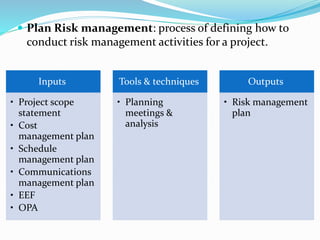
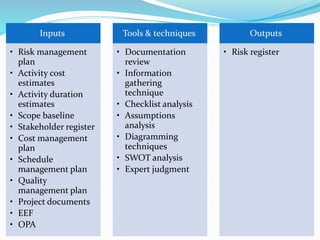
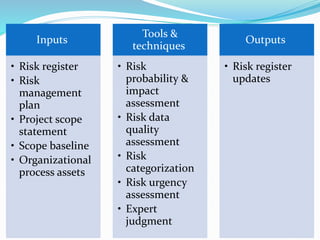
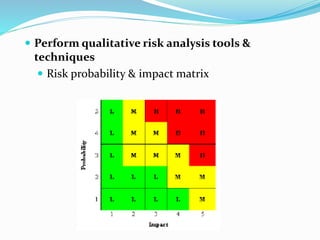
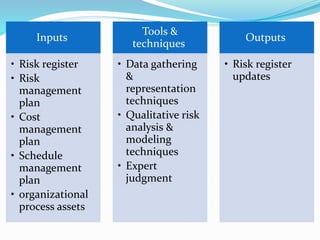
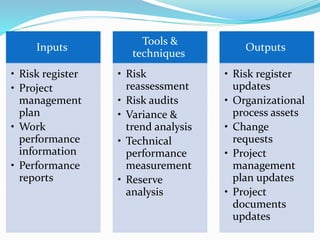
This document outlines the six steps of project risk management: 1) plan risk management, 2) identify risks, 3) perform qualitative risk analysis, 4) perform quantitative risk analysis, 5) plan risk responses, and 6) monitor and control risks. It describes the inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs of each step. The overall purpose is to systematically manage potential threats and opportunities to achieving the objectives of a project.