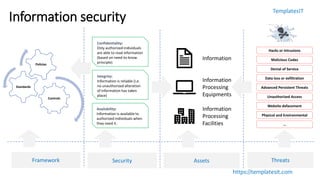
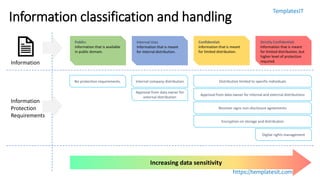
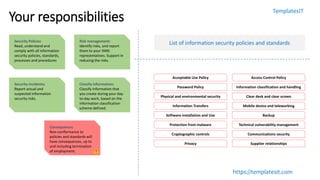
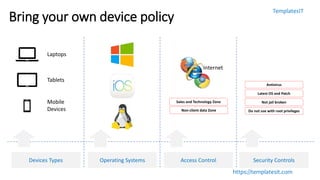
The document outlines key aspects of information security awareness, including responsibilities, policies, and strategies to mitigate risks such as phishing and malware. It emphasizes information classification, incident reporting, and the importance of compliance with security standards. Additionally, the document highlights the evolving nature of cybersecurity threats and provides a framework for organizational policies and practices.



![TemplatesIT
https://templatesit.com
Security incidents
Any violation of established information security frameworks (including information security policies, standards, processes, procedures & controls)
Use data and IT
assets in accordance
with the acceptable
use policy defined
by the organization.
Any intrusion (hack)
into the computer
systems is a security
incident, which
must be prevented.
Unauthorized access
or use: Performing
activities that are
not authorized.
Data exfiltration or
loss: Stealing data or
causing intentional
or unintentional
destruction of
information.
Computers (servers,
laptops, desktops,
network devices,
etc.) being infected
with malicious code.
Any violation of
information security
policies and
standards is an
information security
incident.
Some examples are:
Read, understand and
comply with policies at all
times.
Comply with Acceptable
Use Policies defined by the
organization.
Adversaries intruding into
the network to cause
unintended ill effects.
Install software on systems
without due change
management process.
Data sent out by people
who are in possession of it,
without authorization.
Computers infected with
virus, ransomware, crypto-
miners etc.
Report: Report any suspected and actual information
security incidents to security.incident@company.com /
[phone]
Objective: Security incident management seeks to minimize
disruptions to the organization due and restores operations as
quickly as possible.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-190611121153/85/information-security-awareness-course-10-320.jpg)


