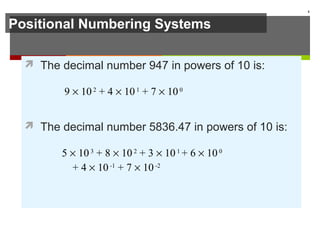
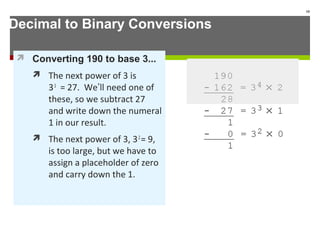
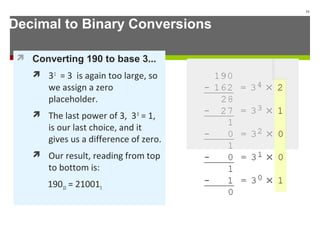
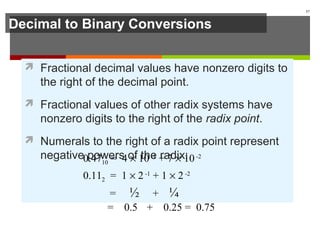
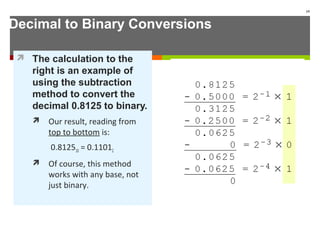
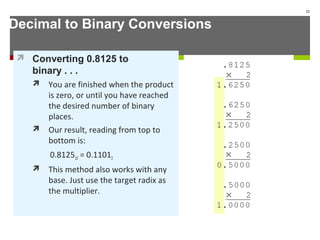
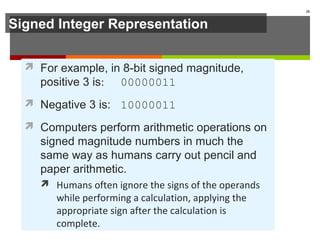
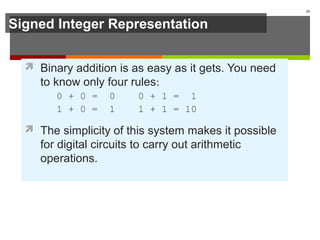
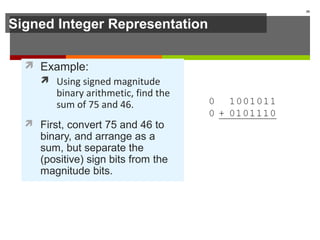
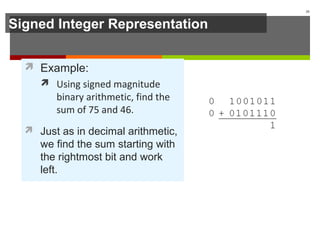
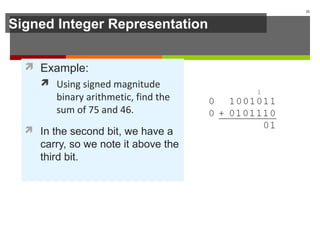
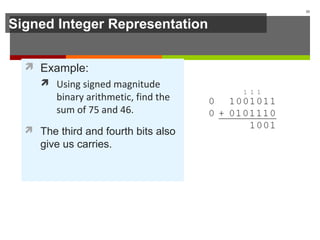
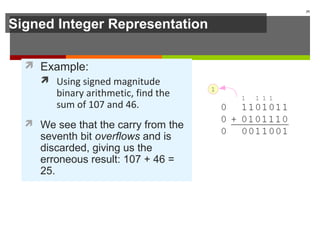
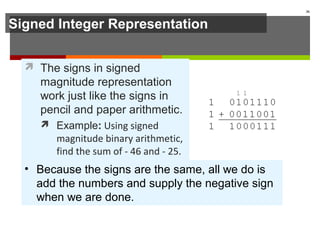
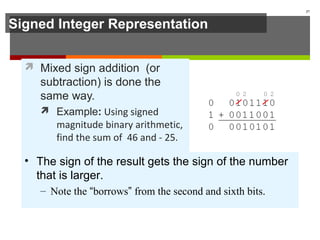
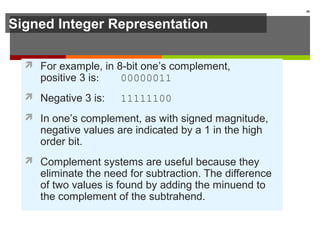
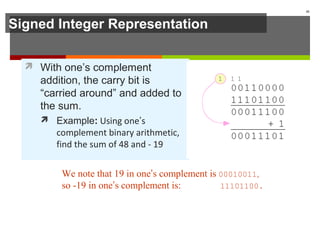
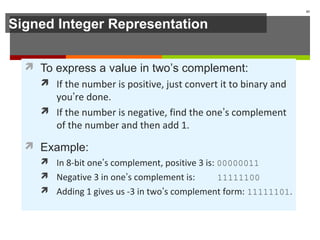
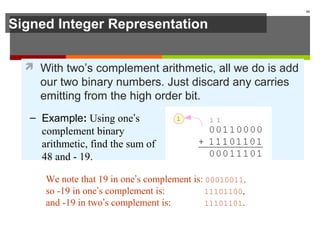
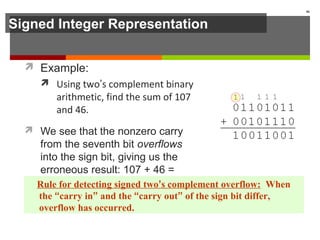
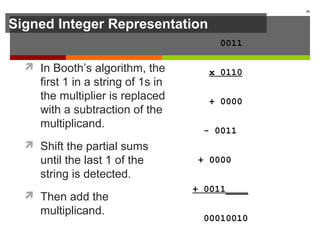
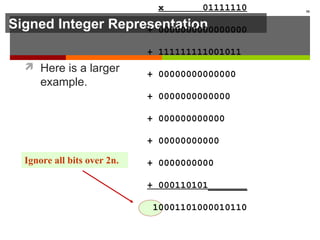
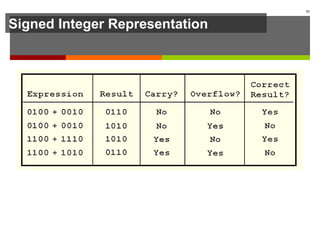
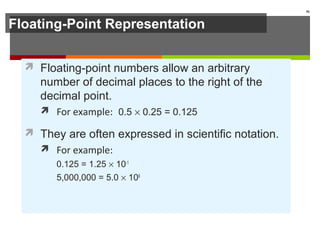
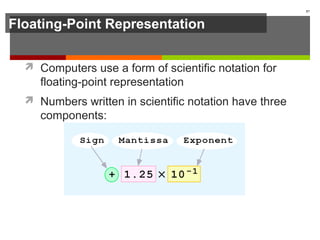
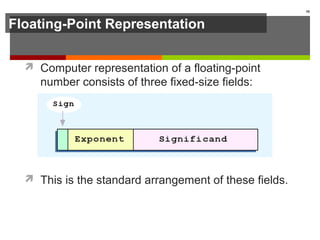
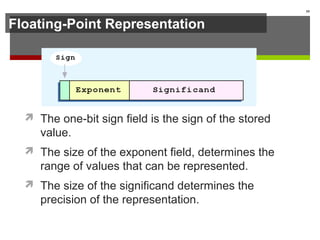
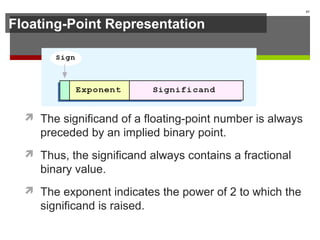
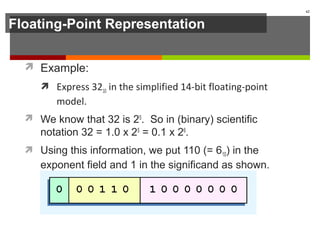
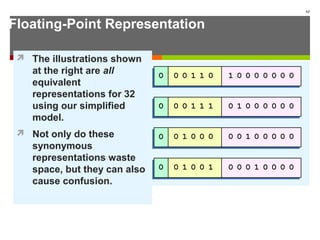
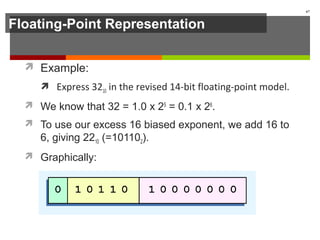
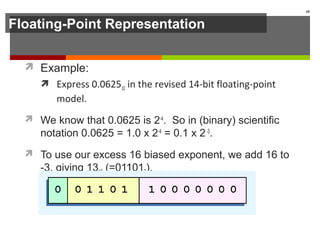
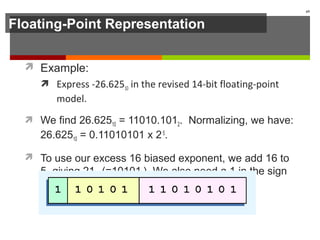
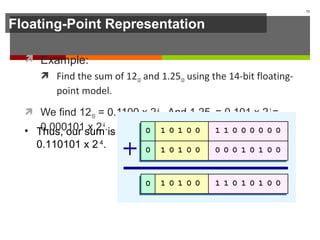
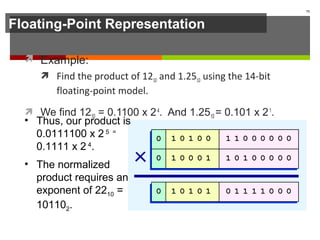
The document discusses data representation in computer systems. It begins by explaining that computers use the binary system for logic and arithmetic because it is easy to implement in electronics and switches. It then discusses how integers, floating point numbers, and Boolean logic are represented. The document provides details on bits, bytes, words, and how positional numbering systems like binary represent values. It covers converting between decimal and binary, including fractional values. Finally, it discusses signed integer representation using methods like signed magnitude, one's complement, and two's complement.