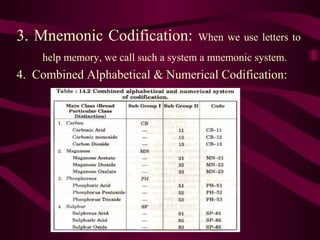
This document discusses classification and codification of materials in manufacturing. It provides definitions of classification and codification, discusses their objectives and principles. Some key points covered are:
- Classification involves grouping materials by nature, use and service before assigning codes for identification.
- Codification assigns unique numerical/alphanumeric codes to materials to accurately identify them.
- Objectives of codification include accurate identification, preventing duplication, and standardization.
- Benefits of classification and codification include systematic grouping, avoiding duplicate stocks, reduction in varieties, and ensuring accurate record keeping.