This document discusses different types of software, including system software and application software. It focuses on system software, describing the main types as operating systems and utility programs. It provides details on the functions of operating systems, examples of different operating systems, and types of utility programs. The key points covered are:
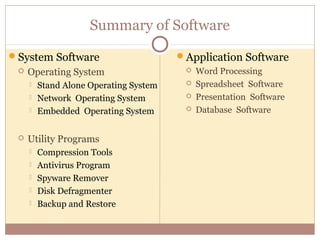
- Software is divided into system software (which includes operating systems and utilities) and application software.
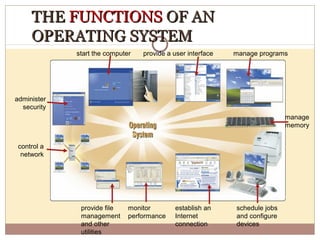
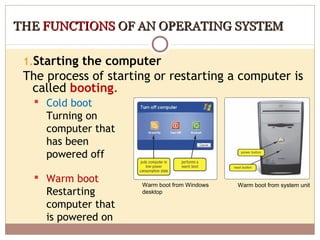
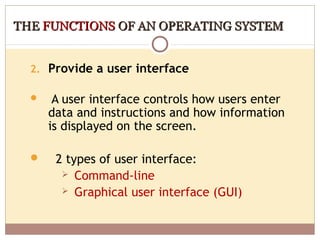
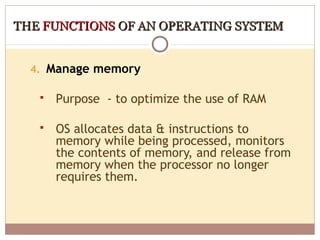
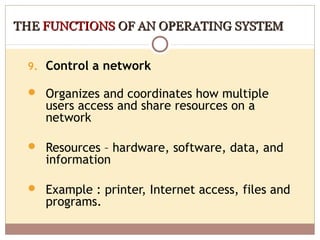
- Operating systems manage and coordinate computer hardware, run programs, provide file management and security, and perform other important functions.
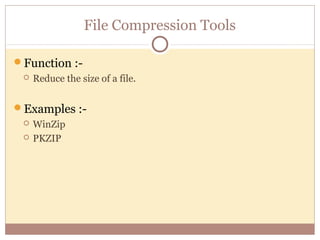
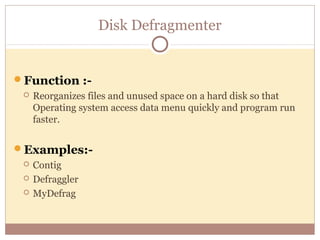
- Utility programs help maintain the computer system with tasks like file compression, disk maintenance, and security programs.