Embed presentation
Downloaded 119 times


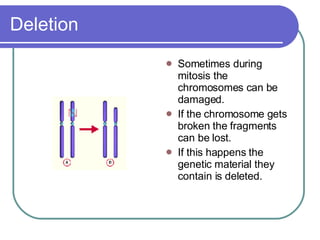

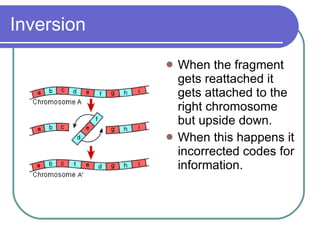
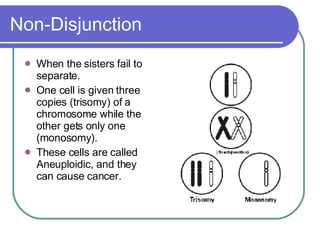


Mitotic errors occur rarely but can have serious consequences if they happen during early cell divisions when forming offspring. There are different types of mitotic errors including non-disjunction where sister chromatids fail to separate properly, leading to aneuploidy. Other errors include deletions from broken chromosomes losing fragments, translocations where broken chromosomes reattach to the wrong area, and inversions where fragments reattach upside down. Aneuploidy from errors can cause conditions like Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and some cancers.







