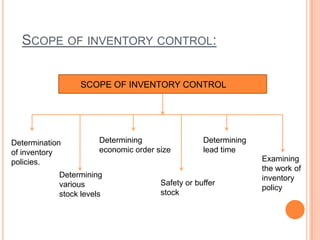
This document discusses inventory management. It defines inventory as materials obtained in advance of need that are held until used or sold. There are different types of inventories like raw materials, work in progress, spare parts, and finished goods. Inventory valuation involves determining inventory quantities and assigning values. Holding inventory incurs costs like storage, ordering, shortages. The objectives of inventory control are to ensure smooth operations while minimizing costs and risks through techniques like determining economic order quantities and stock levels.