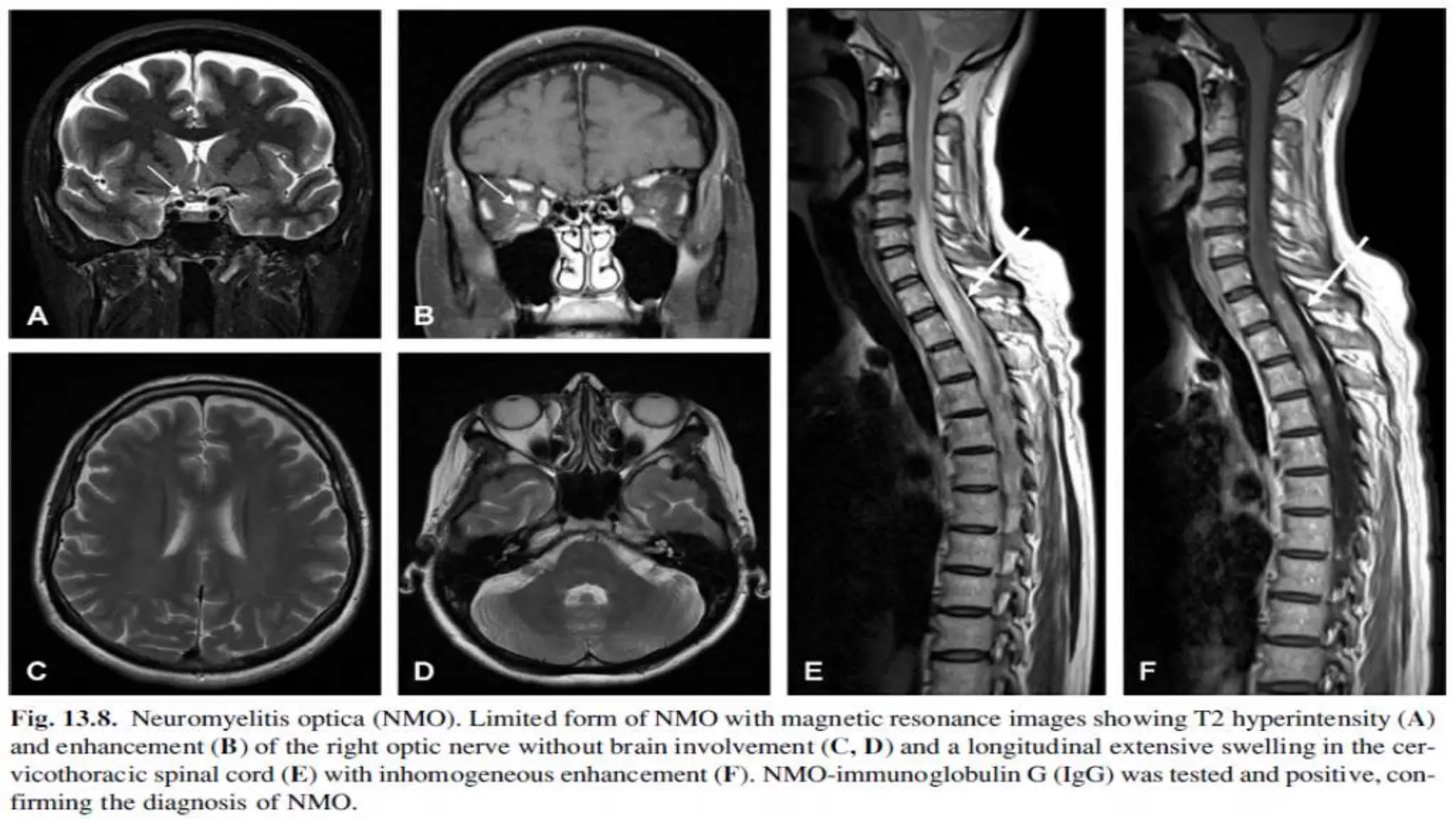
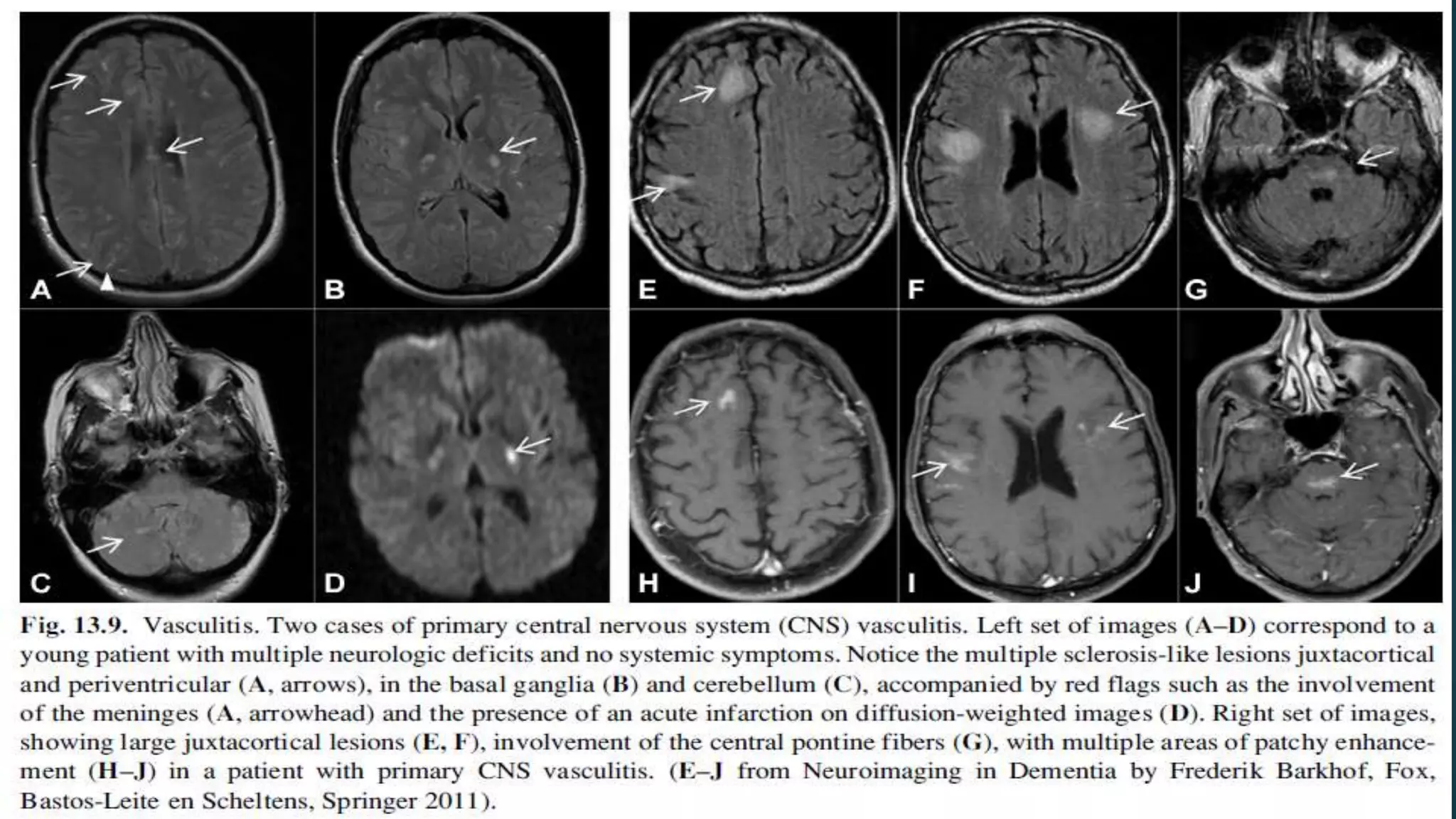
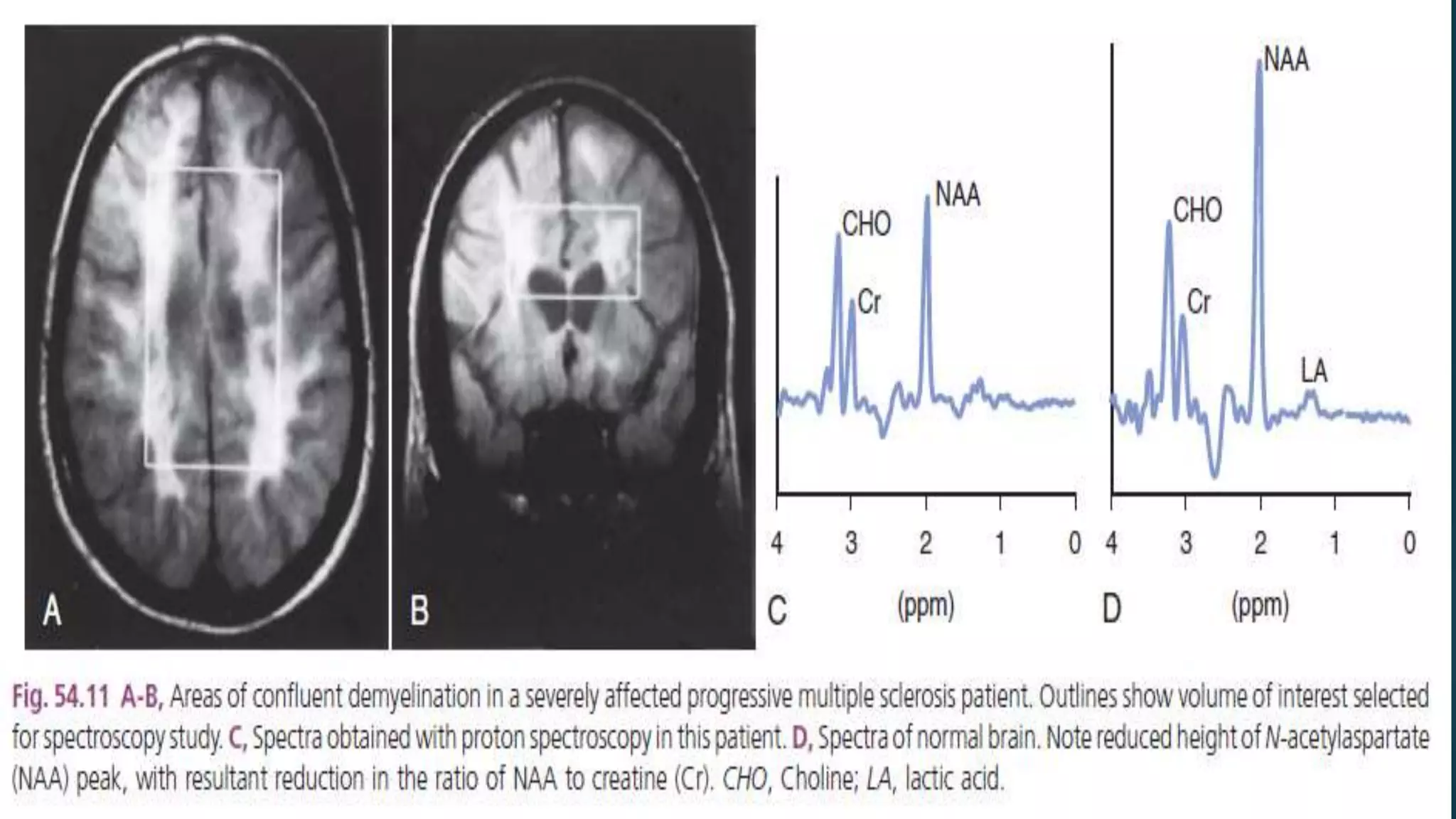
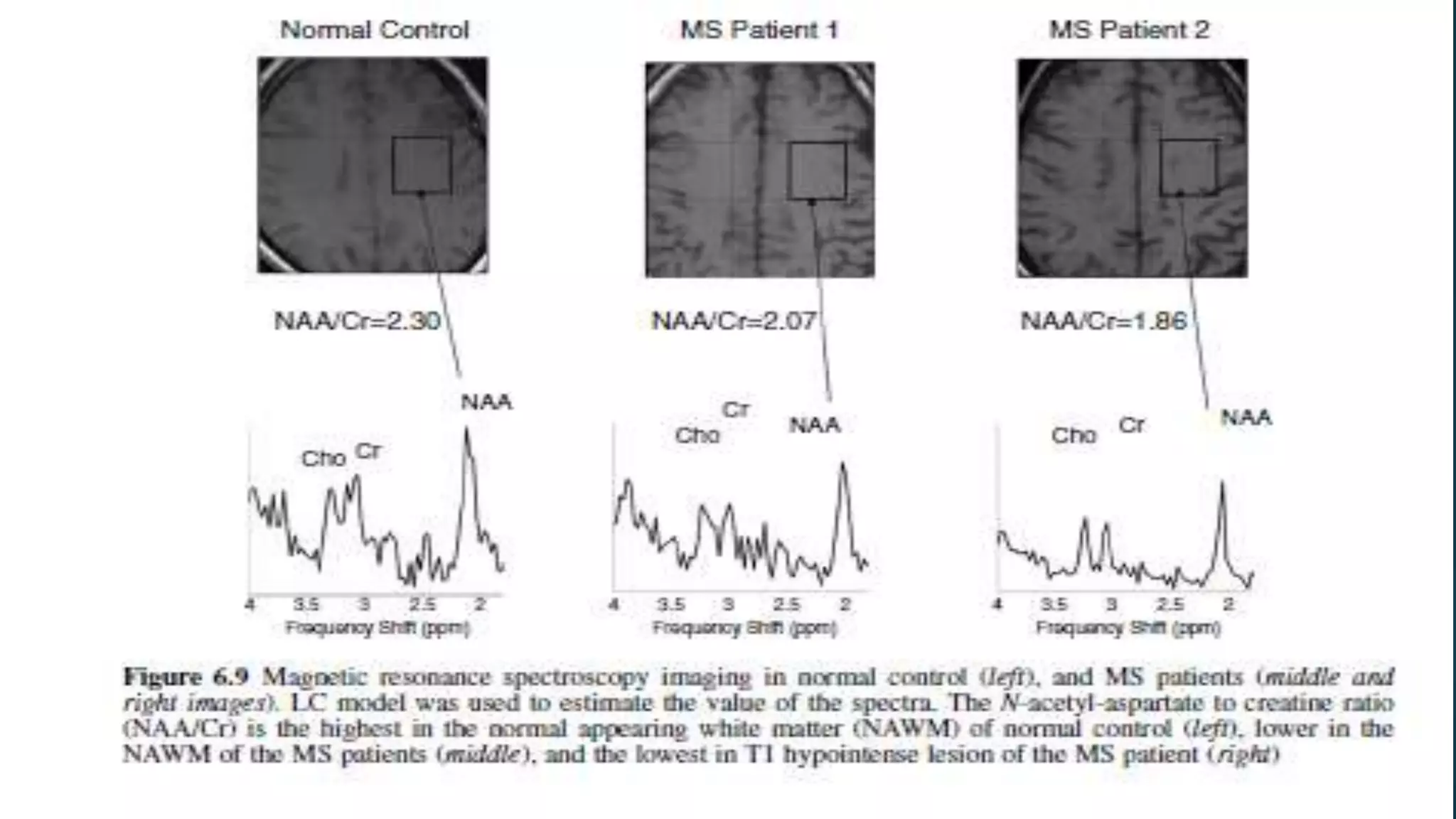
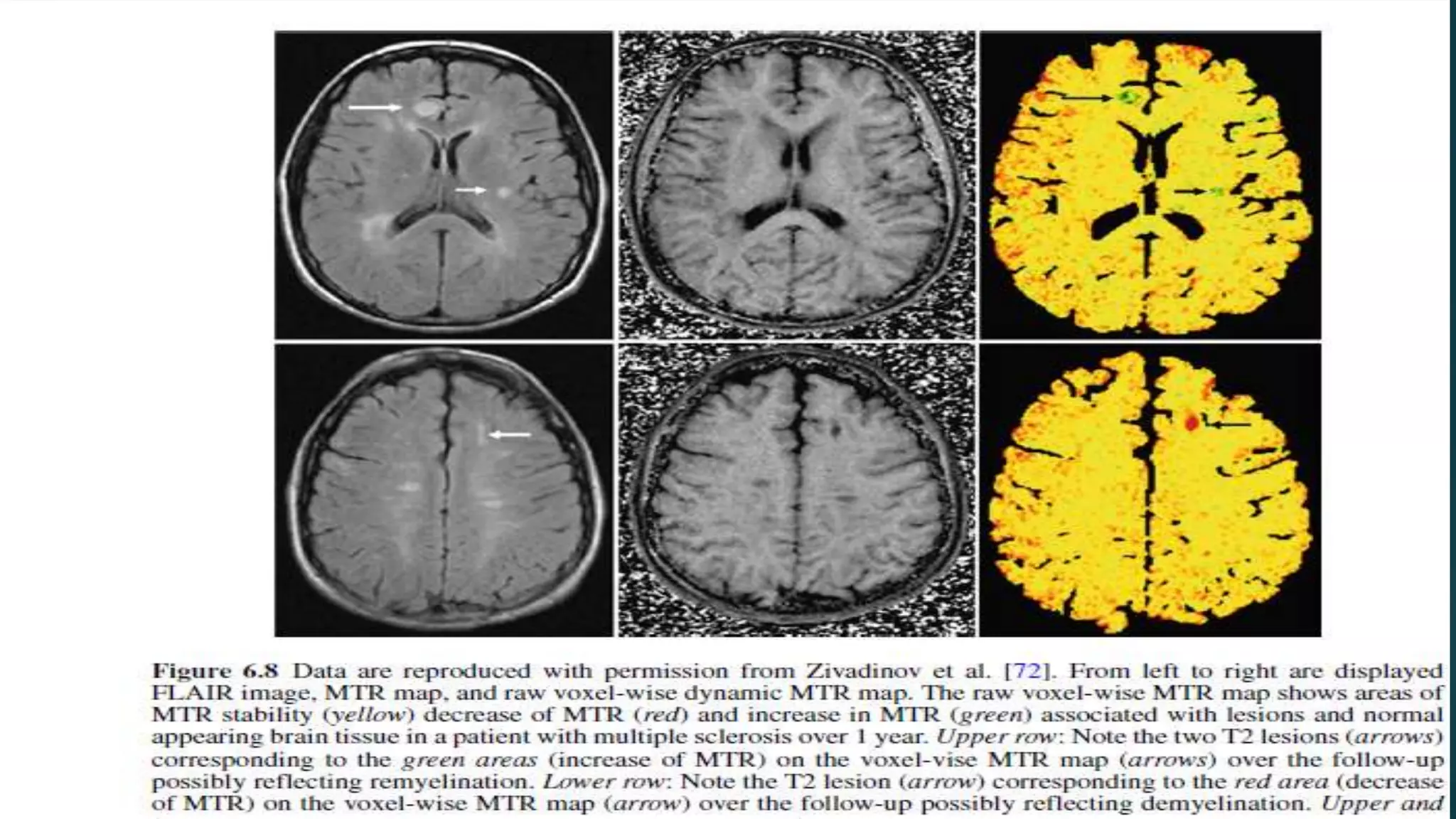
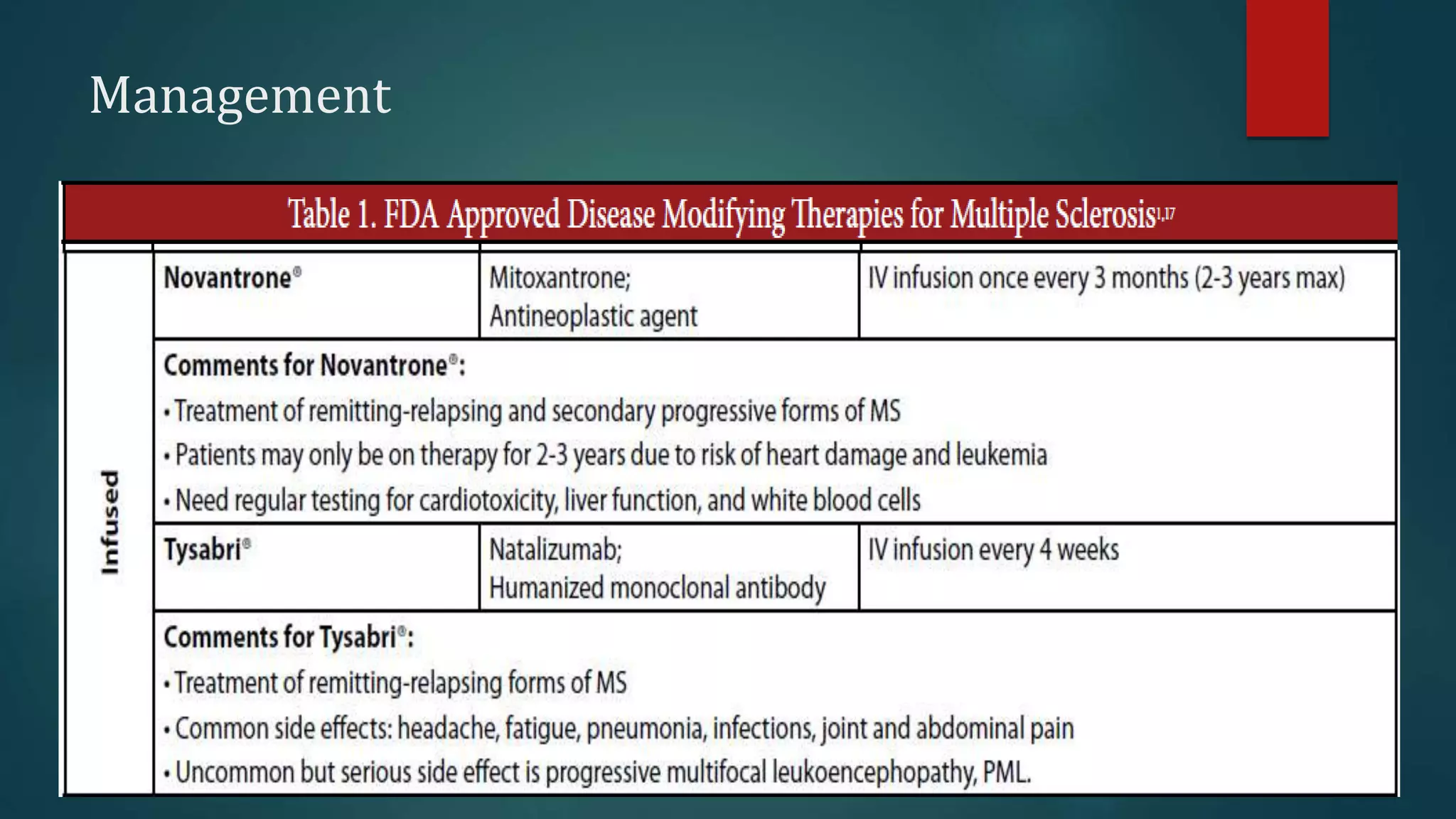
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system characterized by breakdown of the myelin sheath covering nerve axons. It affects over 400,000 people in the US and more than 2.1 million worldwide. Genetic factors, autoimmunity, infection, vitamin D levels, and loss of protective childhood infections may play a role in MS etiology. Clinically, MS presents with a variety of neurological symptoms depending on the location of lesions in the brain and spinal cord, including visual, motor, sensory and cognitive impairments. Disease courses include relapsing-remitting MS, secondary progressive MS, primary progressive MS and progressive-relapsing MS.






![Infection
little direct evidence supports the concept of a role for viral infection.
Innumerable efforts to culture a virus from autopsy-derived or biopsy
material have yielded no consistent result.
human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 [HTLV1]) have proven negative.
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV6), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and Chlamydia
pneumoniae have been the focus of interest.
High serum levels of EBV antibodies have also been associated with an
increased risk of MS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multiplesclerosis-151202003146-lva1-app6892/75/Multiple-sclerosis-8-2048.jpg)

![Vitamin D
MS patients typically have lower serum 25(OH)D levels than healthy controls .
Polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene have been of particular
interest.
candidate gene approach include two vitamin D metabolism-related genes,
CYP2R1 [which encodes the enzyme responsible for the conversion of vitamin
D to 25(OH)D] and DBP/GC (encoding the vitamin D-binding protein)
these inverse associations could also be explained by a direct effect of UVB
radiation, which has immunosuppressive effects independent from vitamin D.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multiplesclerosis-151202003146-lva1-app6892/75/Multiple-sclerosis-10-2048.jpg)