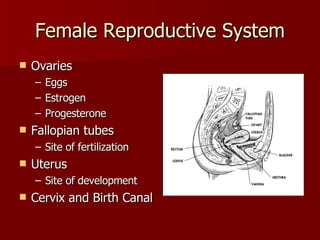
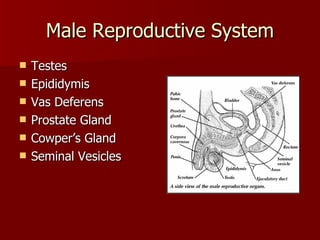
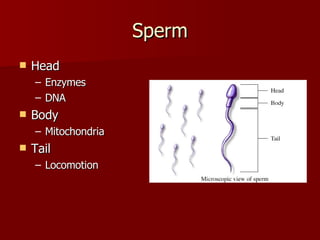
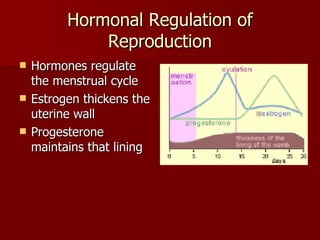
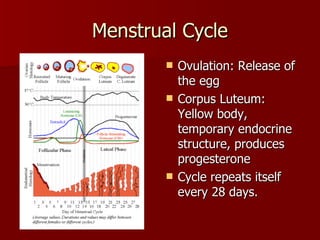
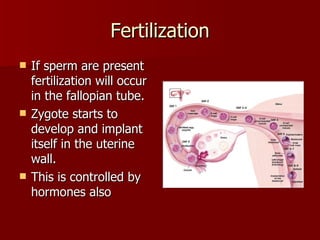
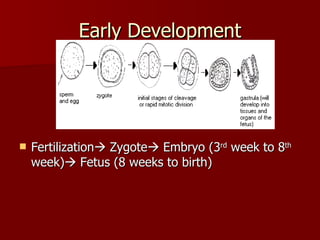
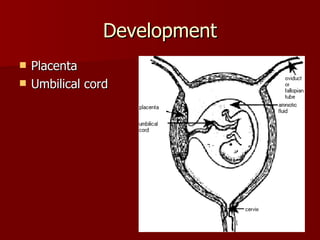
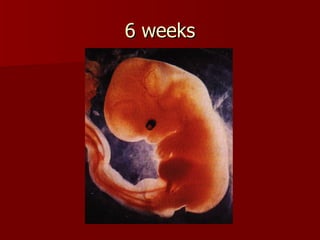
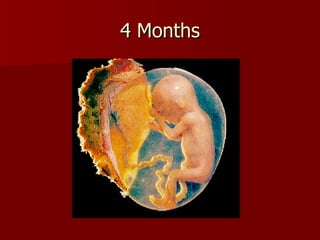
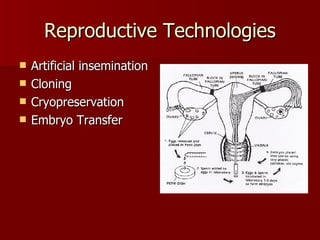
The document summarizes the human reproductive system and development. It describes the production of gametes in males and females and their regulation by hormones. It outlines the key parts of the male and female reproductive systems and explains fertilization and the early stages of development from zygote to embryo to fetus. It notes development is controlled by hormones and can be affected by toxins early on. Reproductive technologies are also mentioned.