The presentation summarizes the von Neumann machine architecture, the stored program concept, and components of the IAS architecture. It explains that von Neumann introduced the stored program concept where both instructions and data are stored in memory. It then describes the basic components of a von Neumann machine including the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. Finally, it details the specific components of the IAS architecture such as the memory buffer register, accumulator, and instruction register.



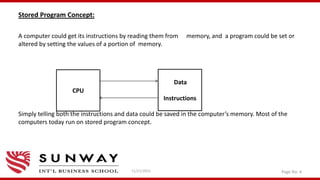

![Von Neumann Machine (Simple Structure) [1]
Central Processing Unit(CPU)
11/21/2021 Page No. 6
Main
Memory
I/O devices
Arithmetic &
Logic Unit (ALU)
Control Unit
(CU)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vonneumannarchitecture-211121092134/85/Von-Neumann-machine-and-IAS-architecture-6-320.jpg)


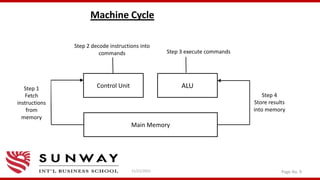
![Structure of IAS[2]
Page No. 10
Arithmetic & Logic Unit
I/O devices
Main
Memory
AC MQ
Arithmetic-Logic Circuits
MBR
IBR
IR
Control
circuits
MAR
PC
Control
Signals
Program
Control
Unit
addresses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vonneumannarchitecture-211121092134/85/Von-Neumann-machine-and-IAS-architecture-10-320.jpg)


![References:
• [1][2]Computer Organization and Architecture 10th edition- William Stallings
• Wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Von_Neumann_architecture)
• Geeks for Geeks (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/)
11/21/2021 Page No. 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vonneumannarchitecture-211121092134/85/Von-Neumann-machine-and-IAS-architecture-14-320.jpg)

