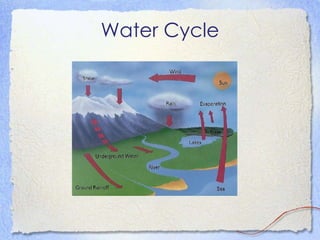
This document introduces the key concepts of ecology, including:
1) Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with their environment and each other.
2) Organisms are organized into levels ranging from cells to the biosphere.
3) The environment consists of biotic and abiotic factors that surround organisms.
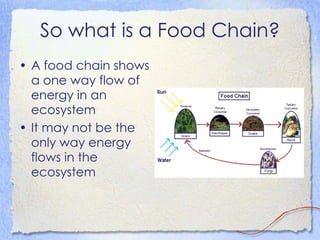
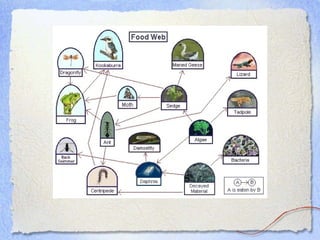
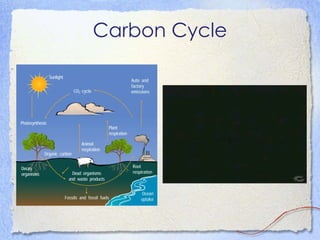
4) All organisms are interdependent and interact through competition, predation, and nutrient recycling.