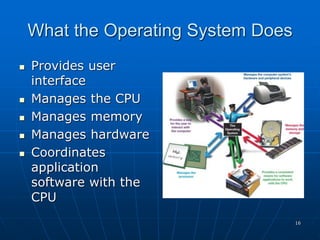
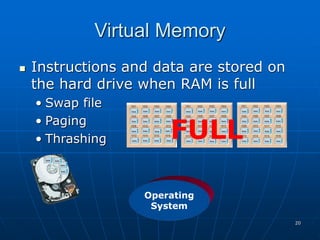
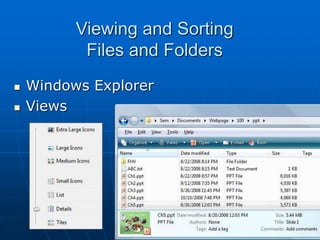
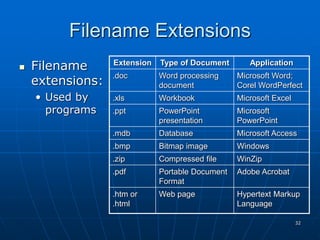
The document discusses system software, operating systems, and file management. It describes how operating systems manage hardware, memory, applications, and user interaction. Common desktop operating systems include Windows, Mac OS, UNIX, and Linux. The document also discusses utility programs that perform system maintenance tasks like managing resources, improving efficiency, and preventing viruses. It provides details on file naming, organization, viewing and sorting files and folders, and performing actions like opening, copying, and deleting files.