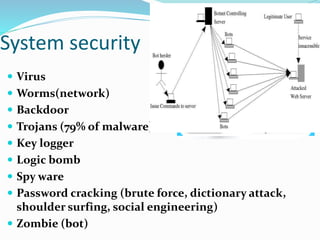
This document discusses various cybersecurity threats and issues. It covers hacking of government and private systems, the scope of hacking (devices, networks, etc.), common cyber attacks and their motives, potential results of attacks, and levels of security. It also provides examples of famous viruses and outlines guidelines, measures, and security procedures to help protect against various threats like identity theft, social engineering, mobile device risks, and network attacks. The key message is that security awareness is the first step to improving protection.