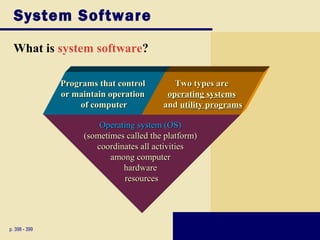
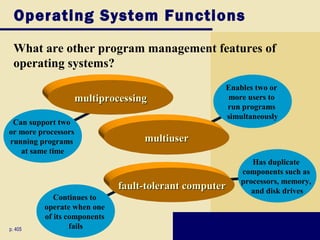
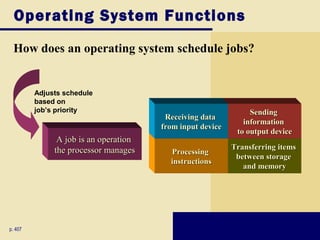
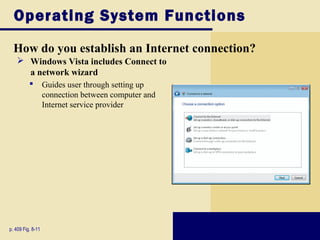
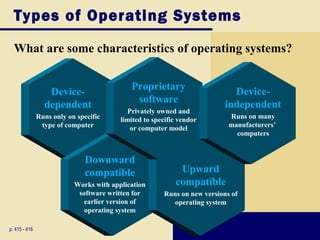
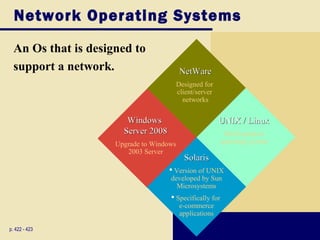
This document discusses operating systems and embedded operating systems. It provides details about various desktop operating systems like Windows, Mac OS X, UNIX/Linux. It also discusses network operating systems for servers and embedded operating systems used in devices like smartphones, PDAs and others. Key topics covered include functions of operating systems, booting process, memory management, scheduling jobs, Windows versions comparison, features of Windows Vista, Mac OS X and Linux operating systems. Embedded operating systems discussed include Windows Embedded CE, Palm OS, Blackberry OS, Embedded Linux and Symbian OS.