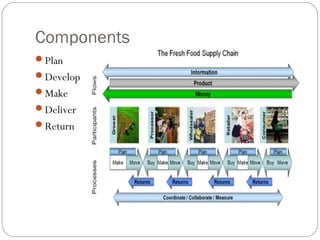
Supply chain management involves the flow of goods and information from raw materials to the customer. It includes procurement, production, and distribution. Key drivers are production, inventory, location, transportation, and information. The components are plan, develop, make, deliver, and return. Products, information, and funds flow between customers and suppliers. Supply chain management aims to coordinate activities among organizations to trade off costs, service, time, risk, and other metrics across the chain.