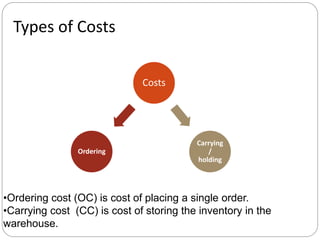
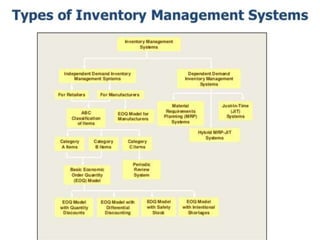
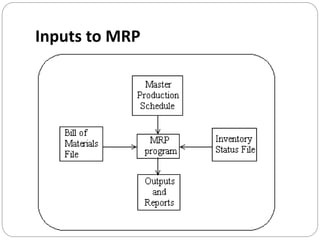
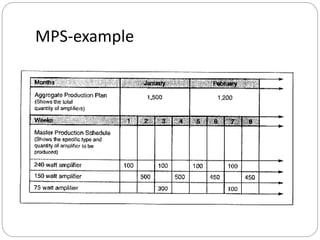
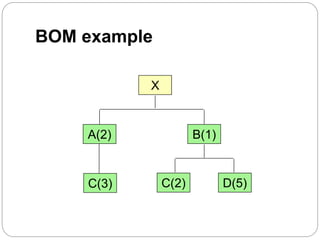
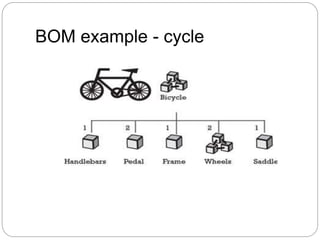
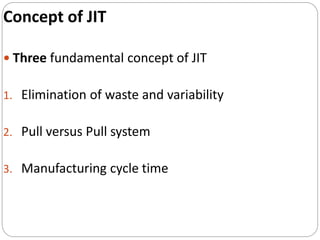
The document discusses inventory management principles including the importance of maintaining optimal inventory levels, the use of Material Resource Planning (MRP) and Just-In-Time (JIT) systems to manage inventory and production efficiencies, and the role of supply chain management in fulfilling customer demands effectively. It highlights key concepts such as anticipation inventory, cycle stock, costs associated with inventory, the elimination of waste in production, and continuous improvement through methodologies like Kaizen and Kanban. Additionally, it examines the benefits and drawbacks of these systems, emphasizing the need for accurate information and timely supplier relationships.