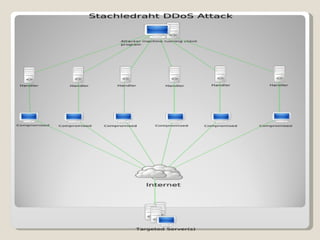
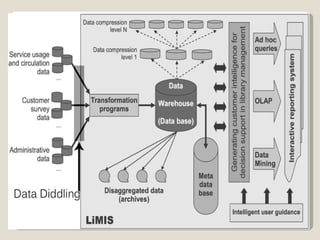
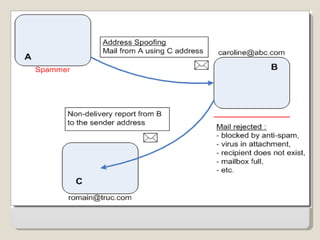
The document discusses the history, classification, and prevention of cybercrime, emphasizing the evolution of criminal behavior with the rise of technology since the first recorded cybercrime in 1820. It categorizes cyber crimes into various forms such as financial crimes, hacking, and intellectual property violations and highlights the significance of anonymity in hindering investigations. Prevention strategies include regular audits, employee supervision, the use of antivirus and encryption software, and fostering awareness of cybersecurity practices.