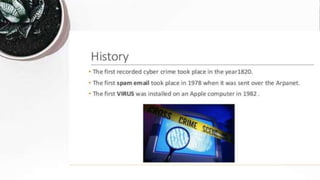
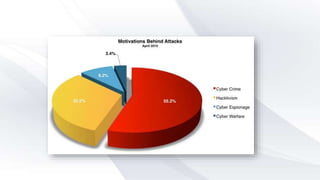
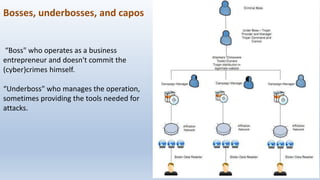
This document discusses cyber crime and security. It begins with an overview of topics to be covered, including the history and basics of cyber crimes, various categories of cyber crimes, and motivations for cyber attacks. It then discusses the history of cyber crimes and defines cyber attacks and cyber crimes. Various types of cyber crimes are outlined, including those against persons, property, and government. Common cyber crime techniques like social engineering, viruses, and ransomware are explained. The document notes that cyber crime groups are starting to operate more like organized crime rings. It concludes by discussing how opportunities provided by Web 2.0 technologies can be exploited for cyber crimes.