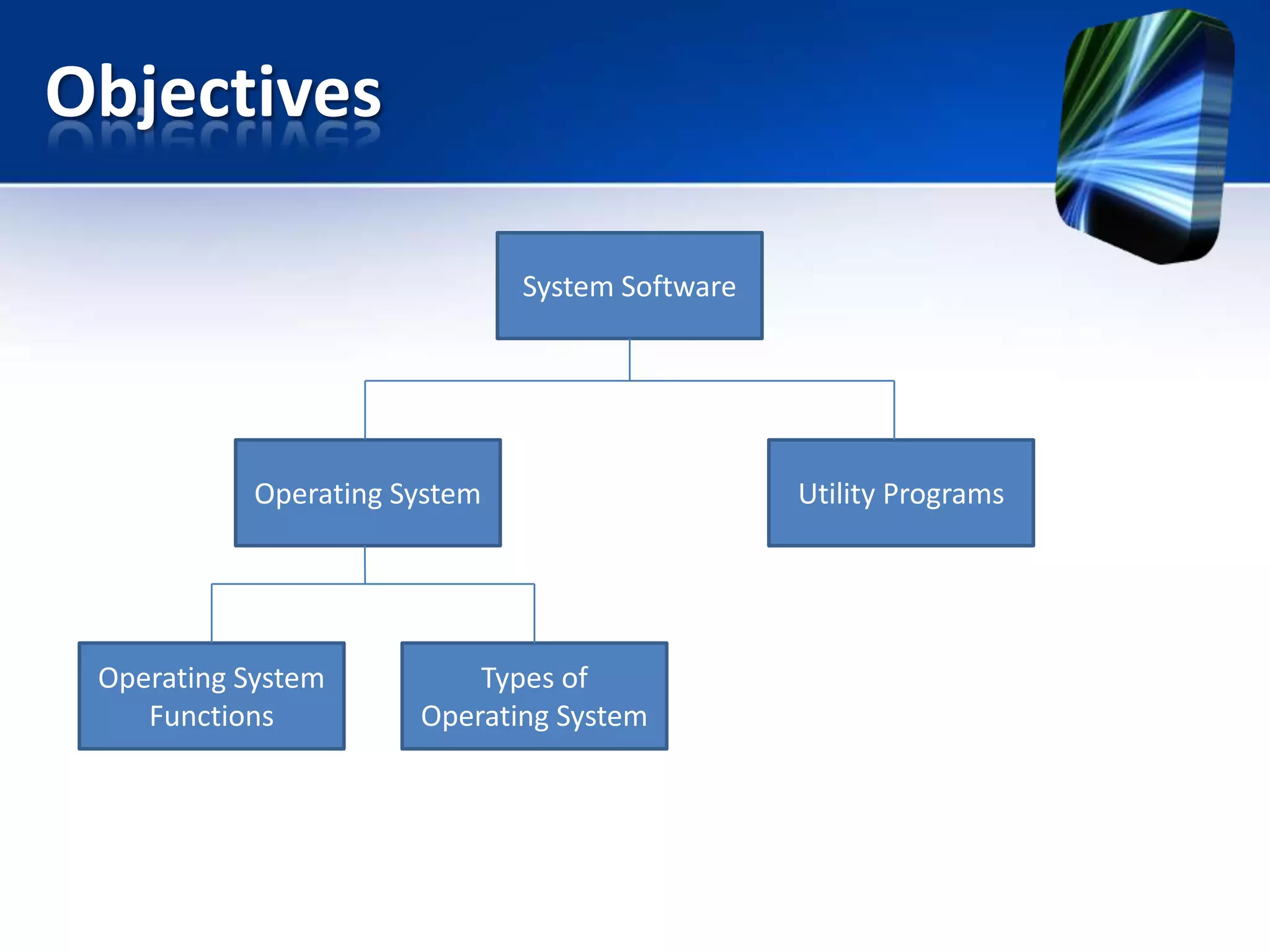
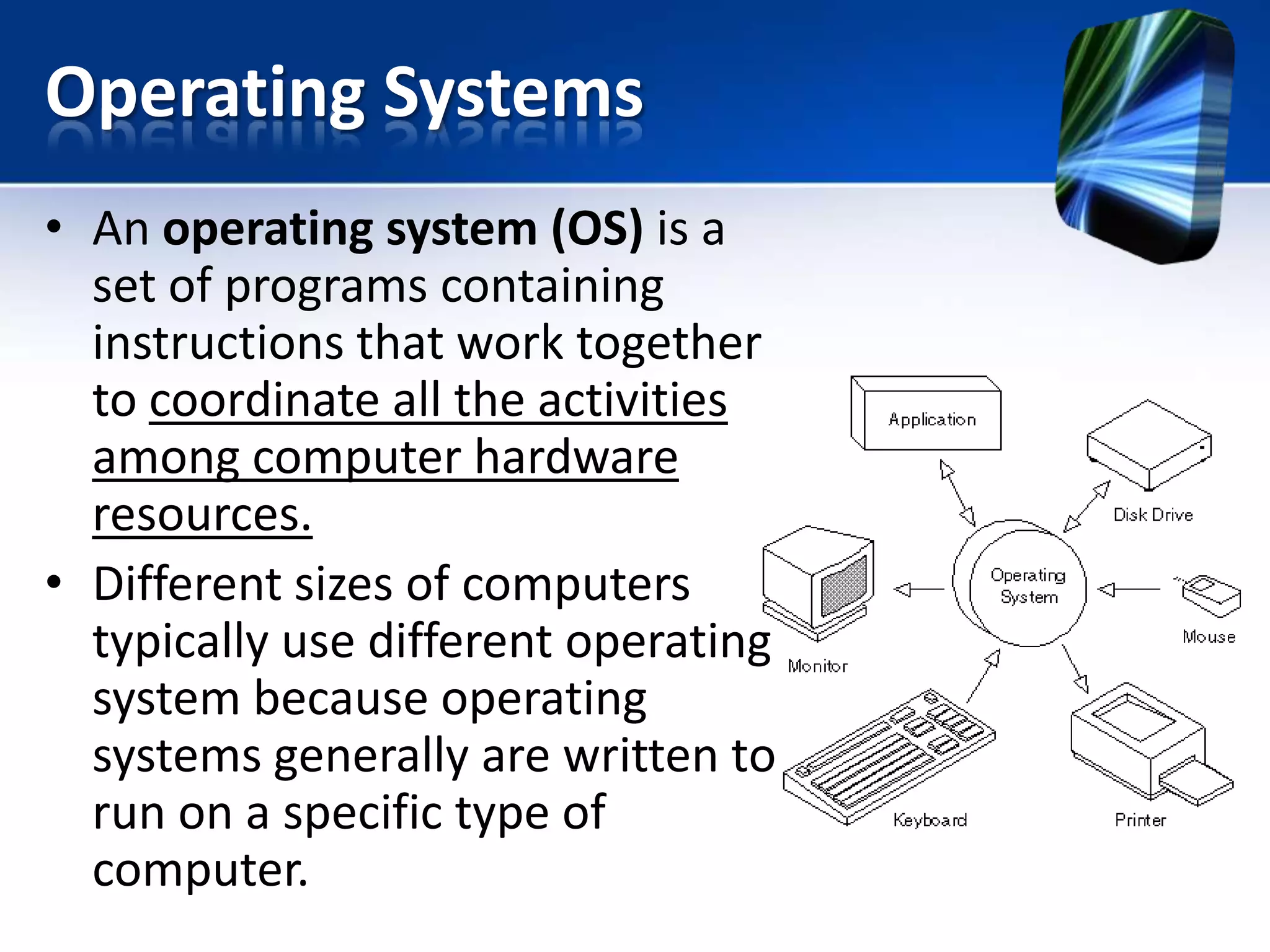
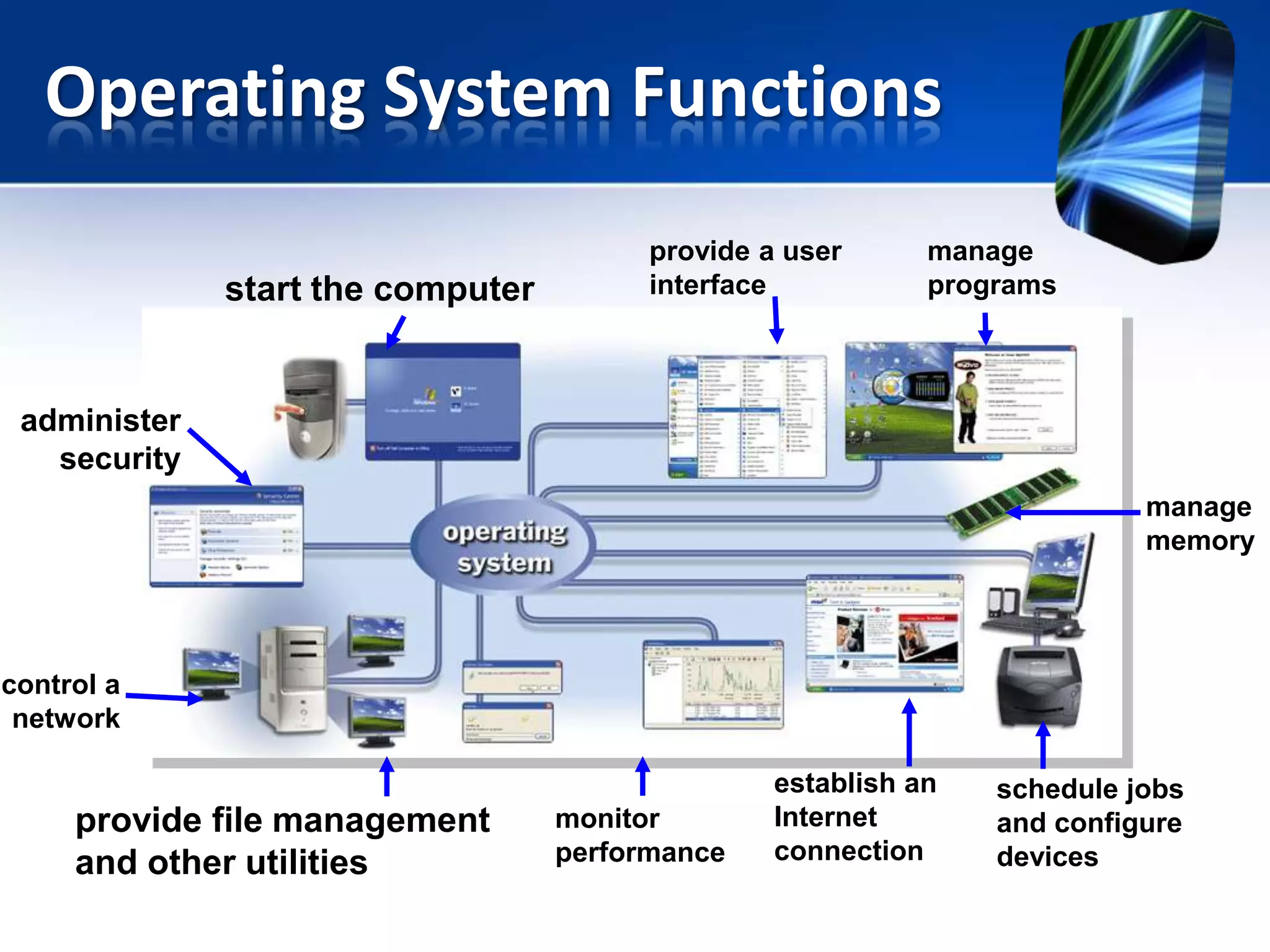
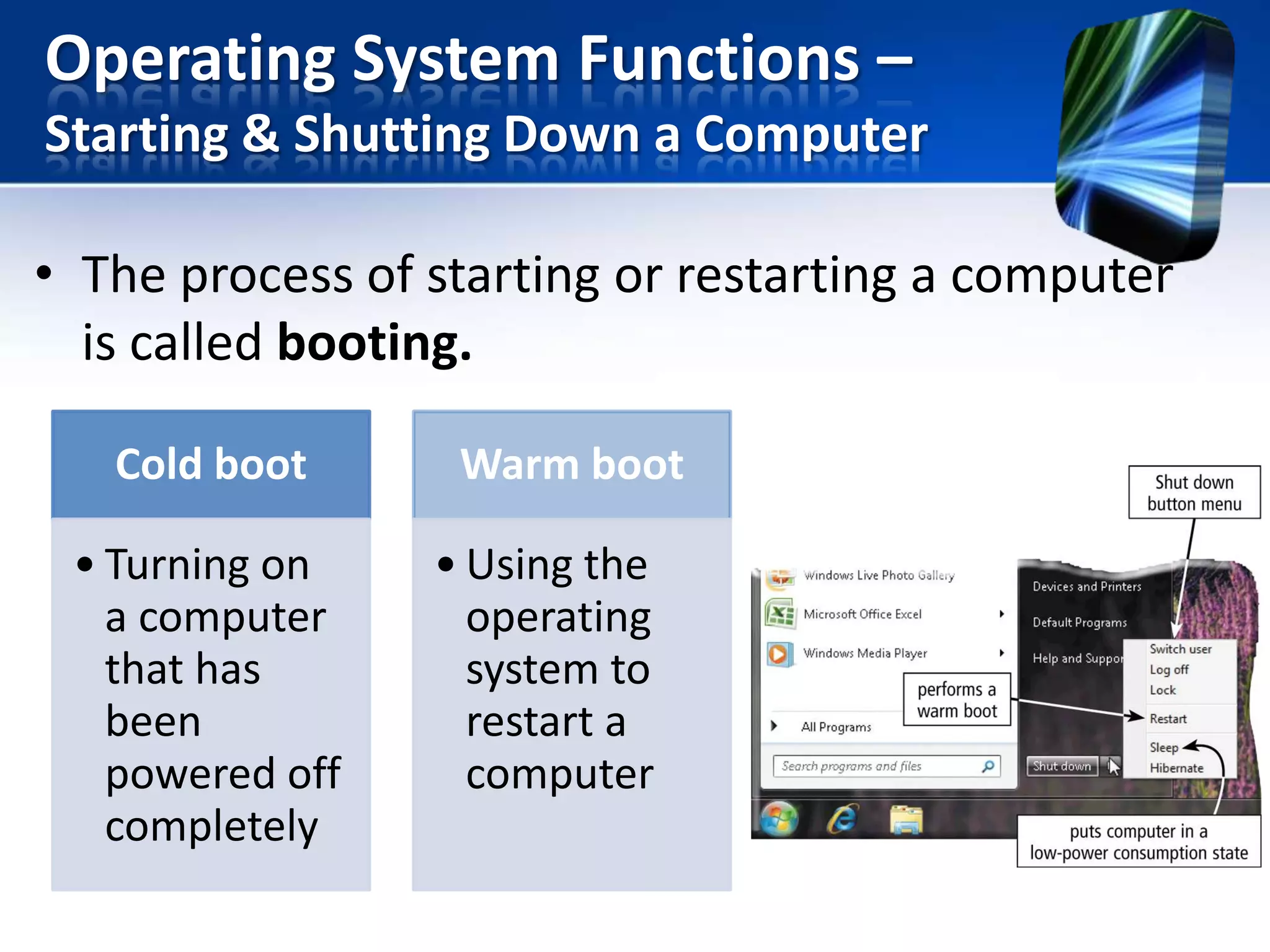
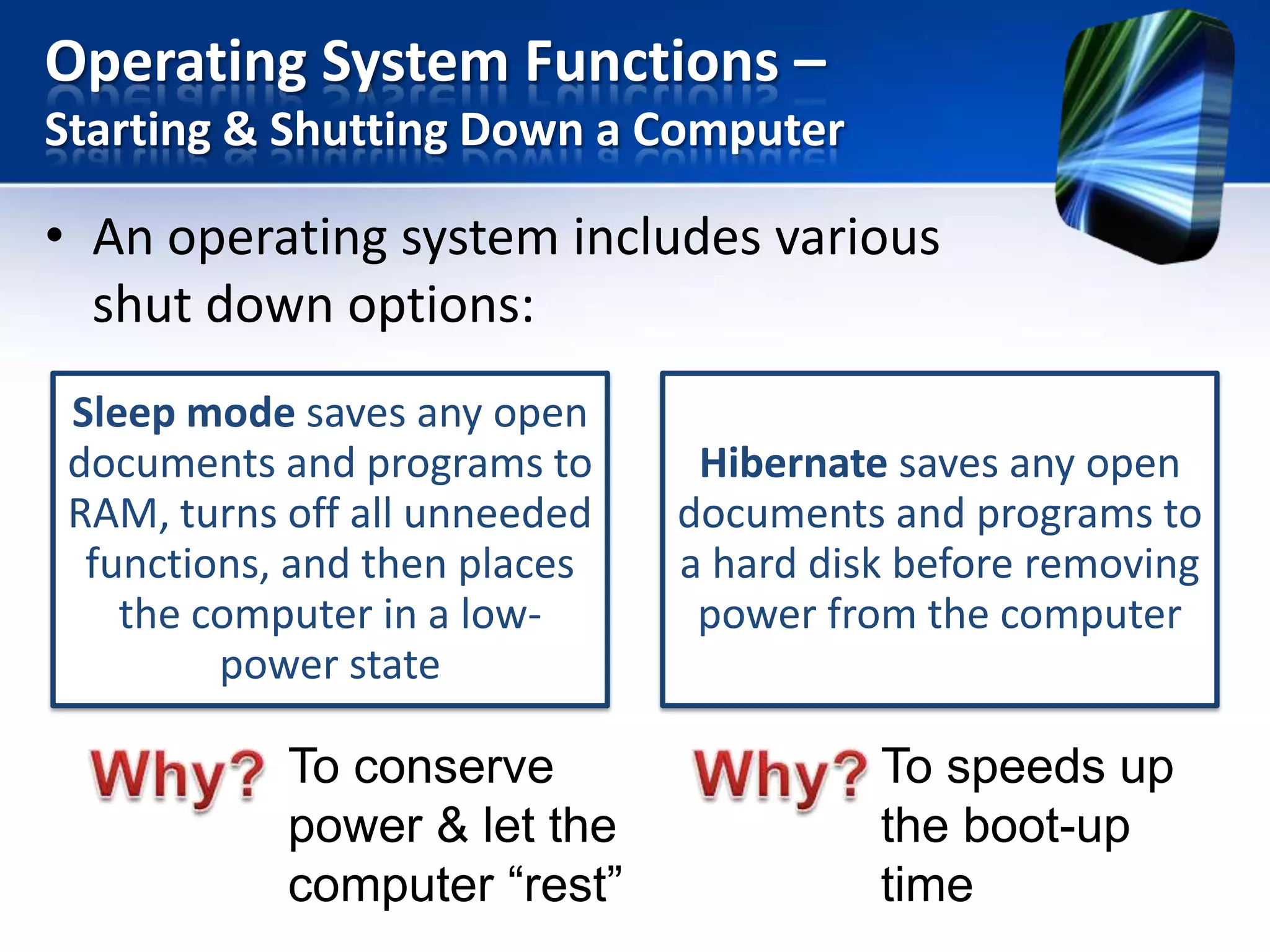
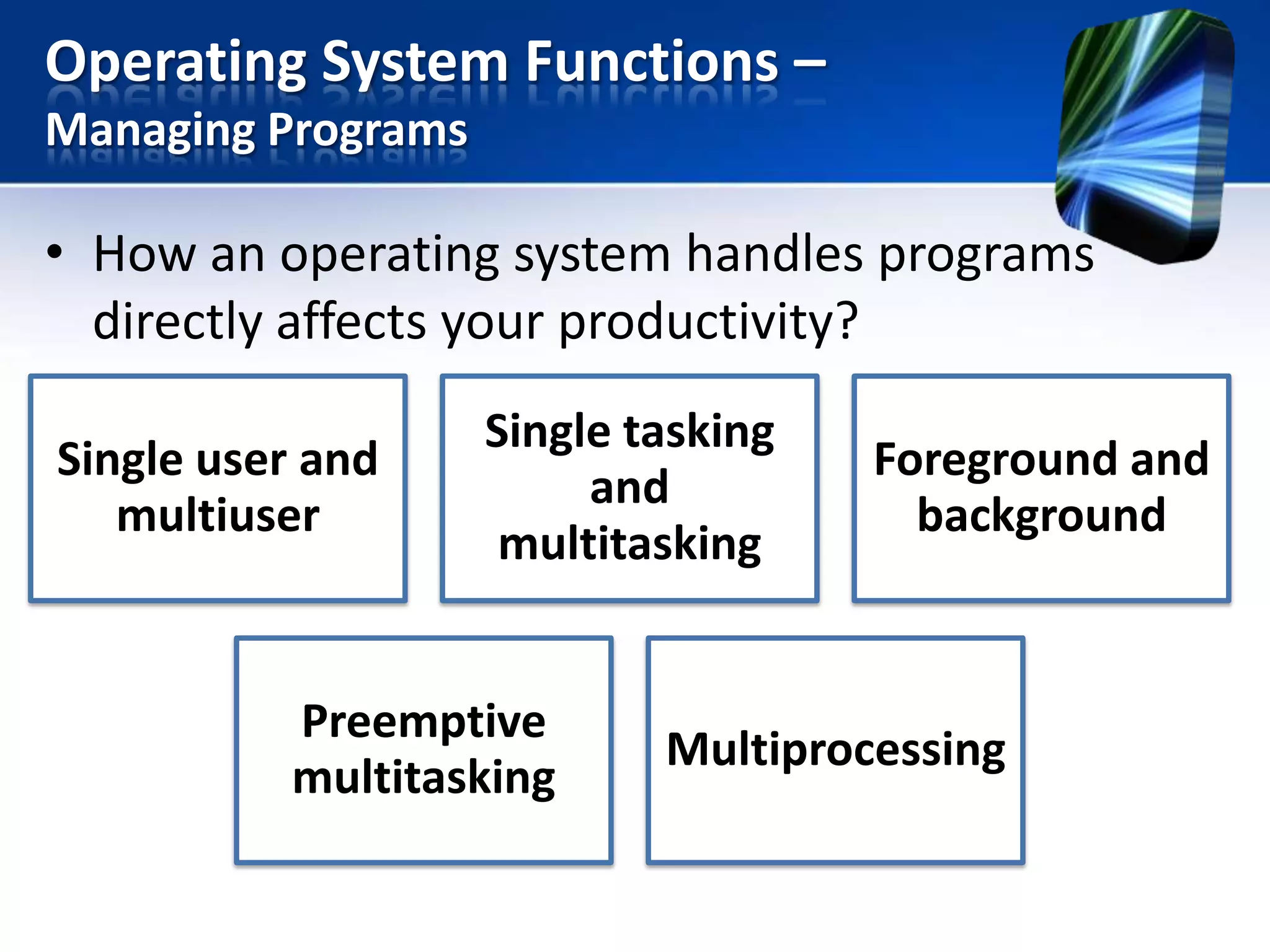
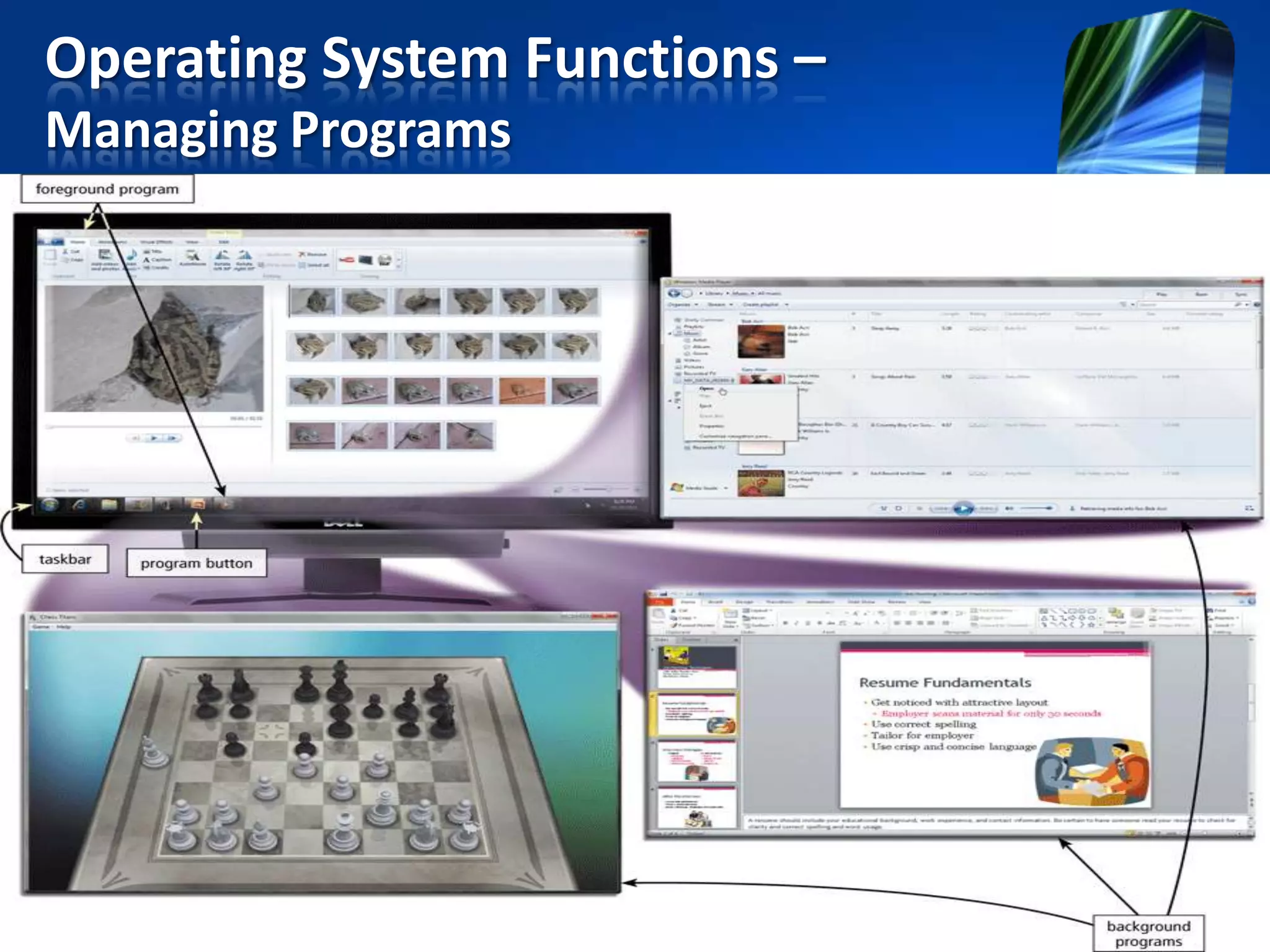
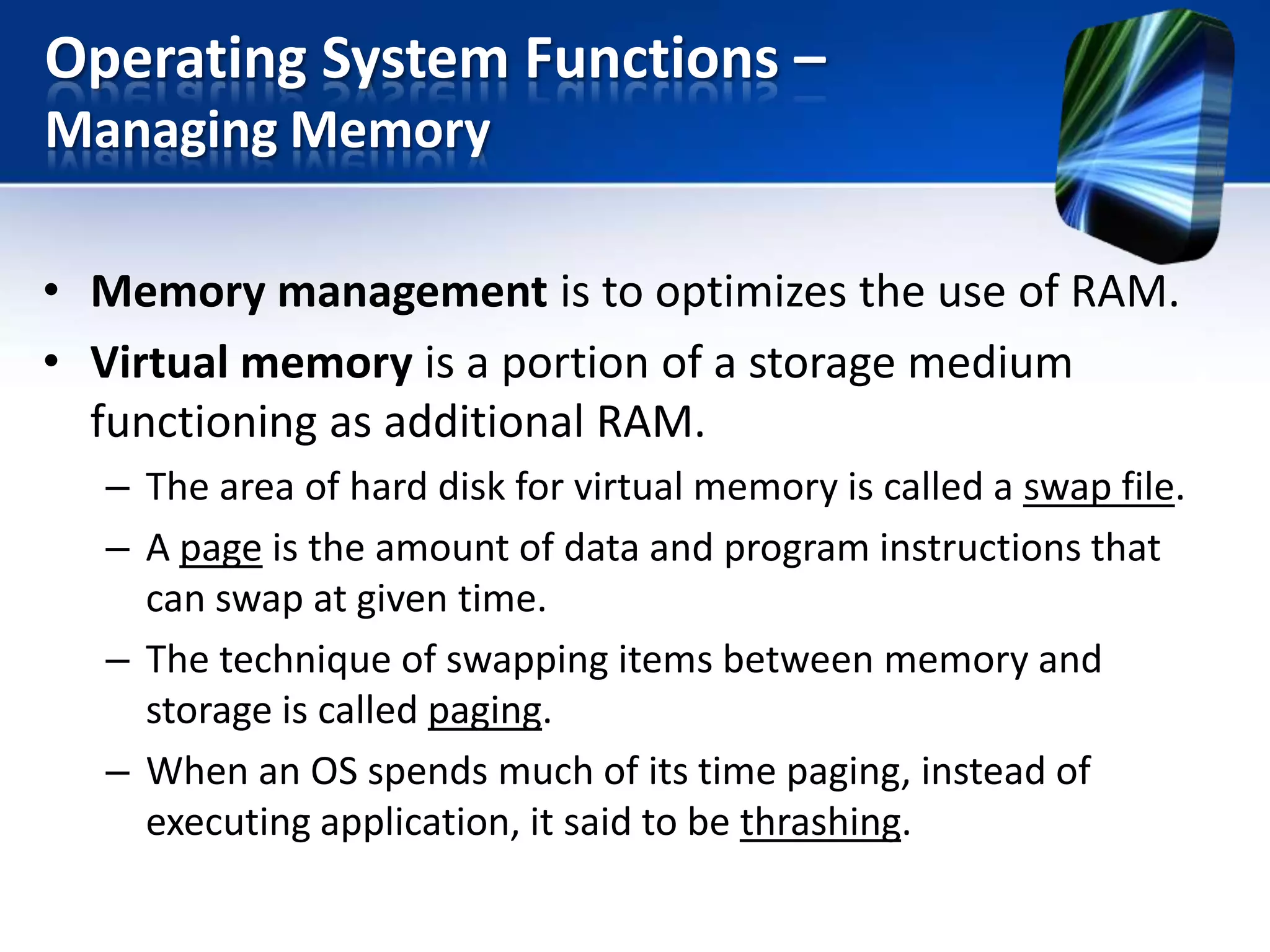
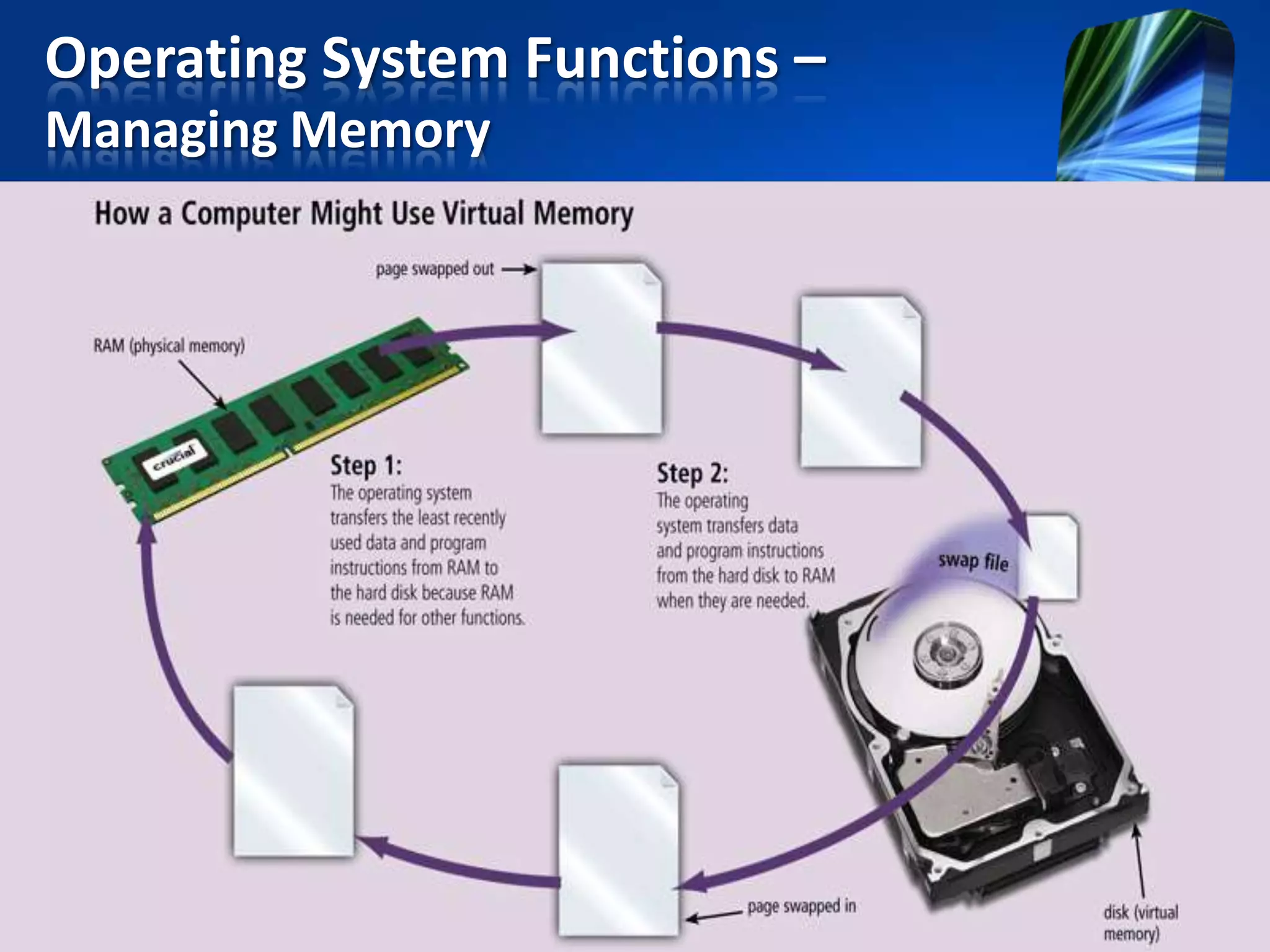
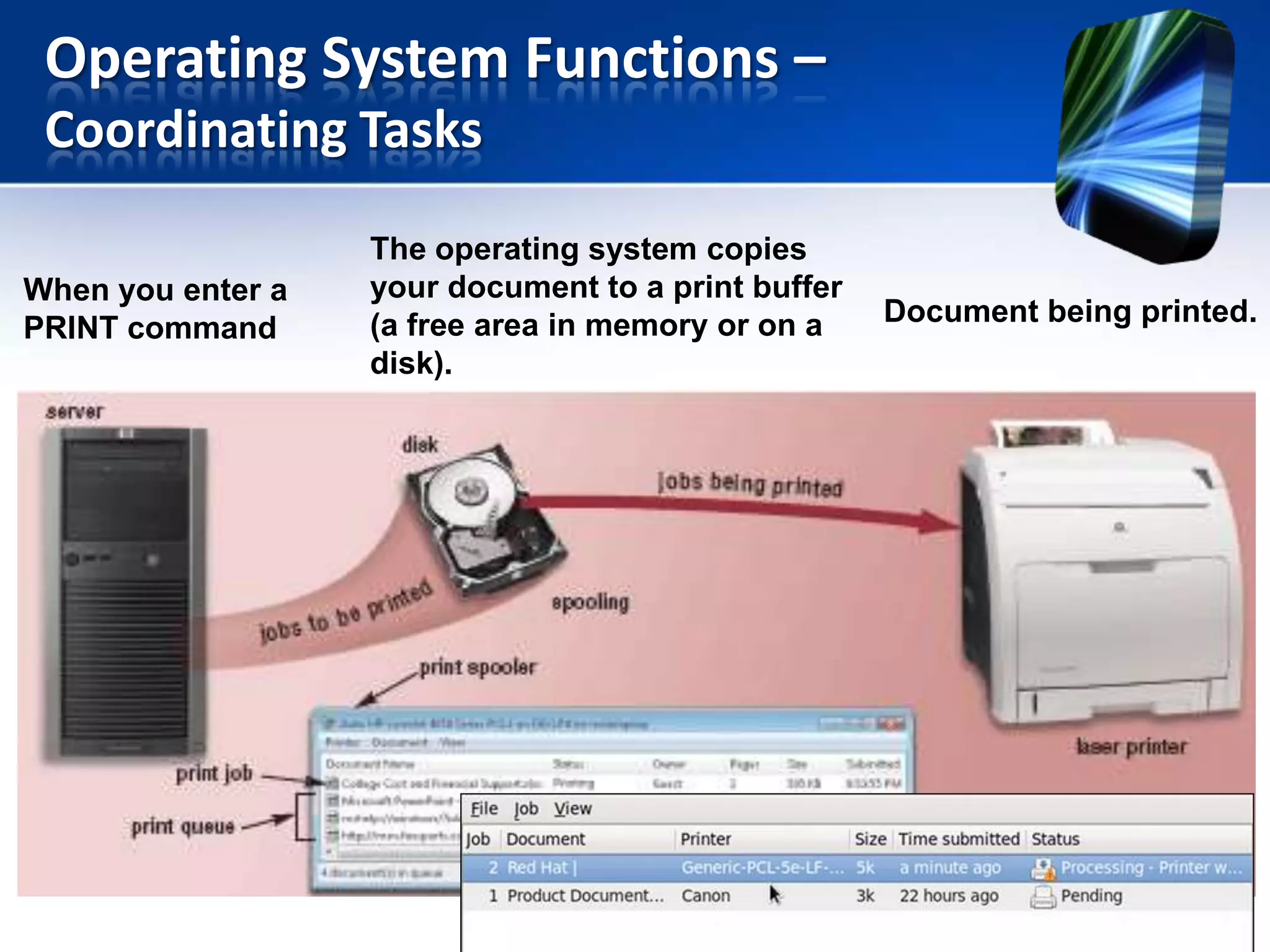
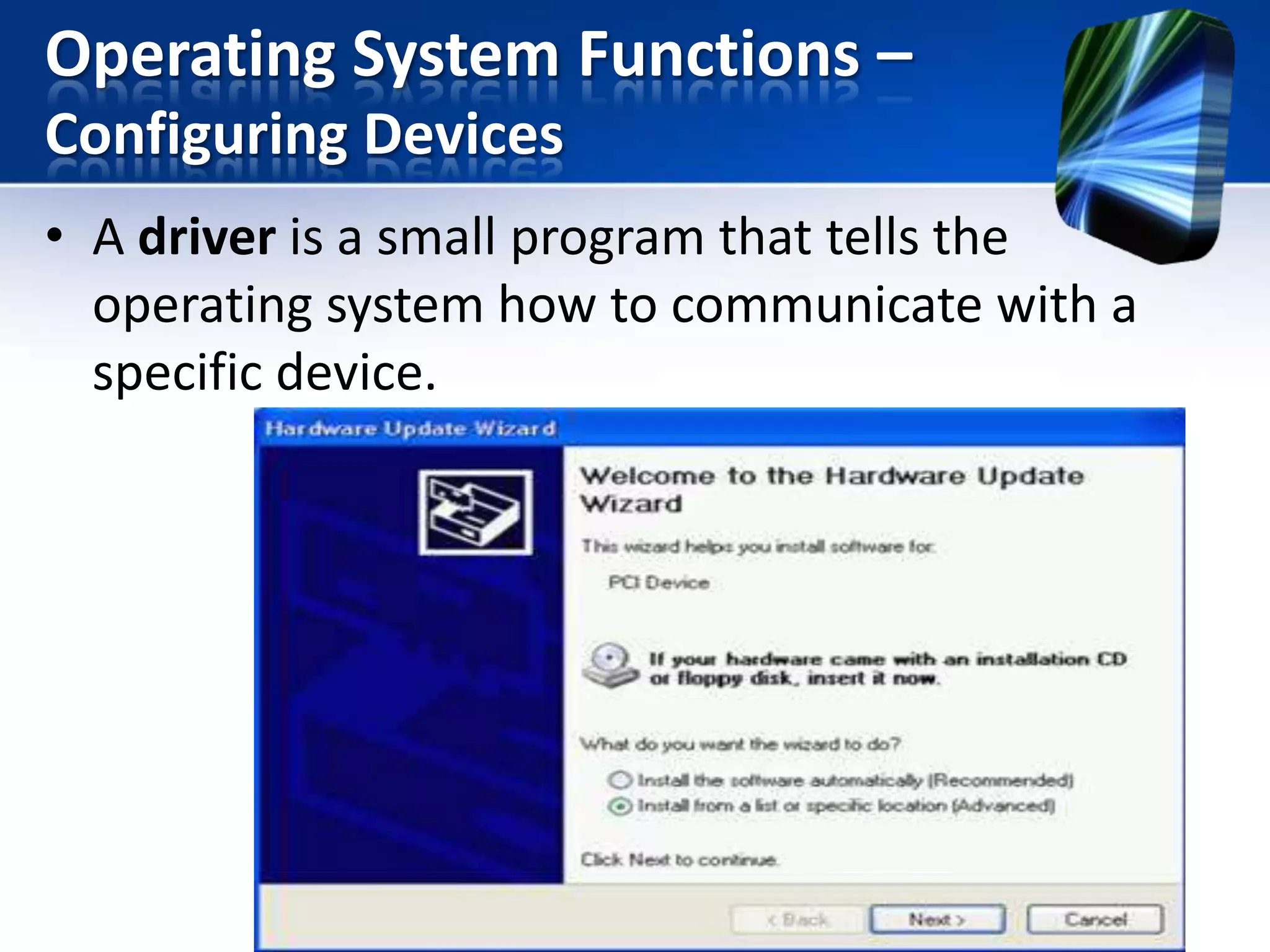
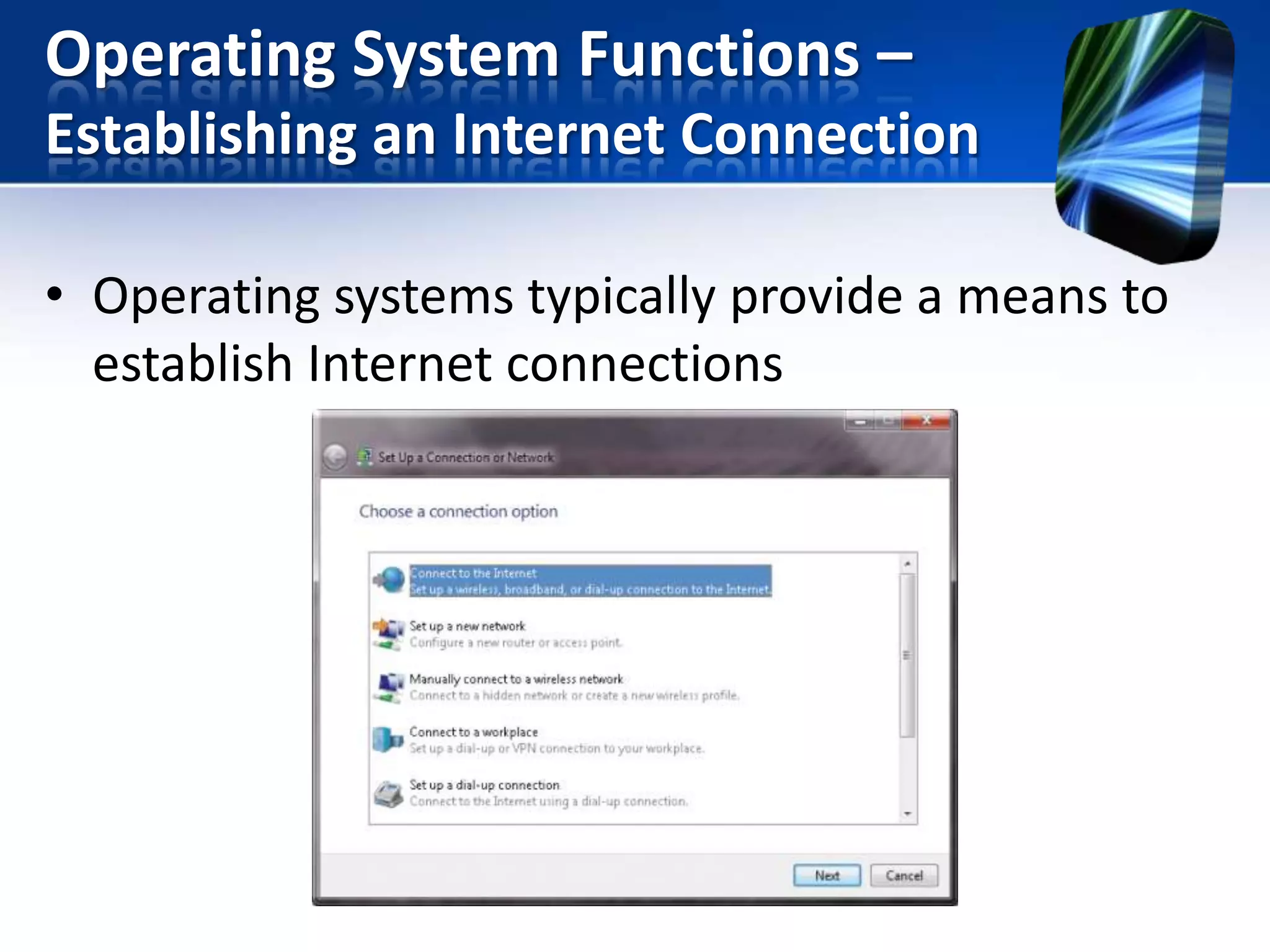
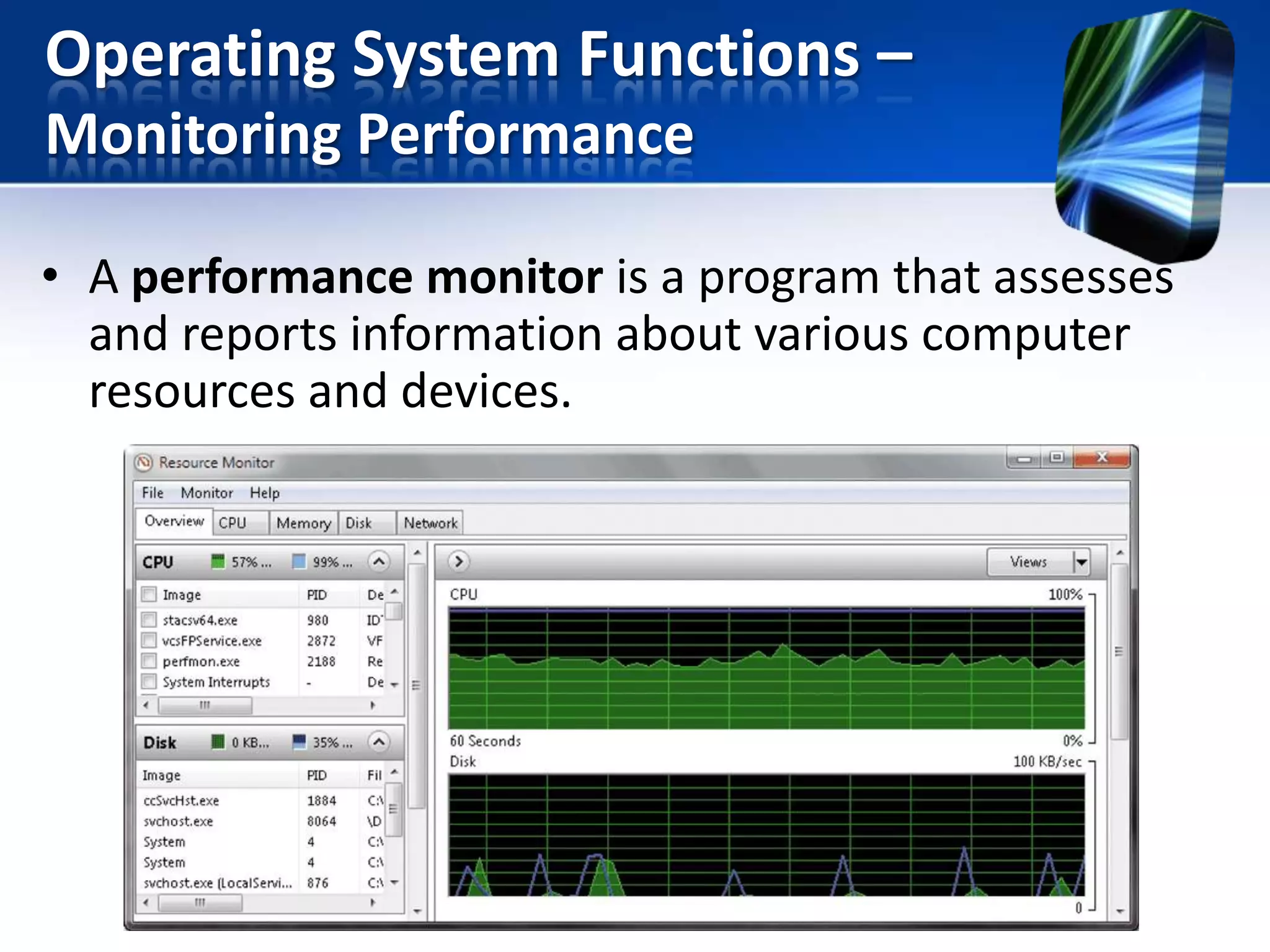
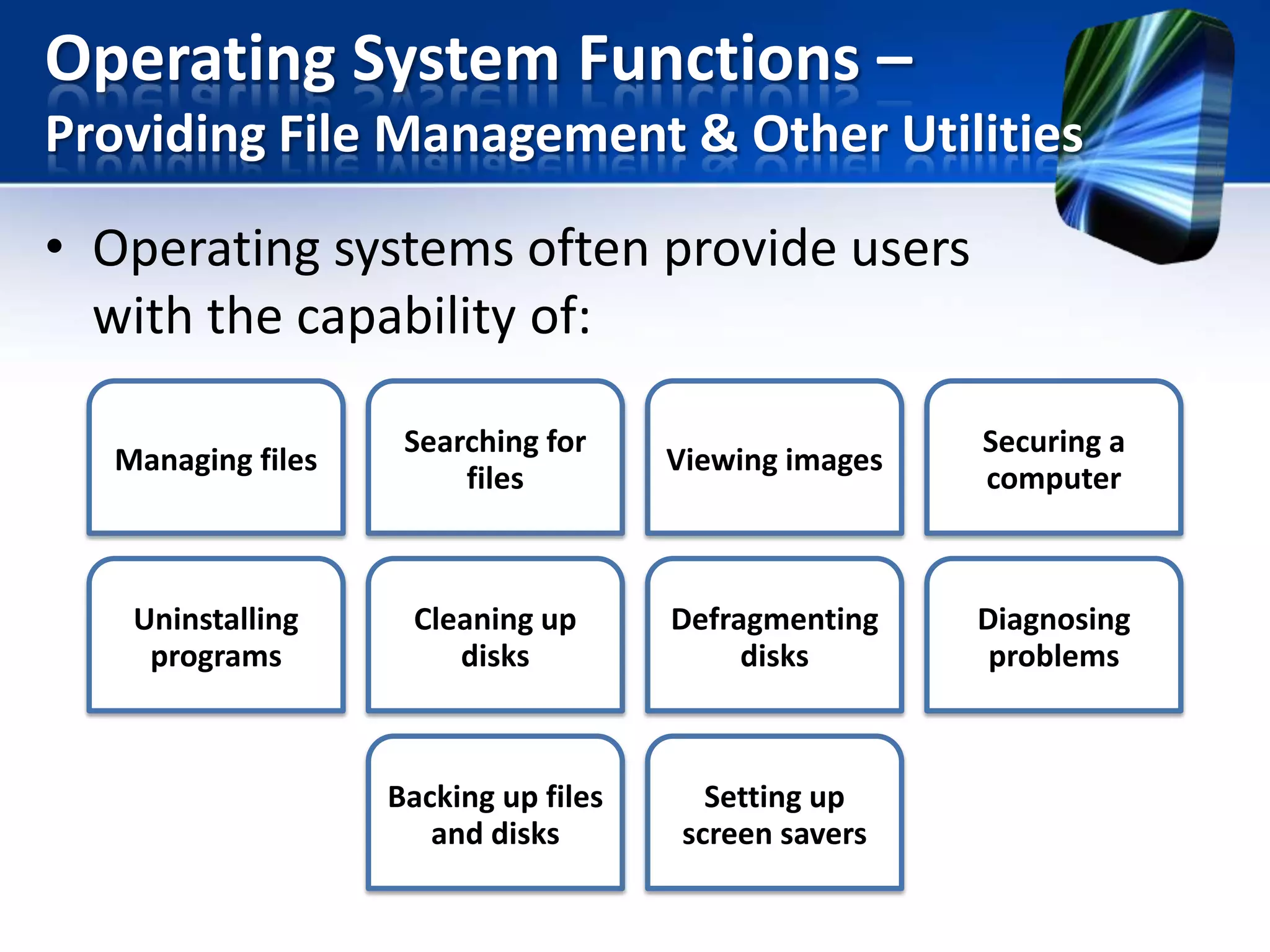
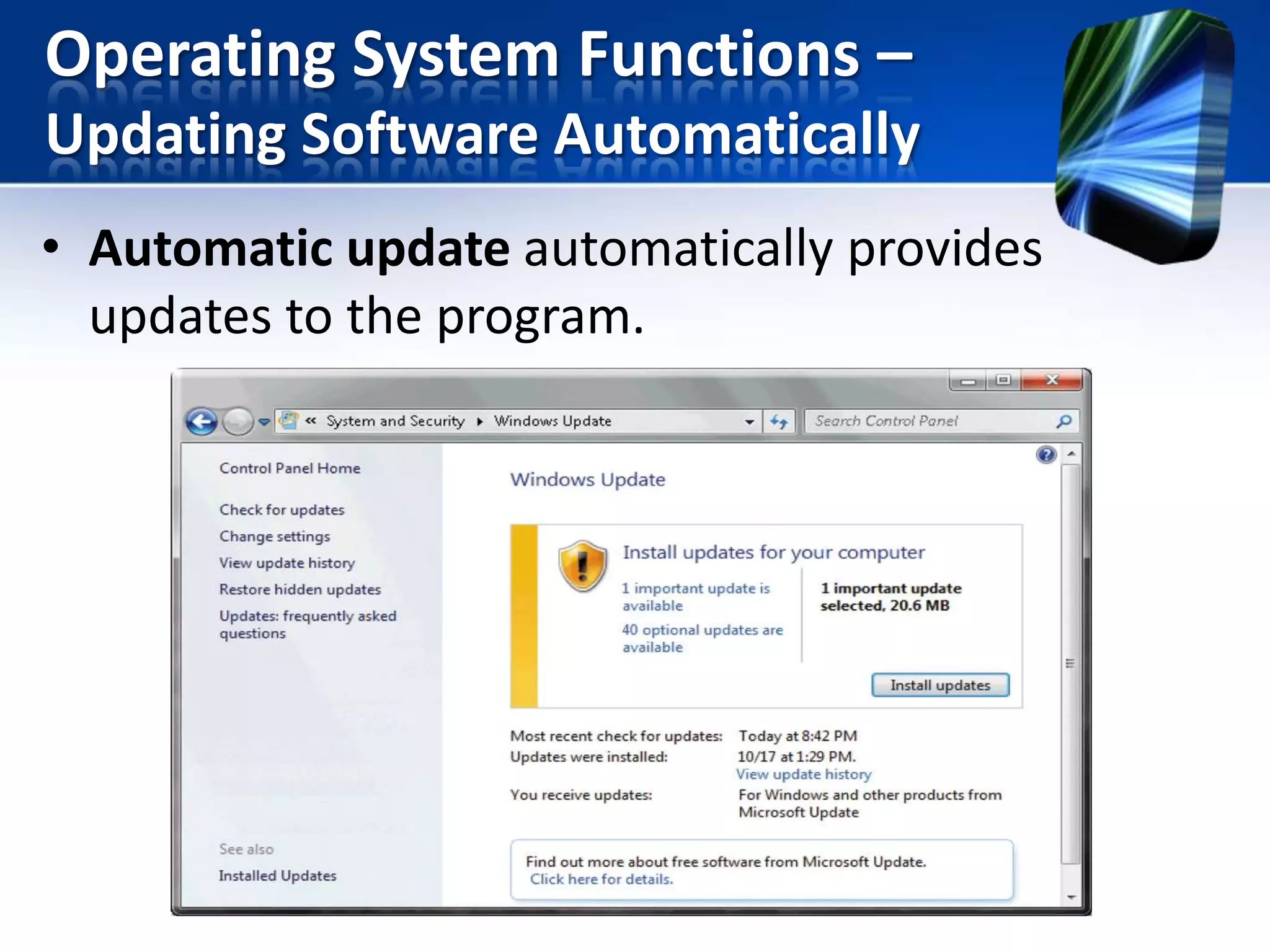
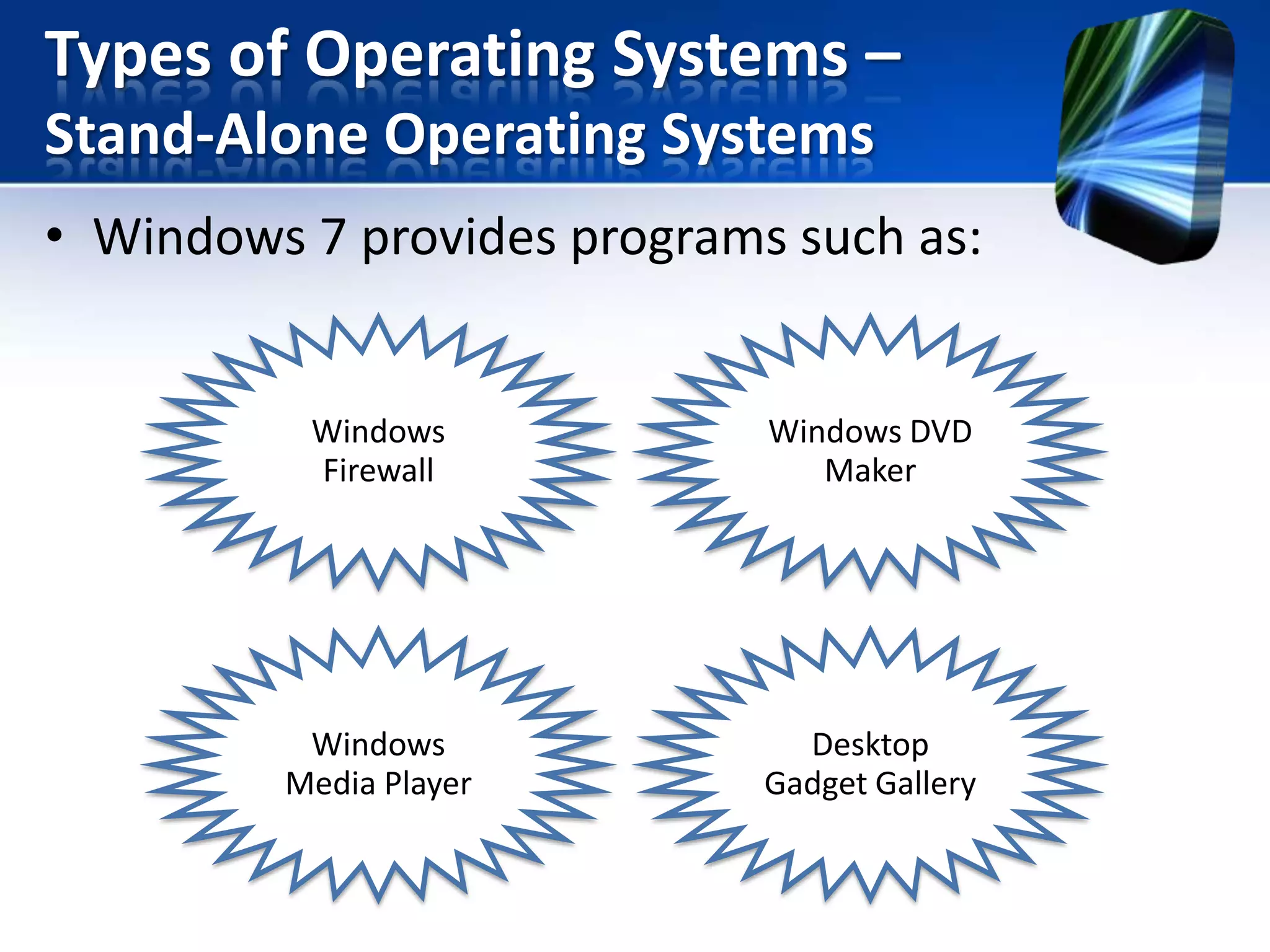
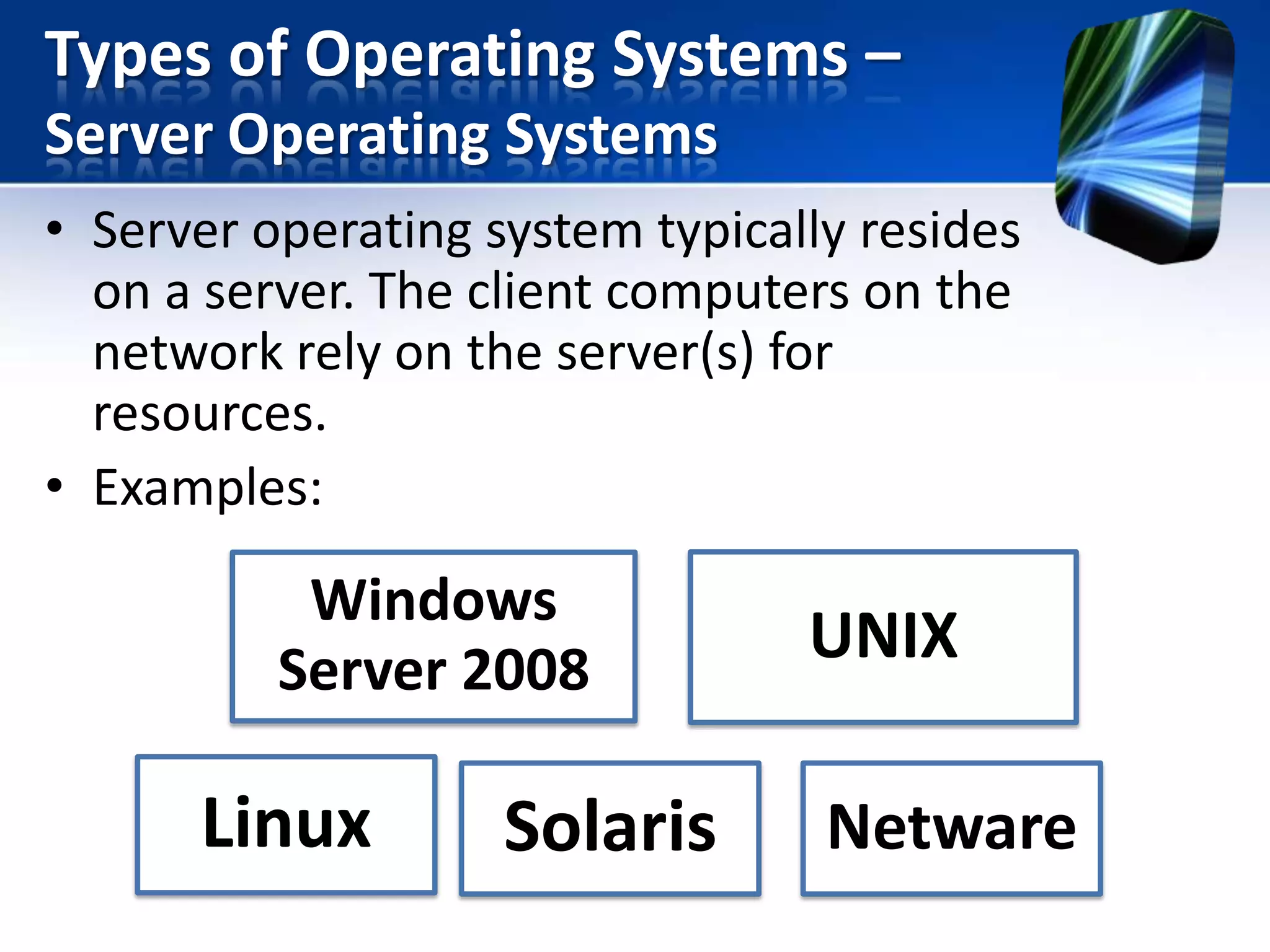
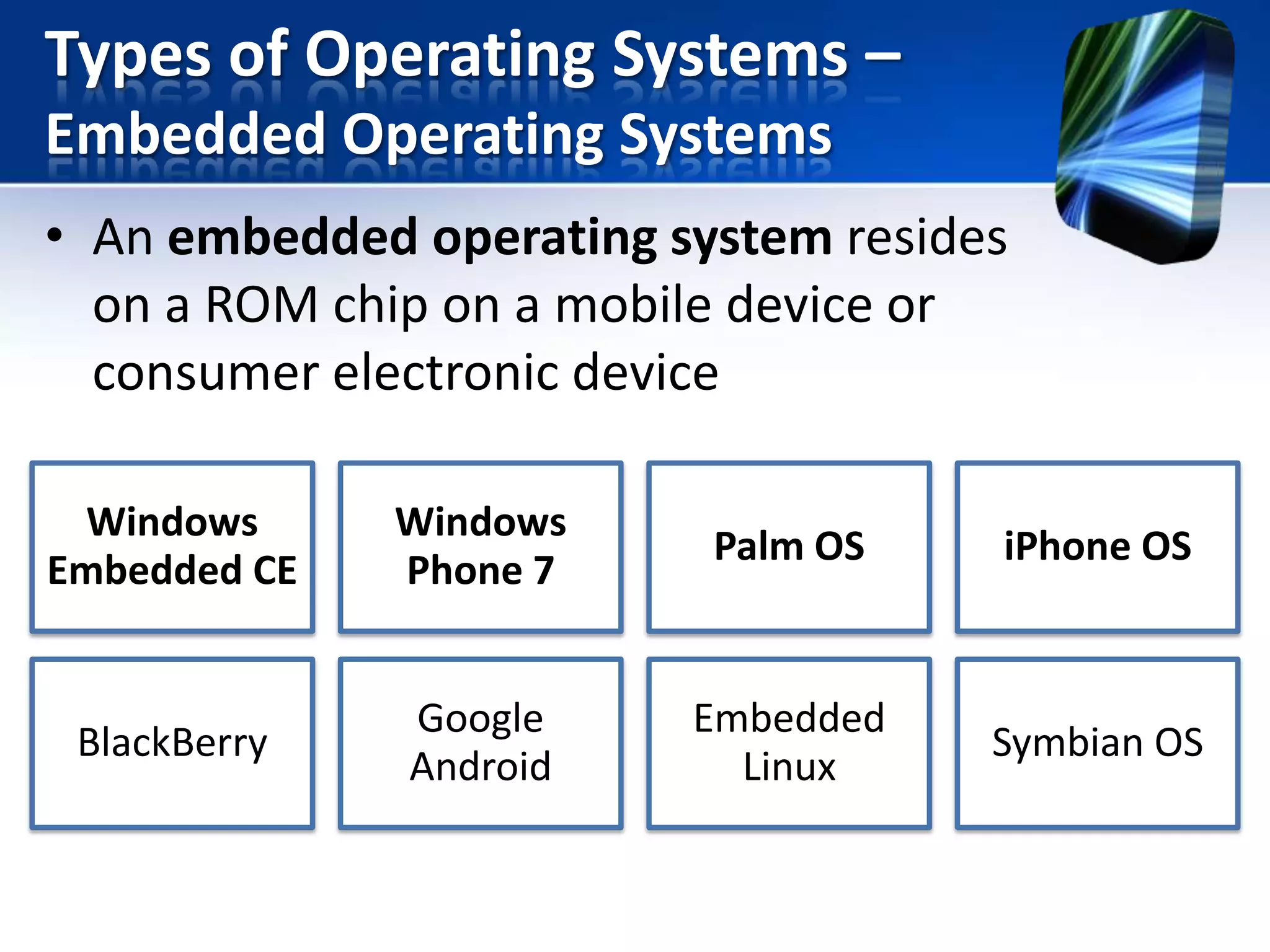
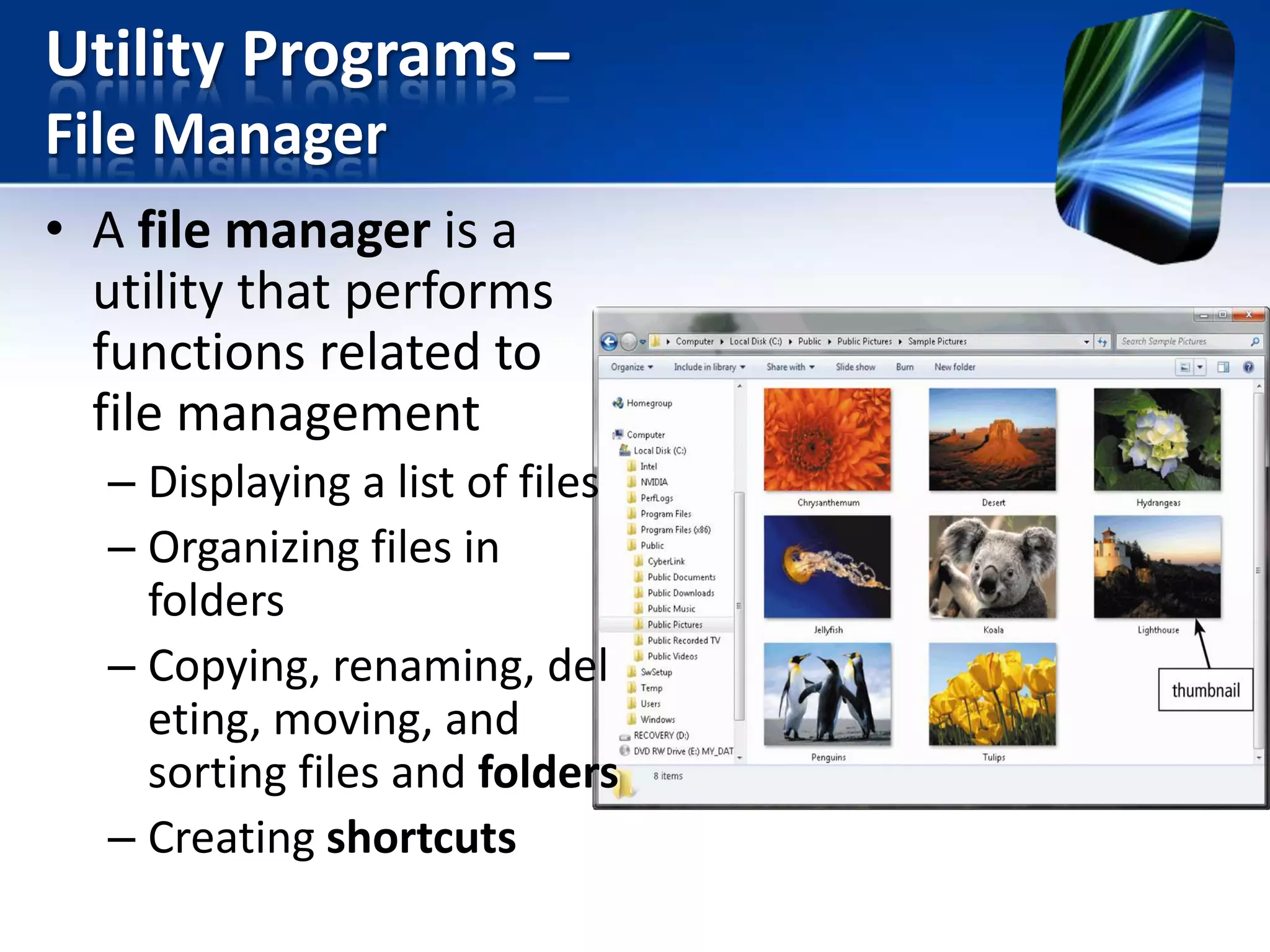
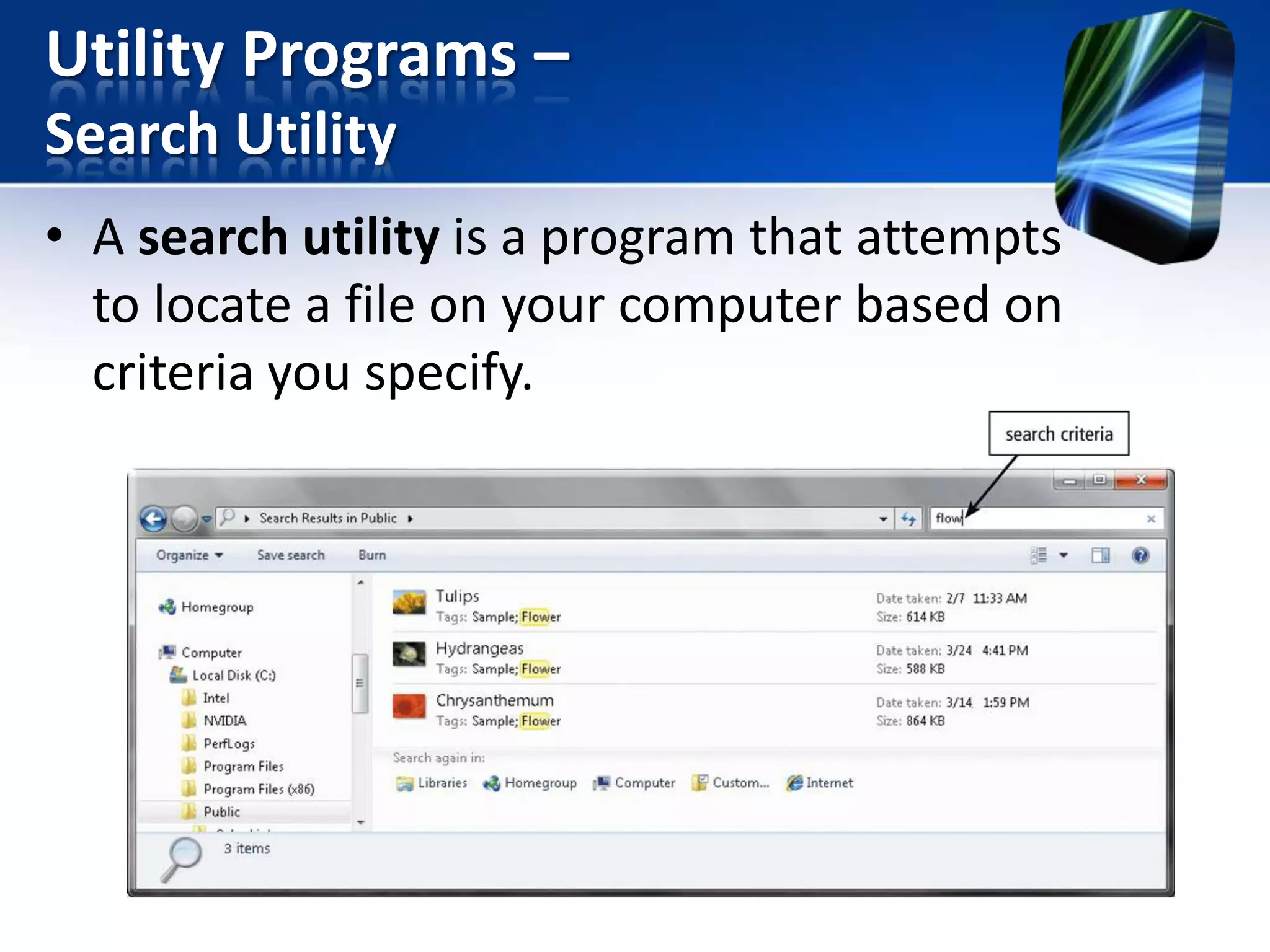
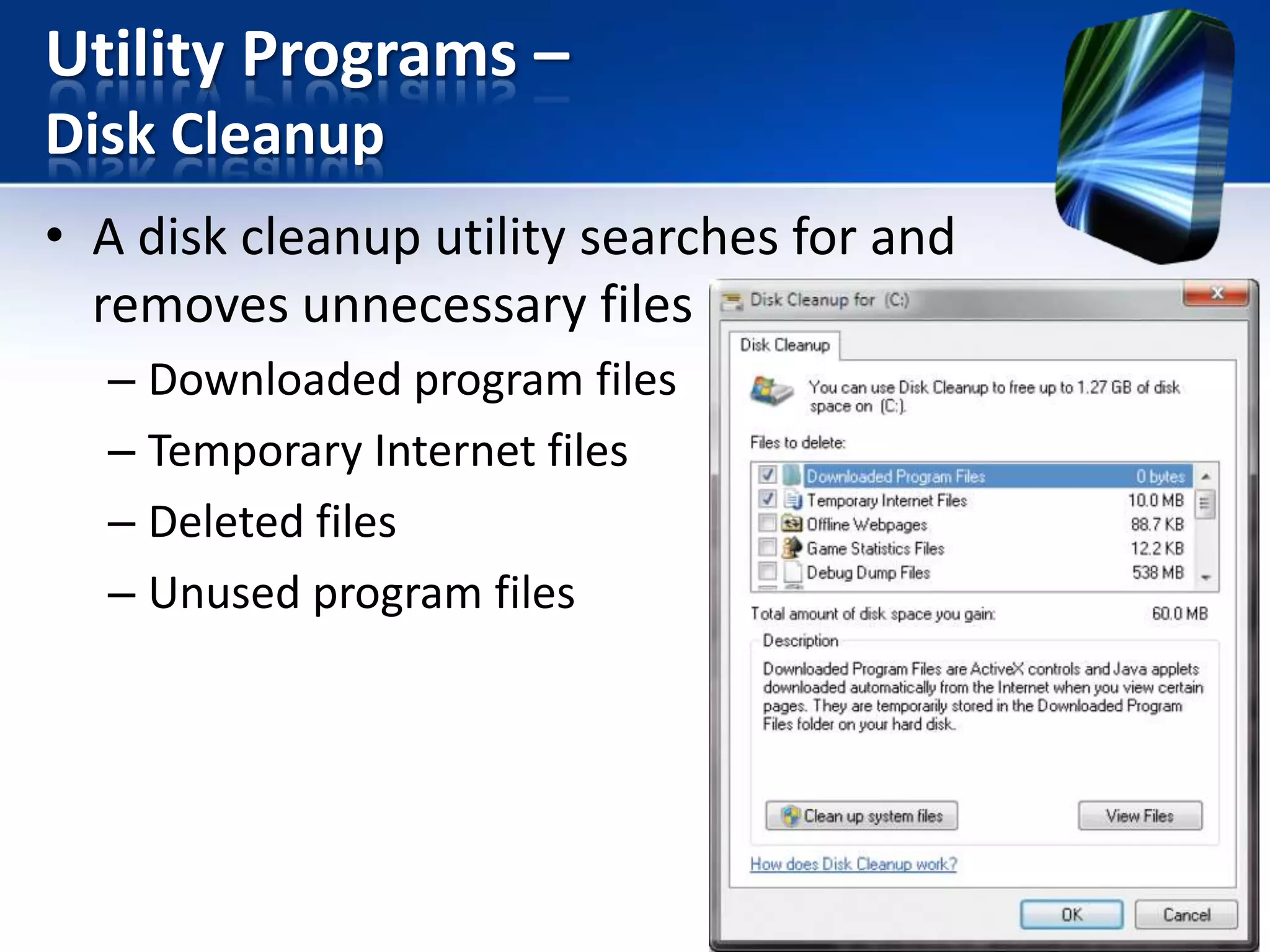
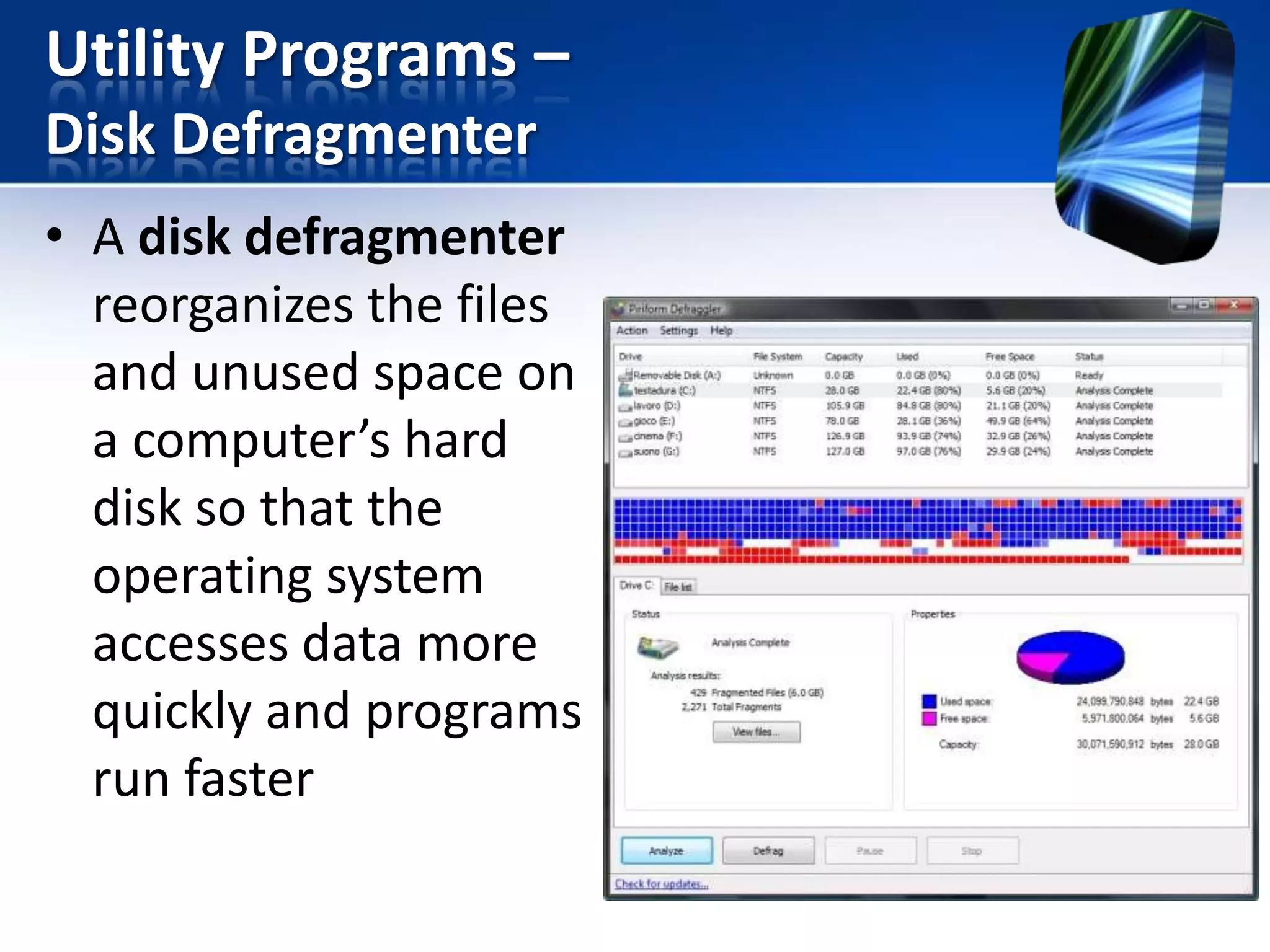
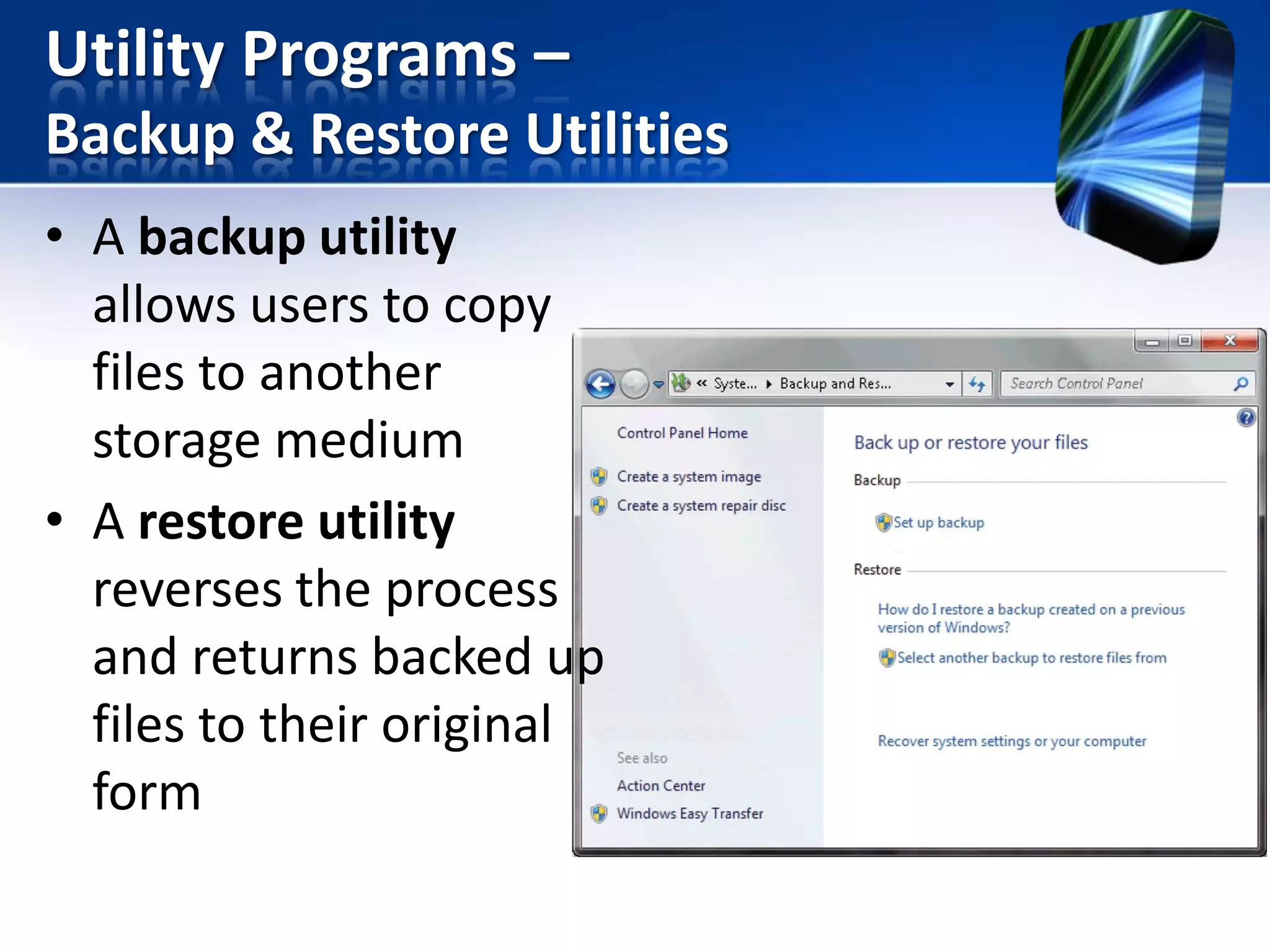
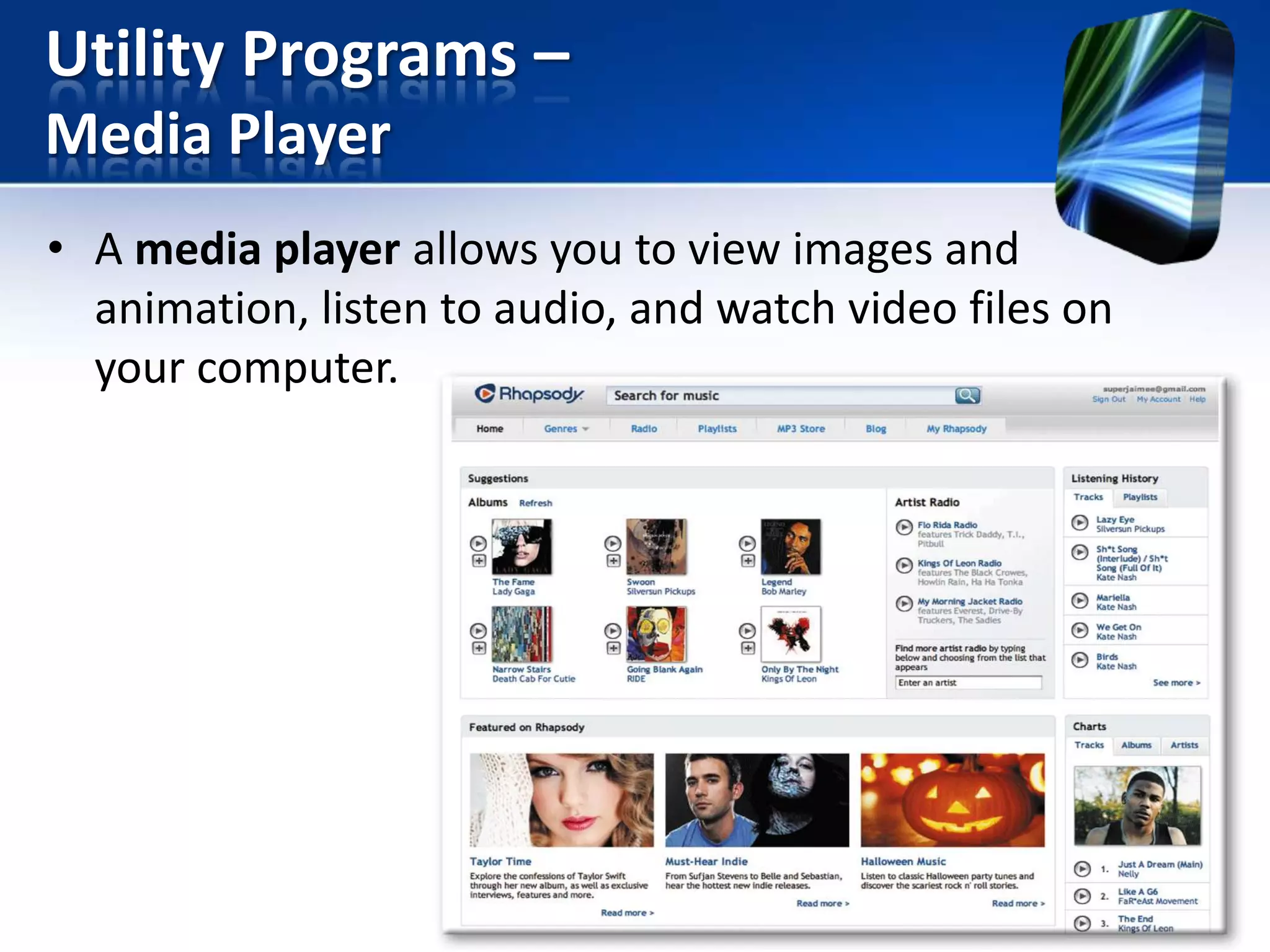
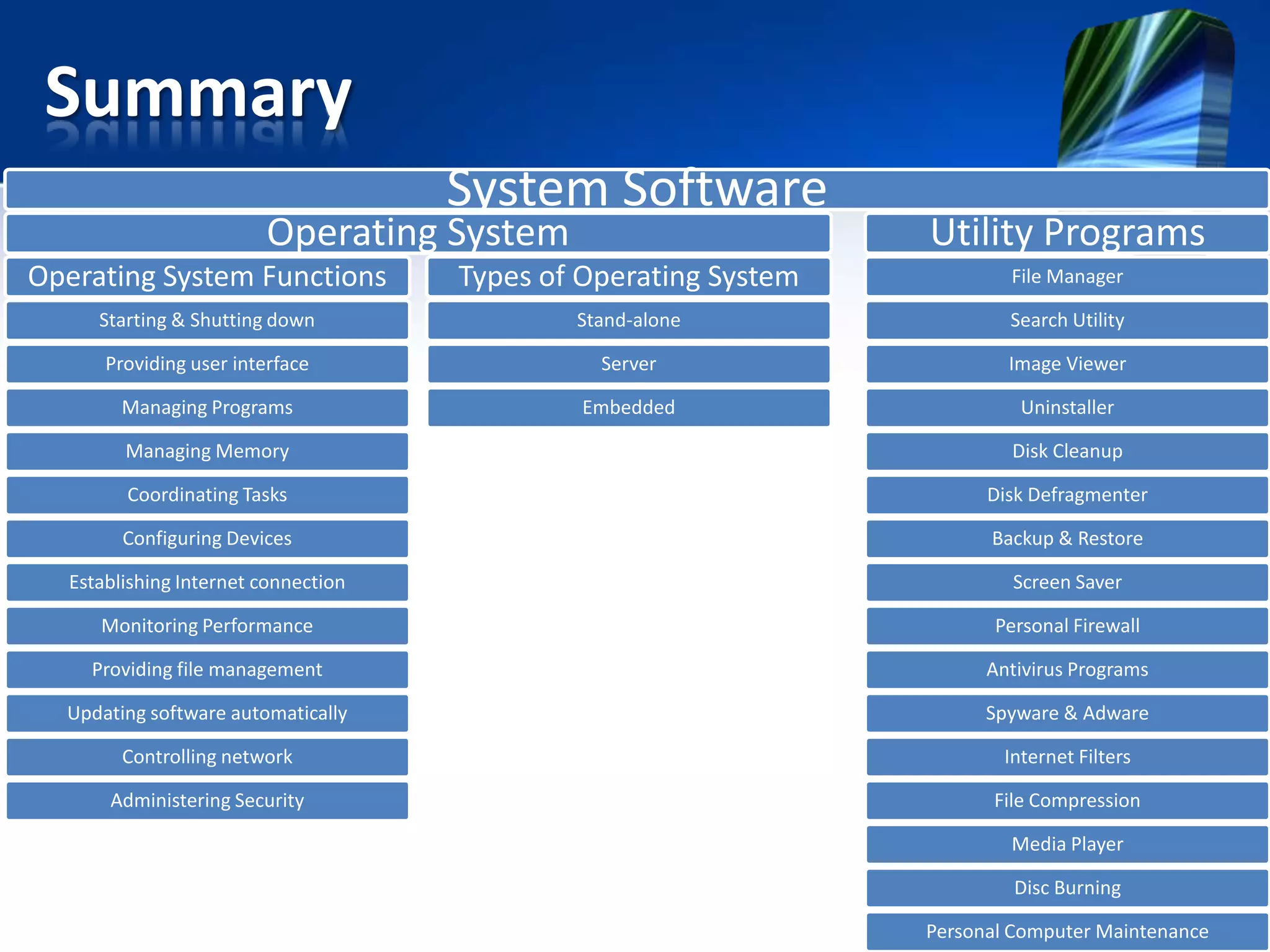
The document discusses operating systems and utility programs. It defines an operating system as a set of programs that coordinate computer hardware resources. Operating systems provide functions like starting up and shutting down computers, managing memory, configuring devices, and establishing network connections. There are different types of operating systems including stand-alone operating systems designed for personal computers, server operating systems that manage networks, and embedded operating systems used in mobile devices. The document also briefly describes some common operating systems and their uses.