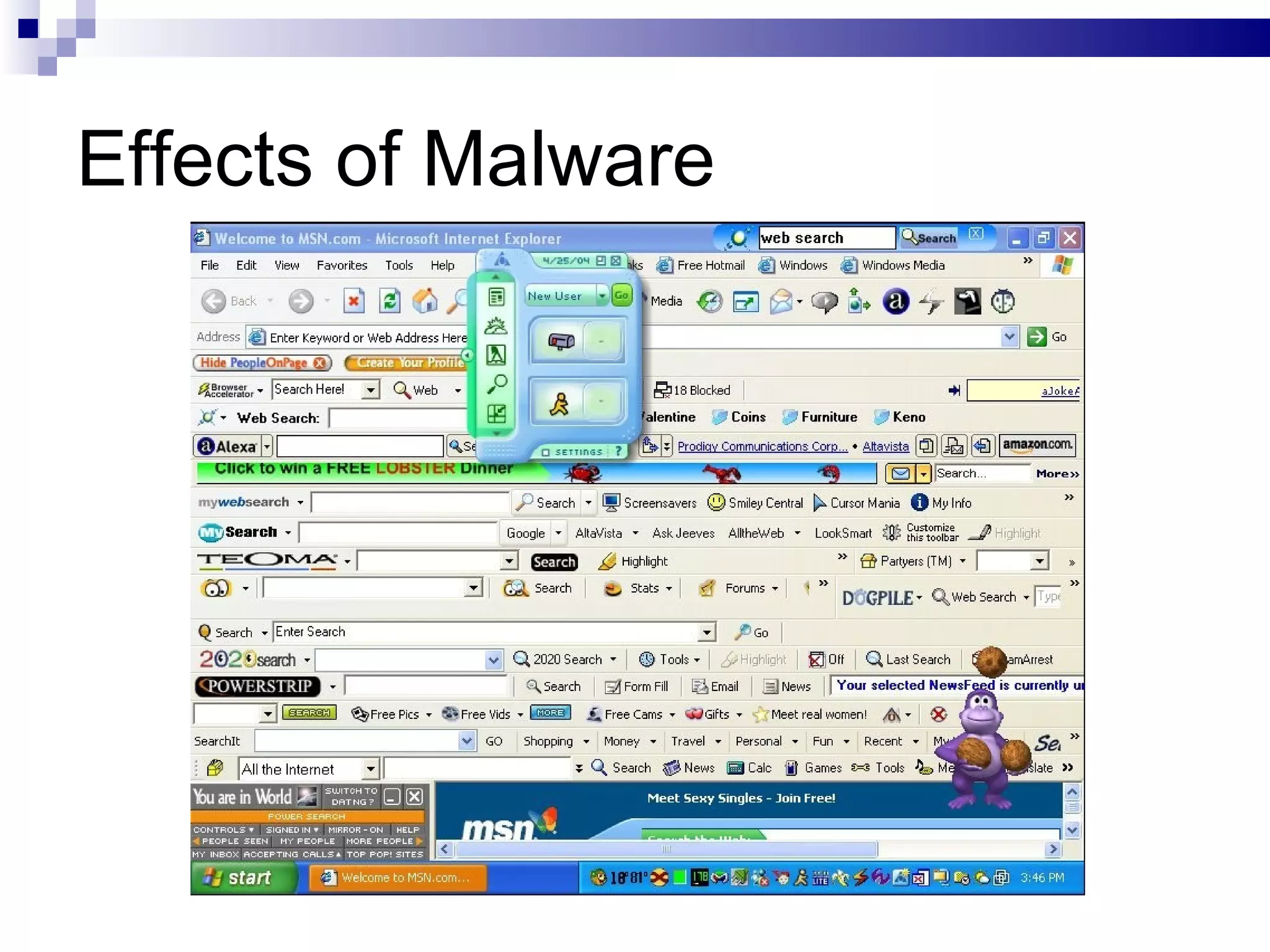
This document discusses various types of computer crimes and risks. It describes computer crimes as any illegal acts committed using computers, noting that most are insider jobs and often go unreported. It also outlines different forms of online fraud, identity theft, malware like viruses and worms, and spyware. The effects of these threats are described as proliferation through networks, modification or deletion of files and settings, denial of service attacks, unwanted advertising and changes to browsers. It concludes with recommendations for reducing risks like restricting physical and logical access, fortifying systems with firewalls and encryption, and maintaining clean facilities with anti-virus software and auditing.