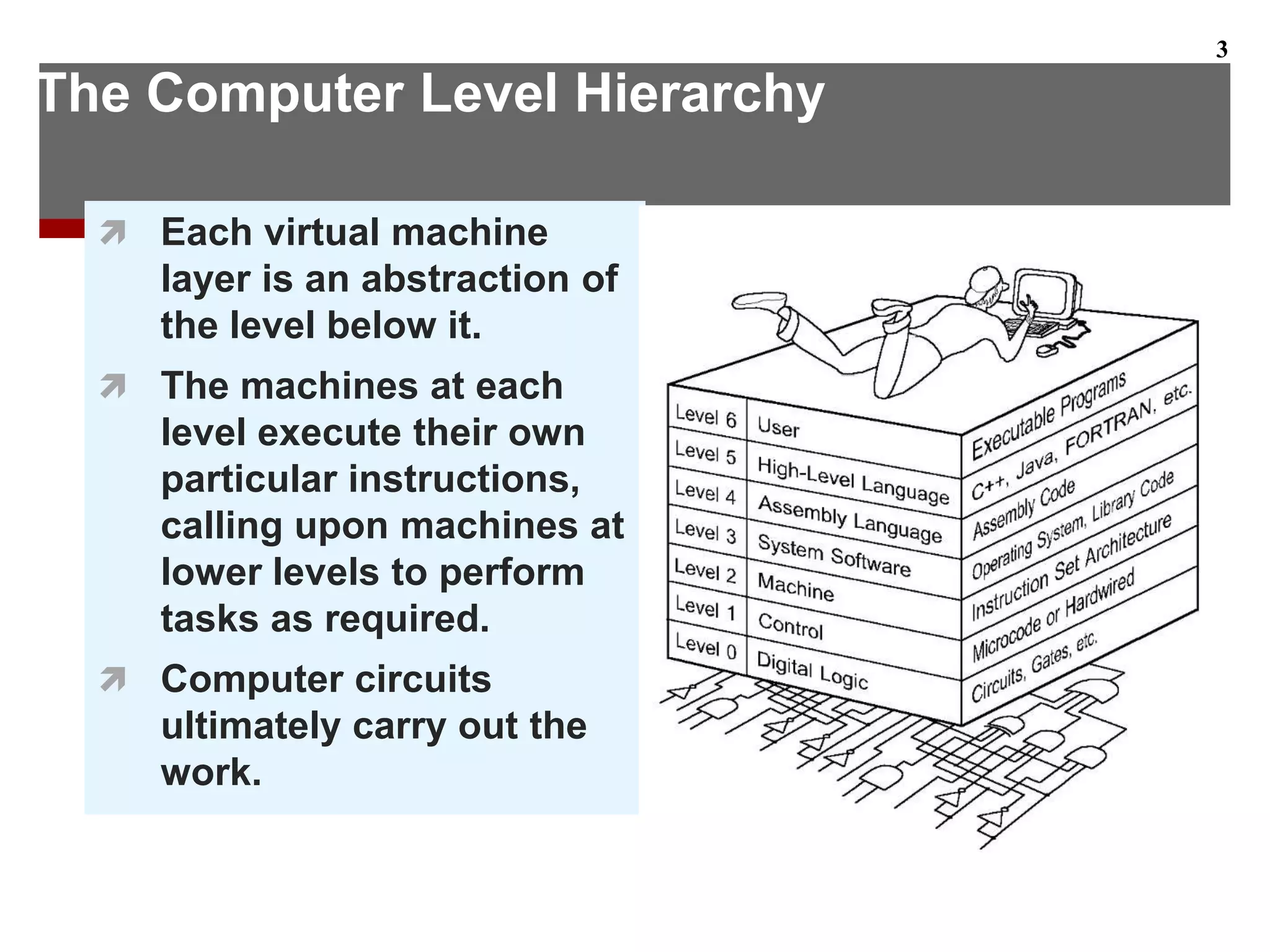
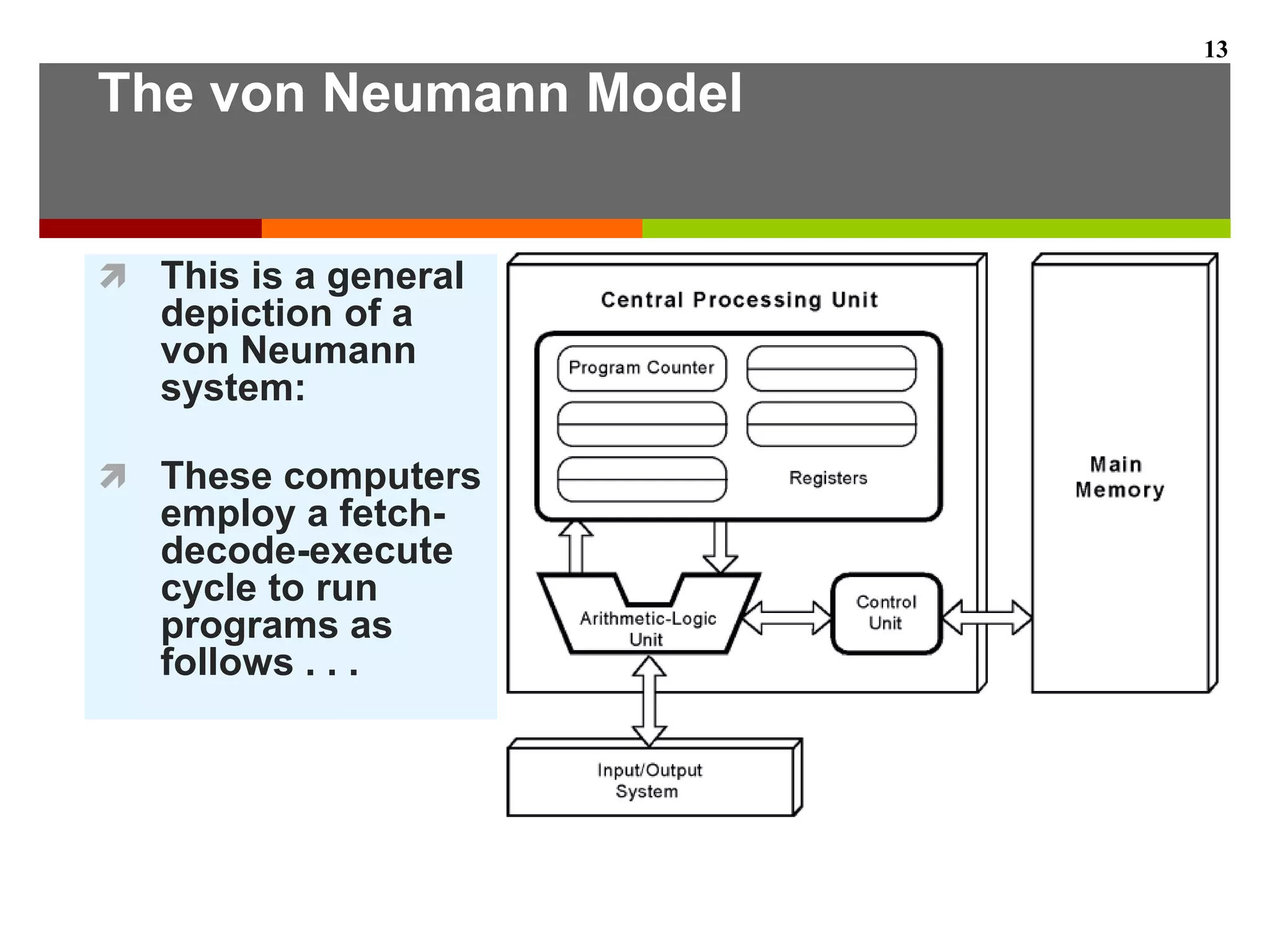
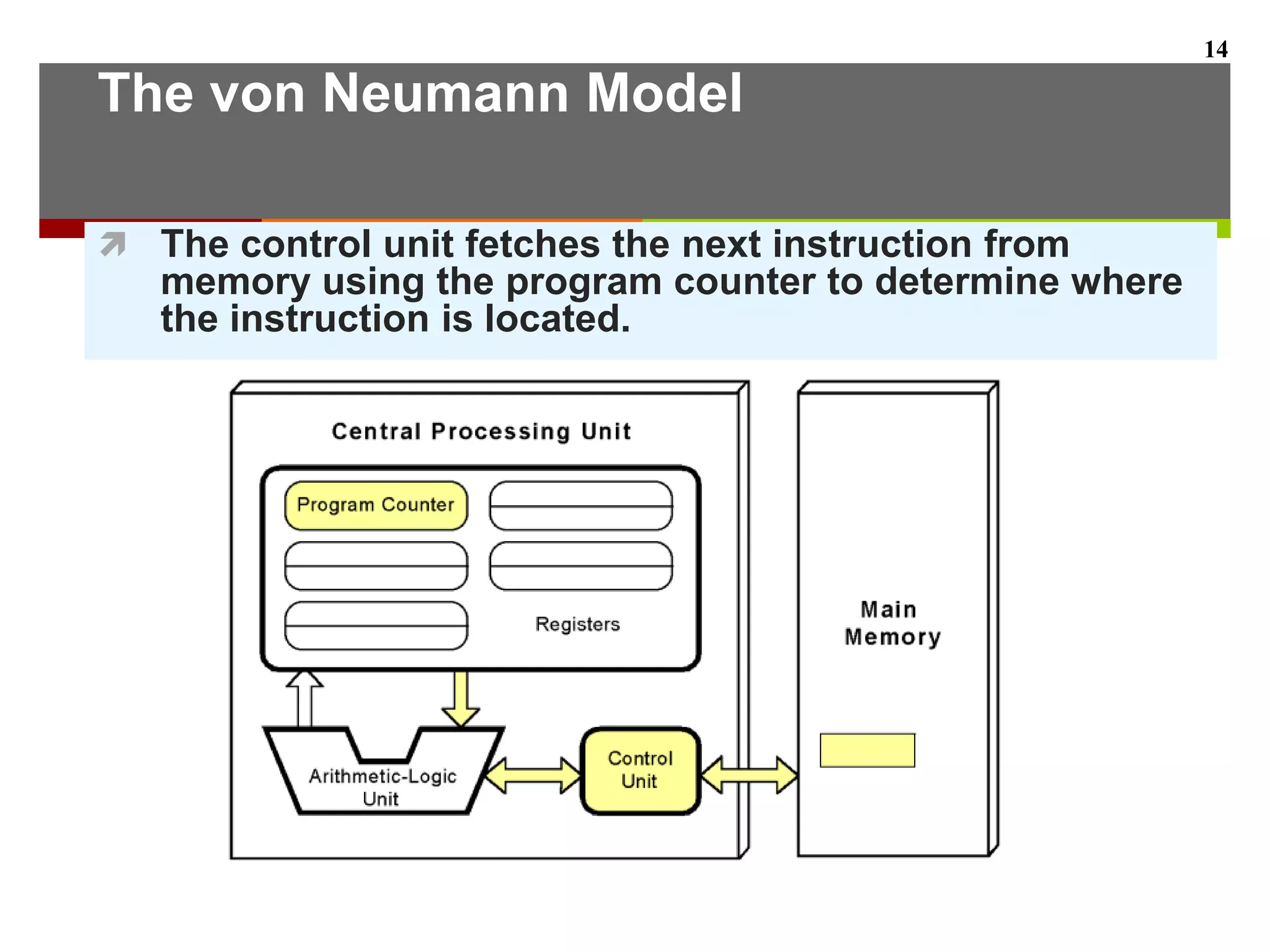
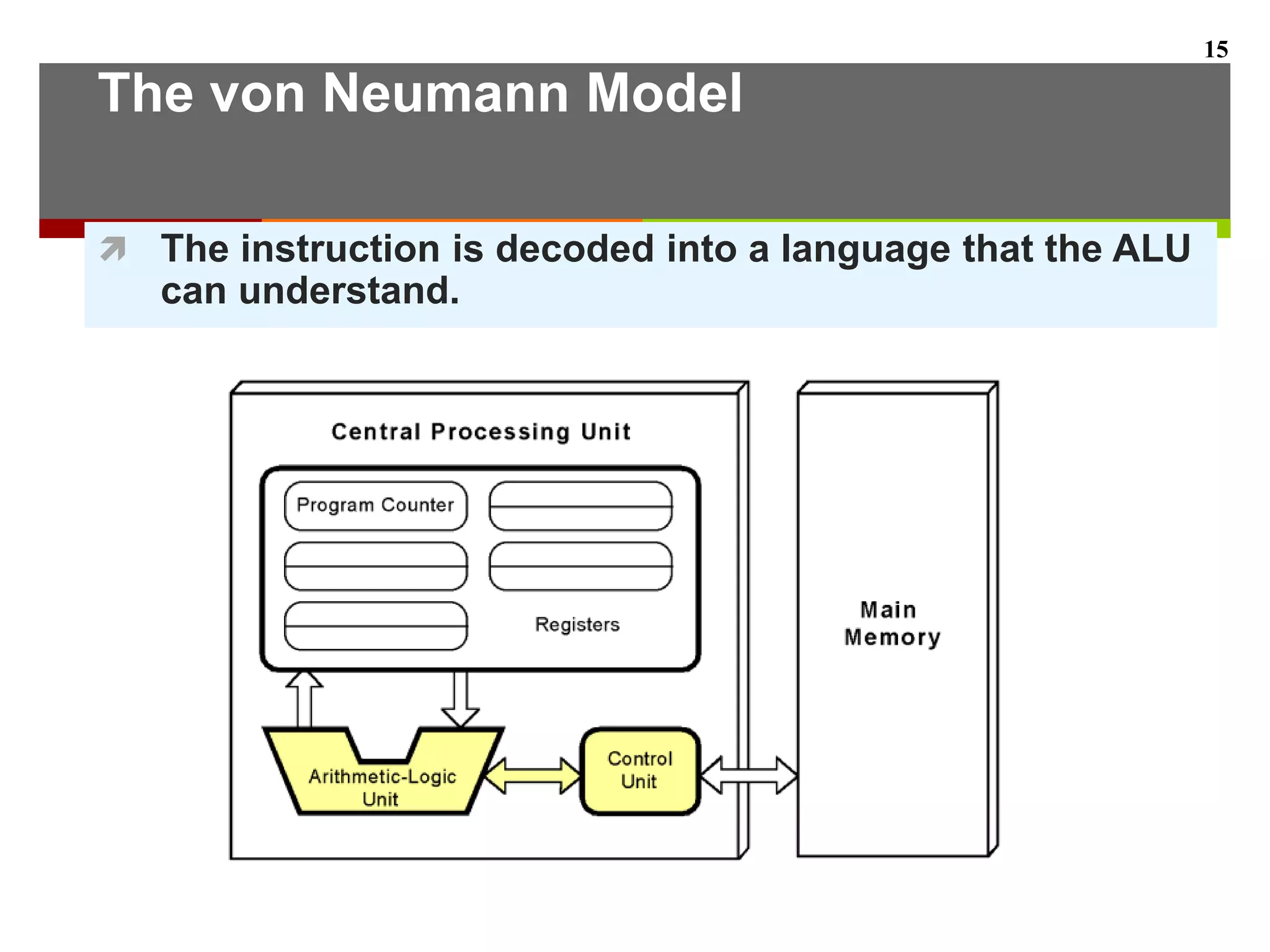
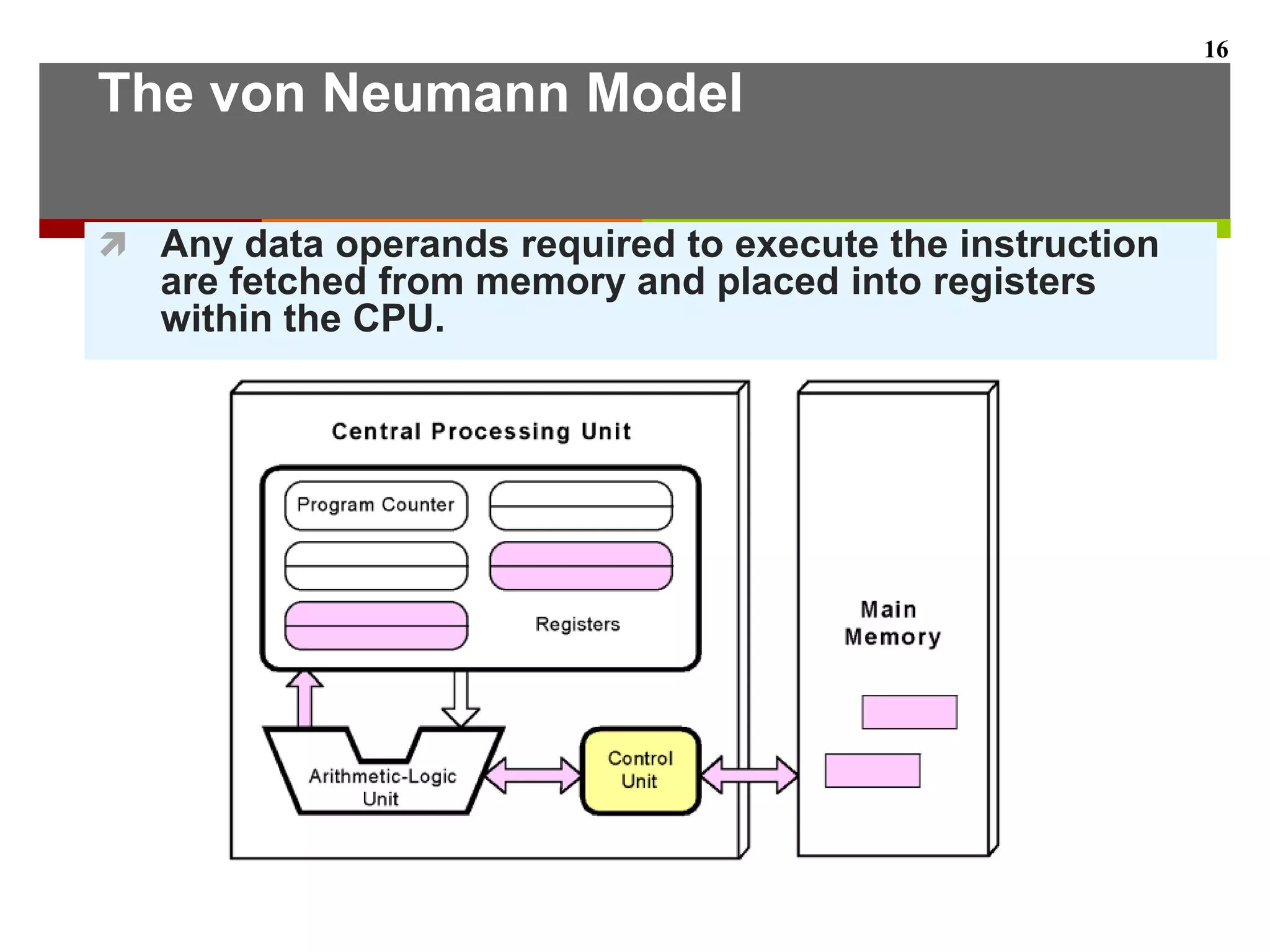
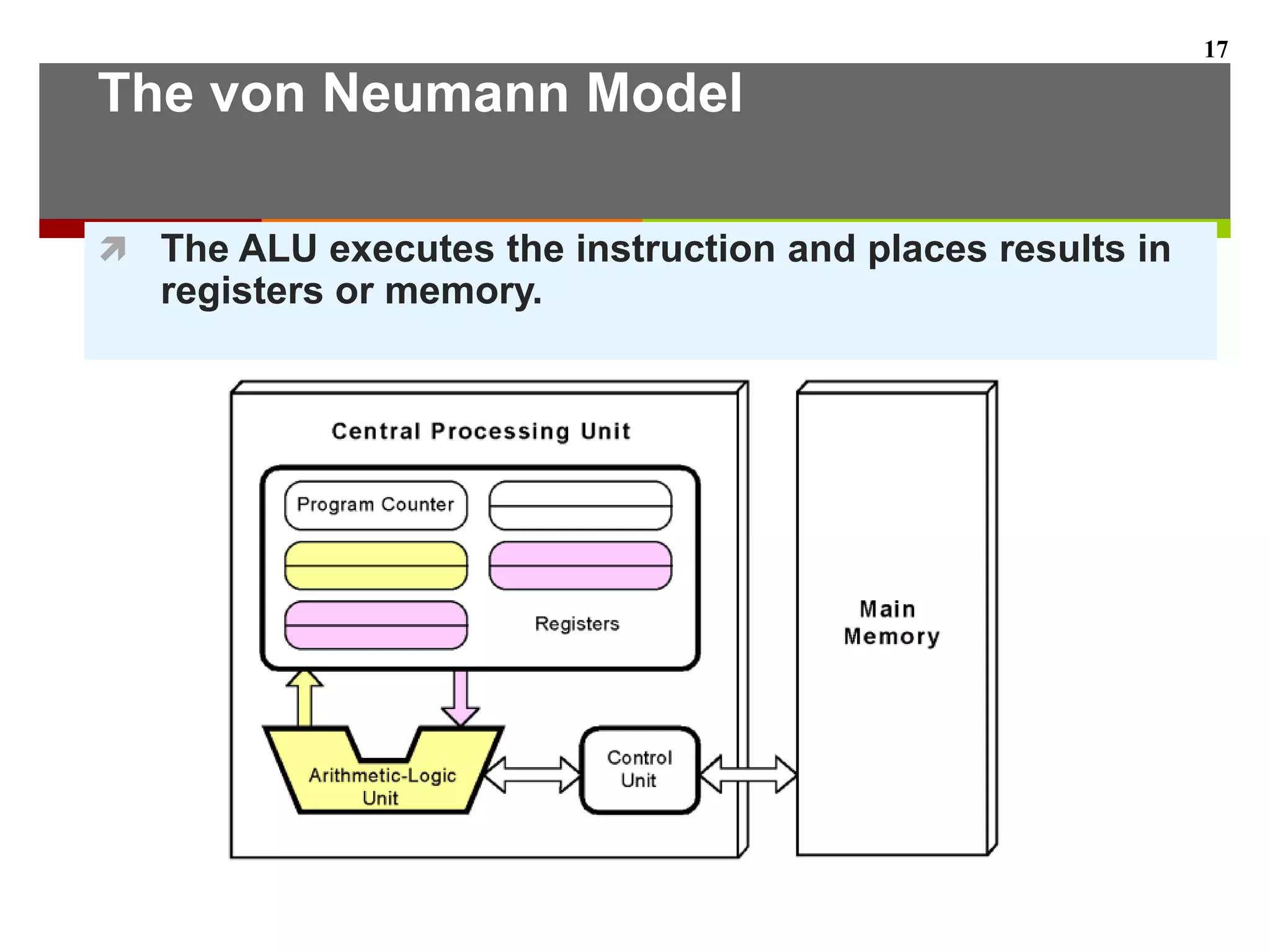
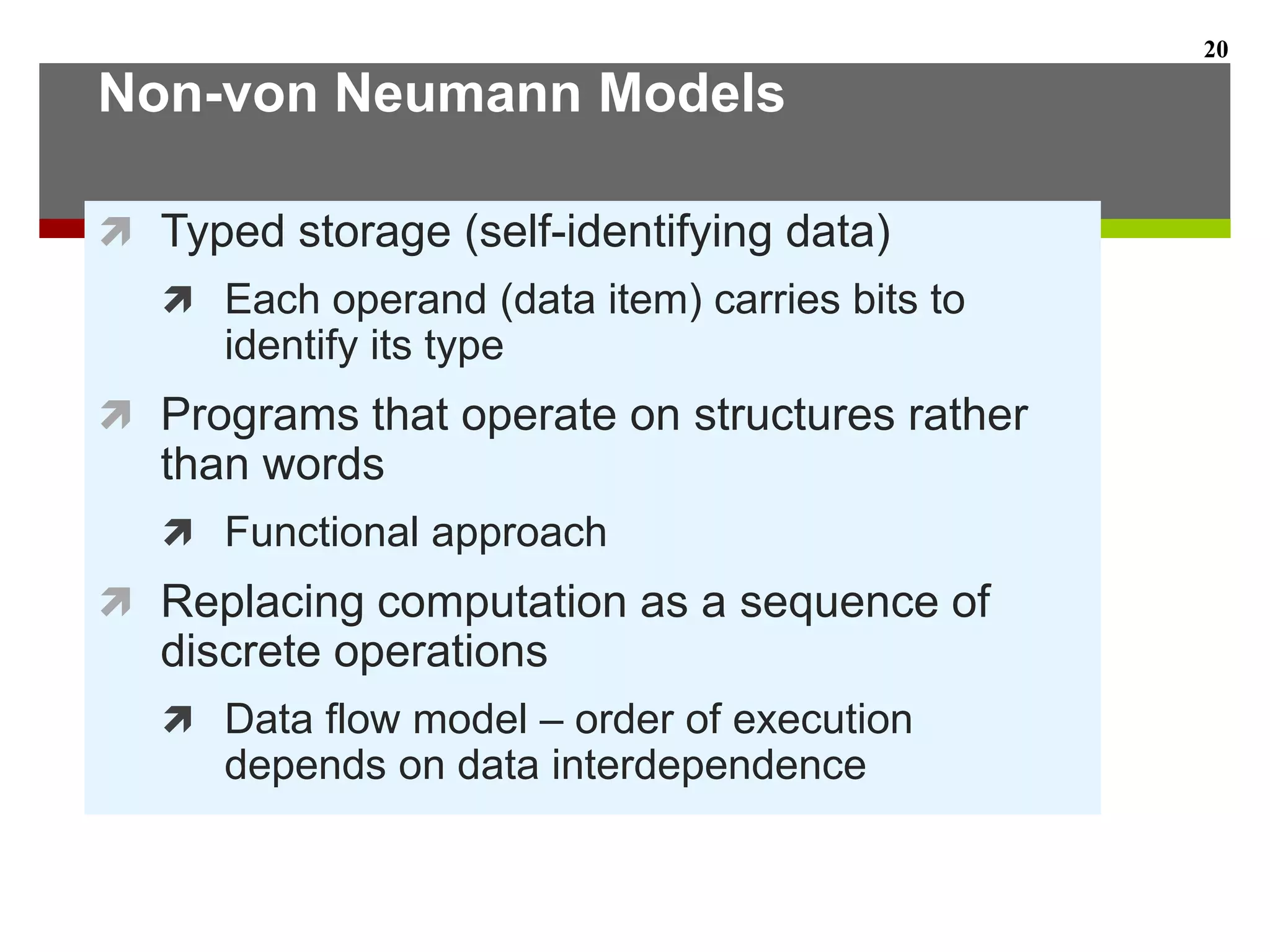
This document describes the different levels of the computer hierarchy. It begins with the user level (Level 6) and high-level language level (Level 5) where users interact. It then describes lower levels including the assembly language level (Level 4), system software level (Level 3), machine level (Level 2), control level (Level 1), and digital logic level (Level 0) where circuits are implemented. The document also explains the von Neumann model of stored-program computers and how they fetch, decode, and execute instructions in sequential order. Improvements to von Neumann models include adding additional processors for increased computational power.