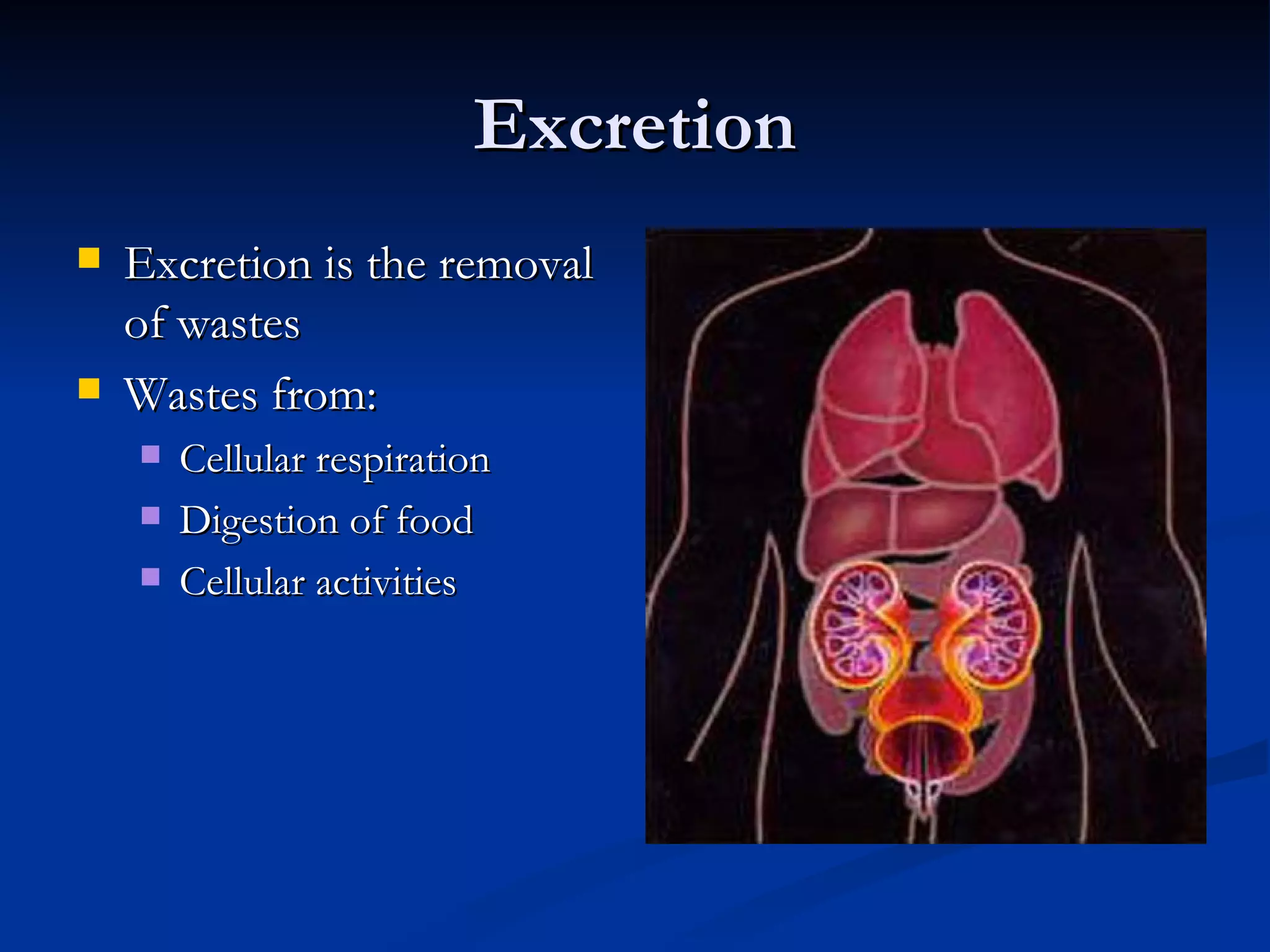
The excretory system removes waste from the body through the skin, lungs, liver, large intestines, and kidneys. The kidneys are the most important organ as they regulate blood pH and remove excess water and urea to create urine. Urea is formed when ammonia from cellular waste combines with carbon dioxide, producing a soluble compound that is easily excreted from the body. The lungs, skin, and large intestines also remove gaseous and solid wastes to help maintain homeostasis.