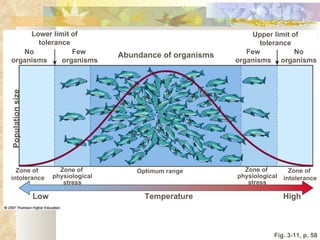
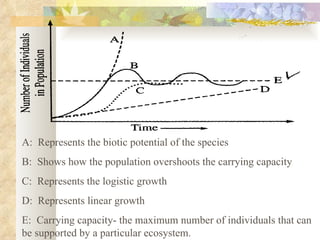
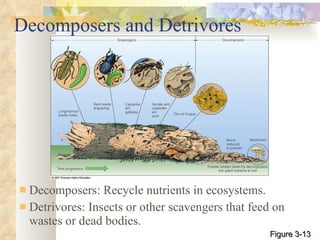
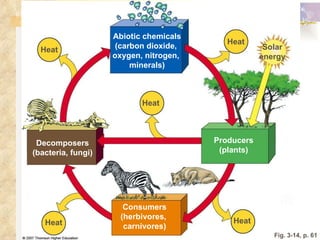
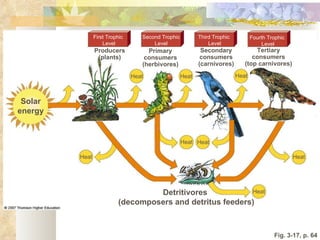
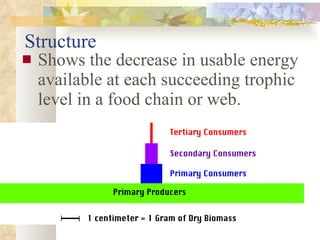
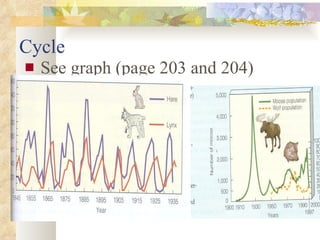
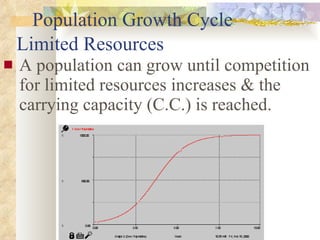
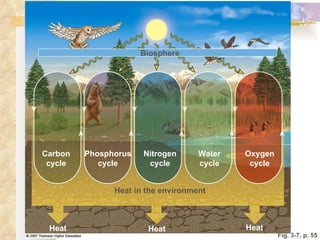
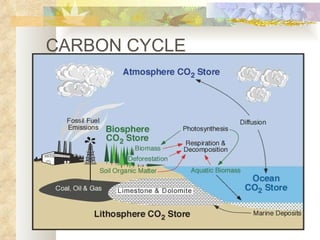
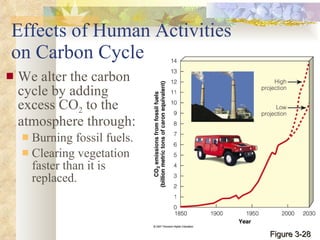
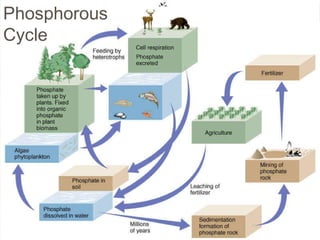
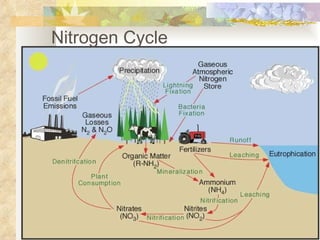
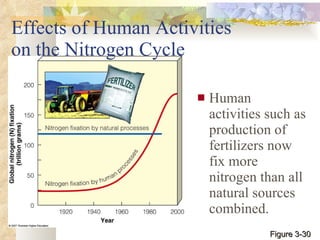
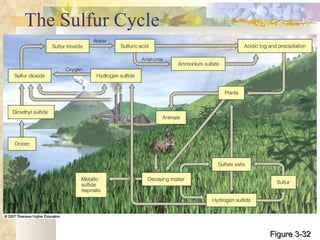
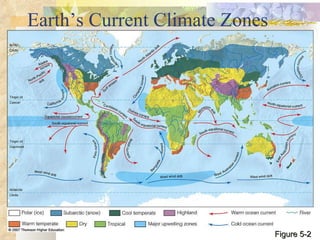
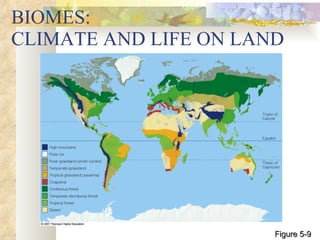
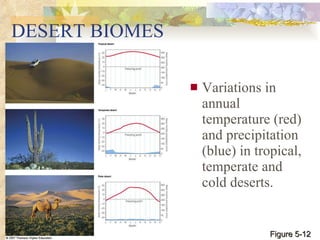
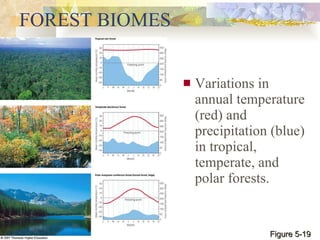
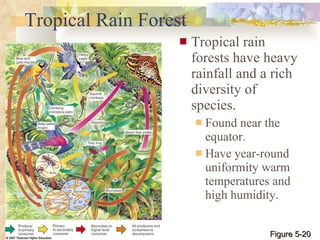
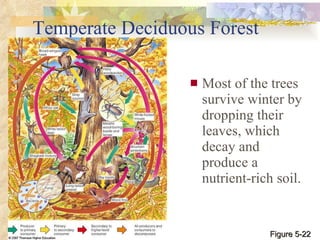
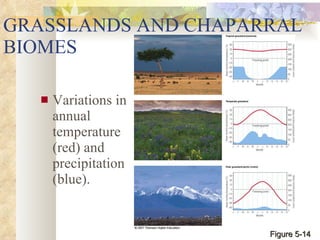
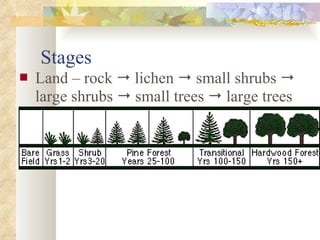
The document provides an overview of key concepts from chapters 3, 5 and 7 of a textbook on terrestrial ecology. It discusses the basic components and processes of ecosystems, including energy flow and nutrient cycling. It also describes different biomes and how climate determines their distribution, focusing on desert, grassland, forest and mountain biomes. Finally, it examines various species interactions and how human activities have impacted ecosystem functions.