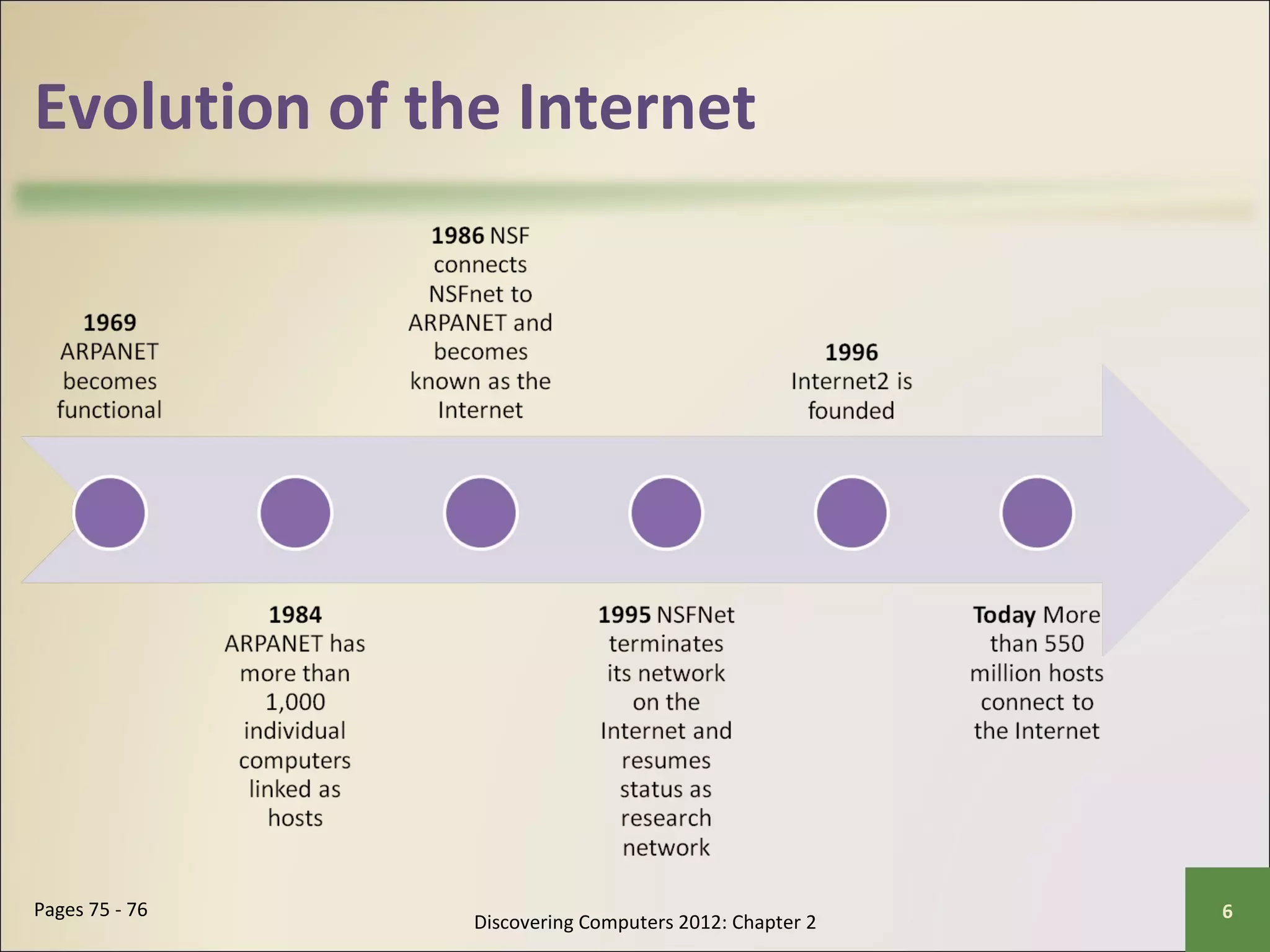
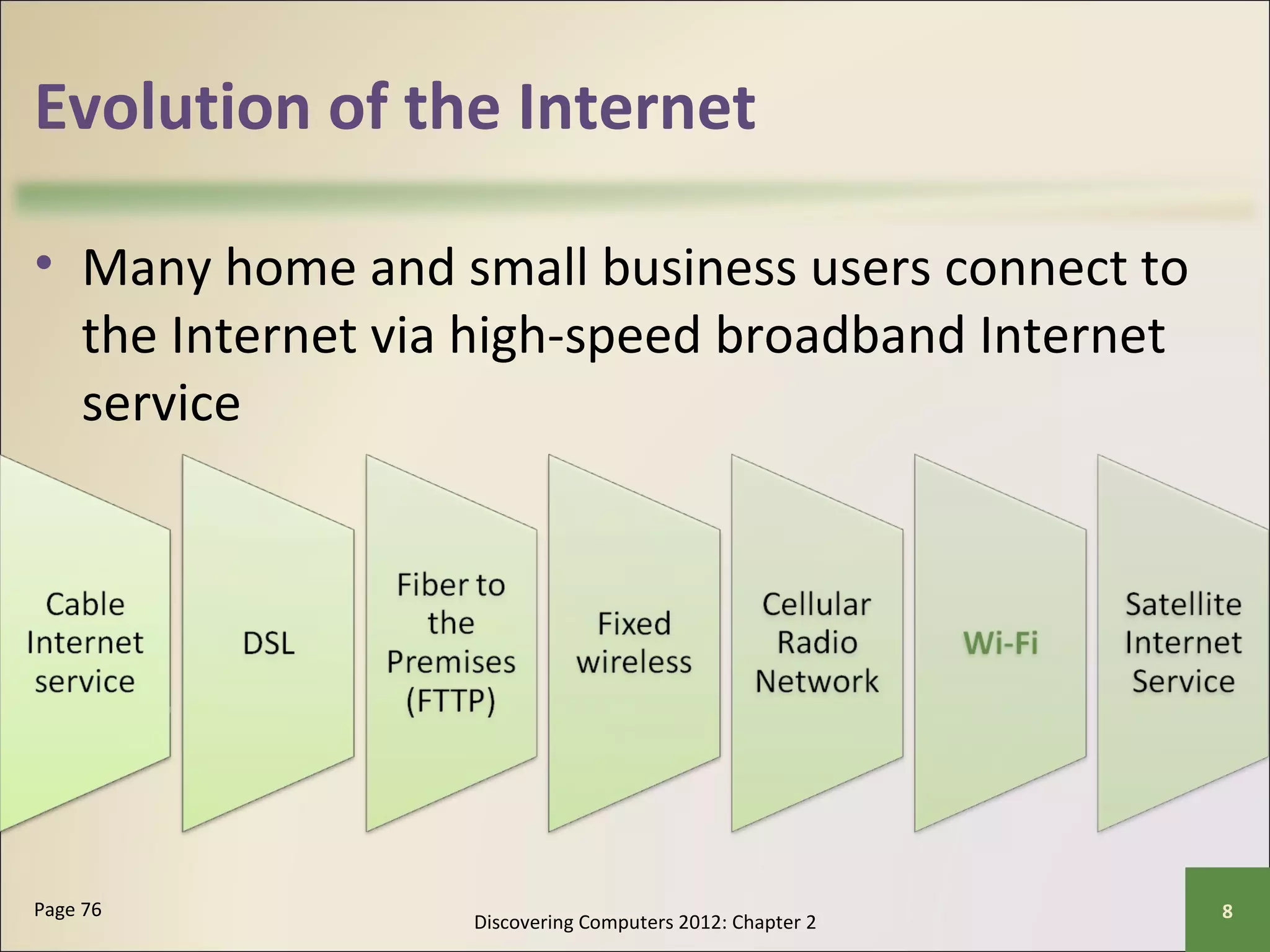
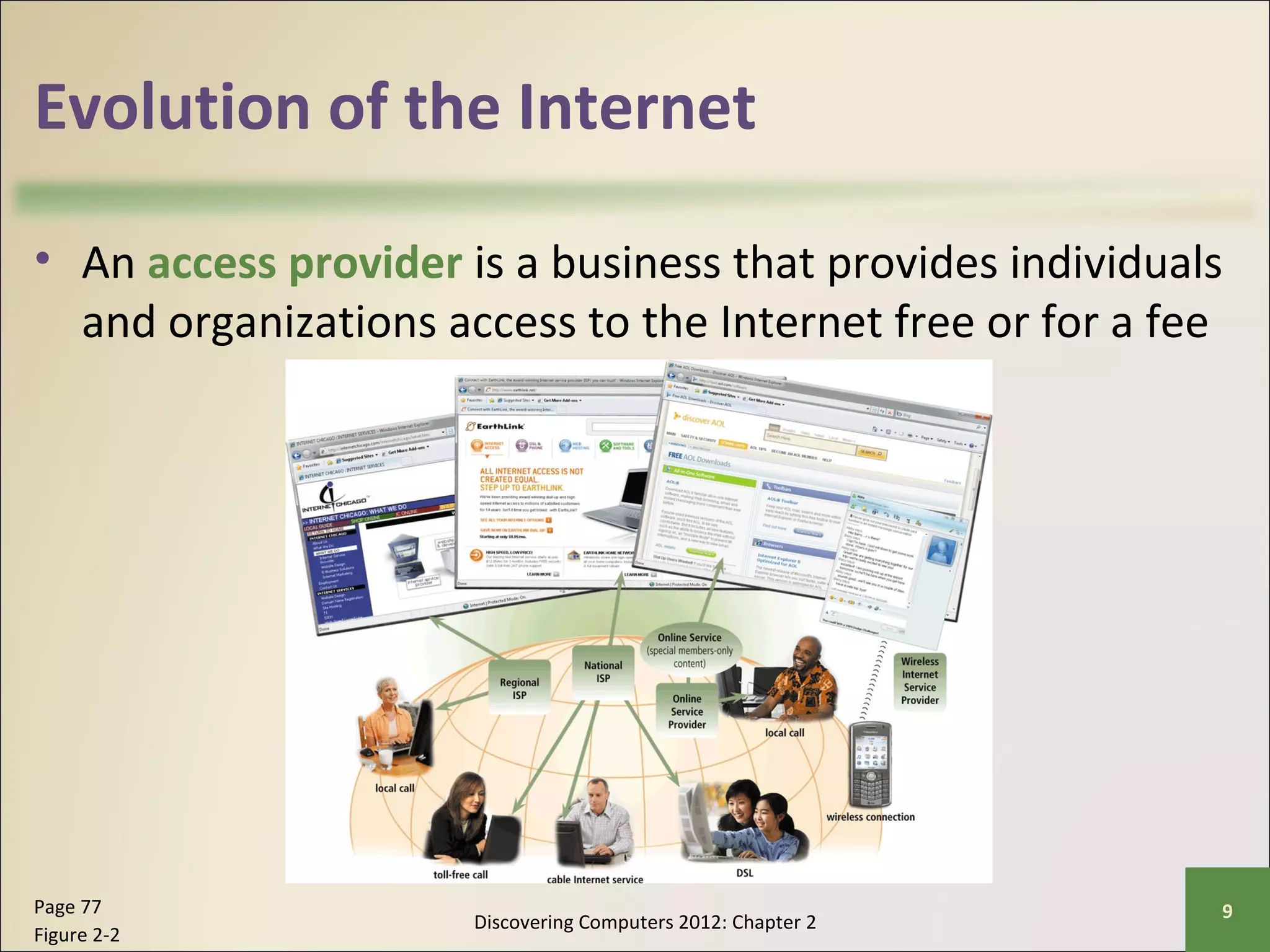
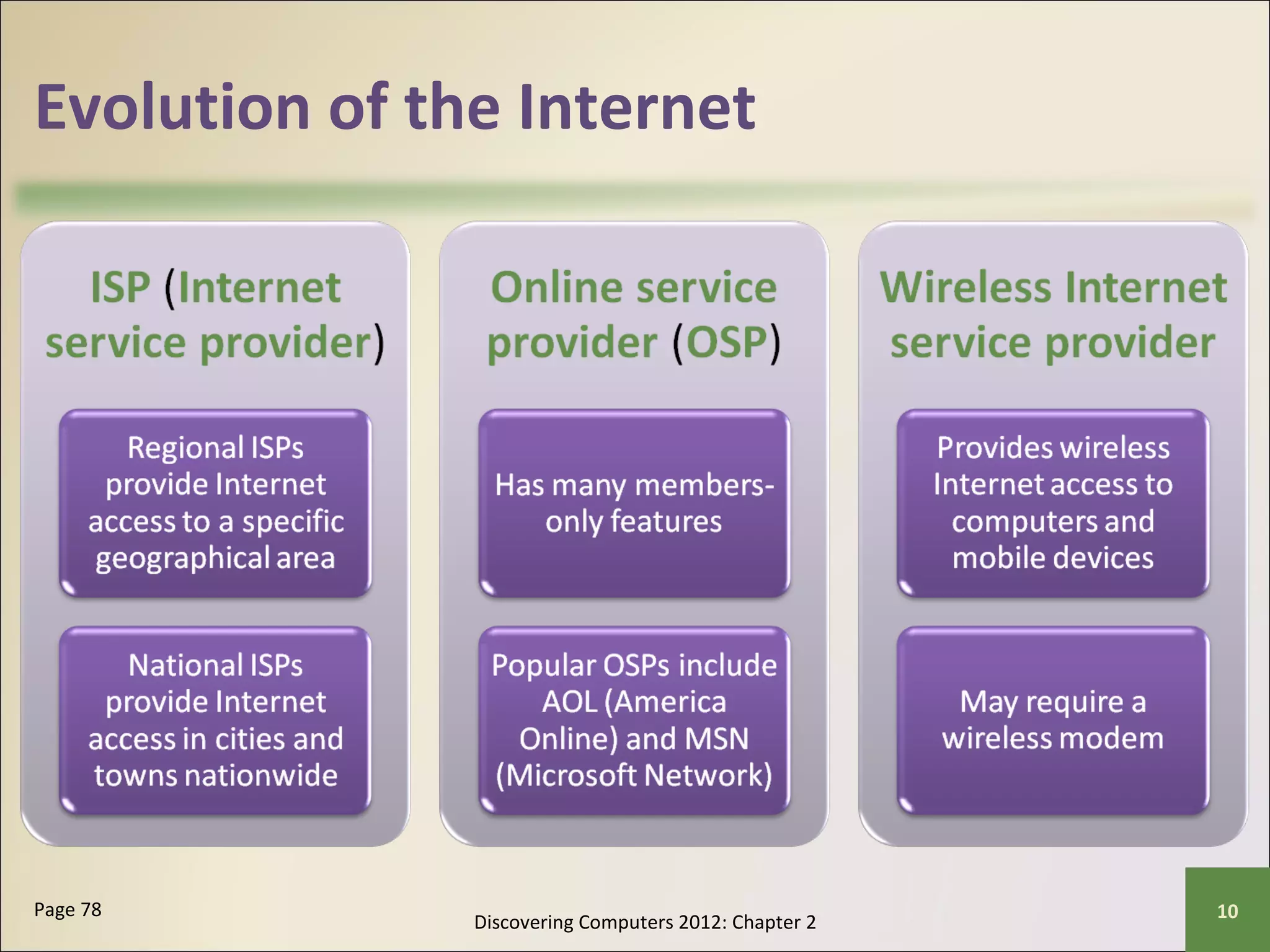
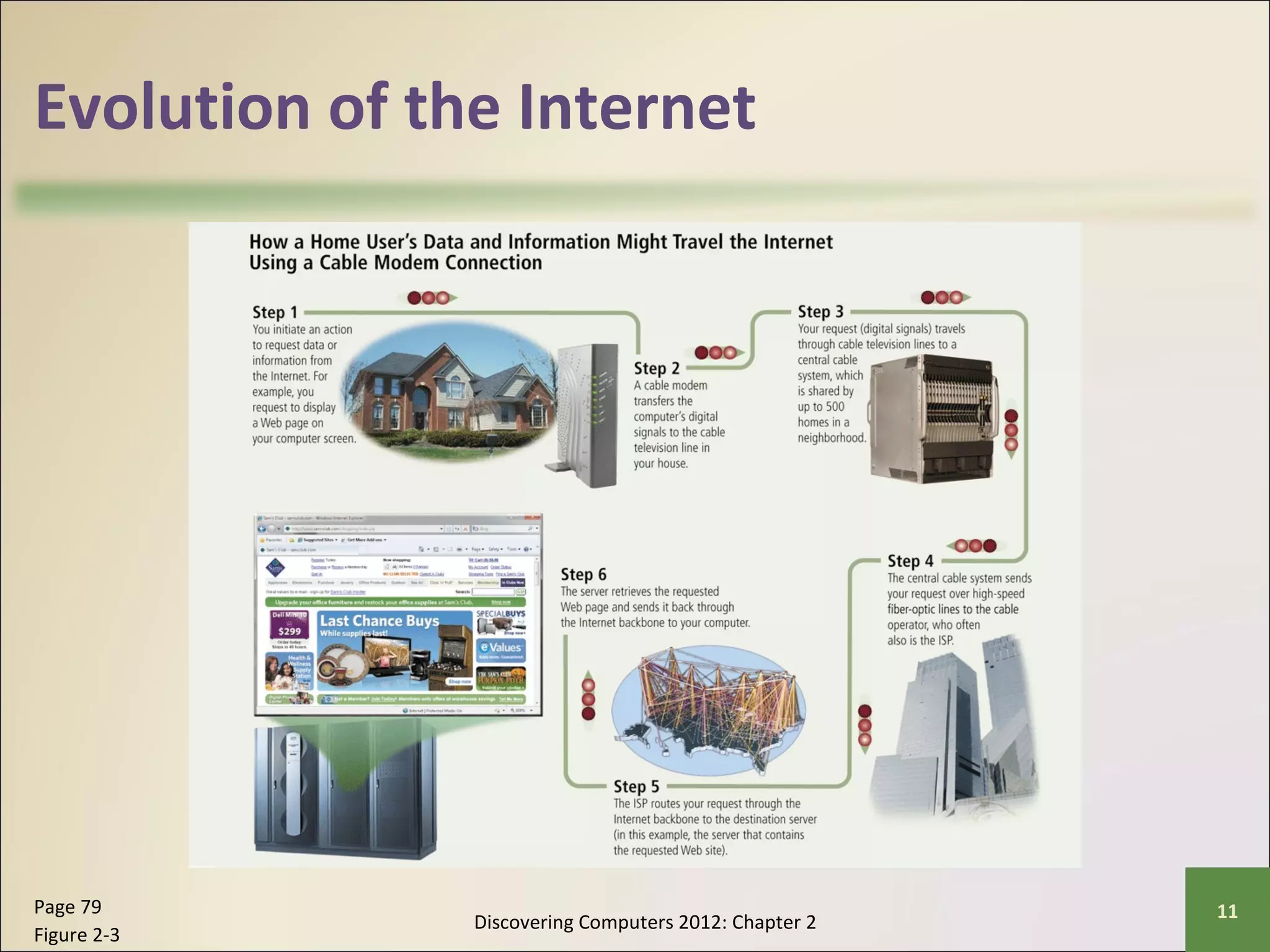
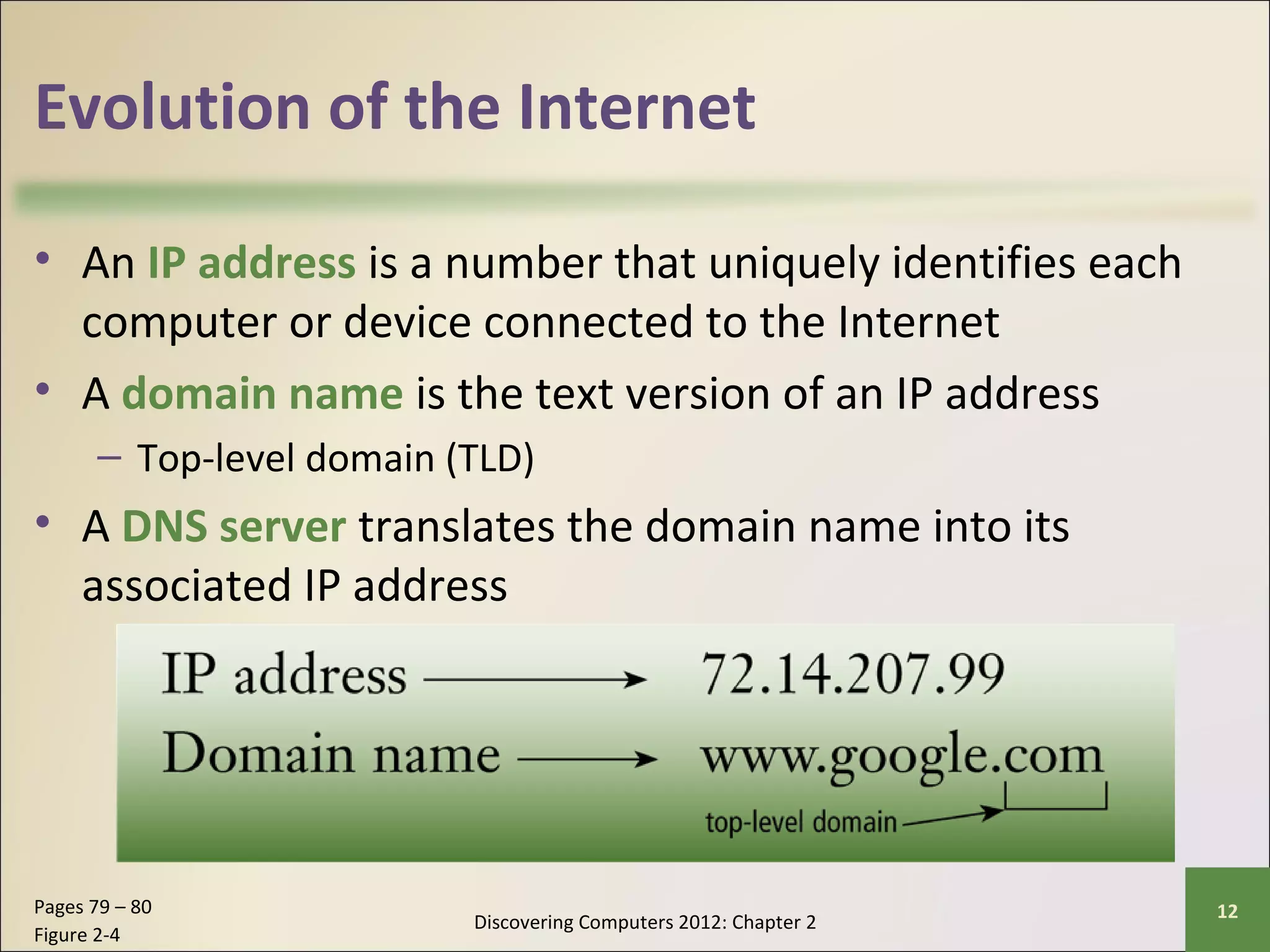
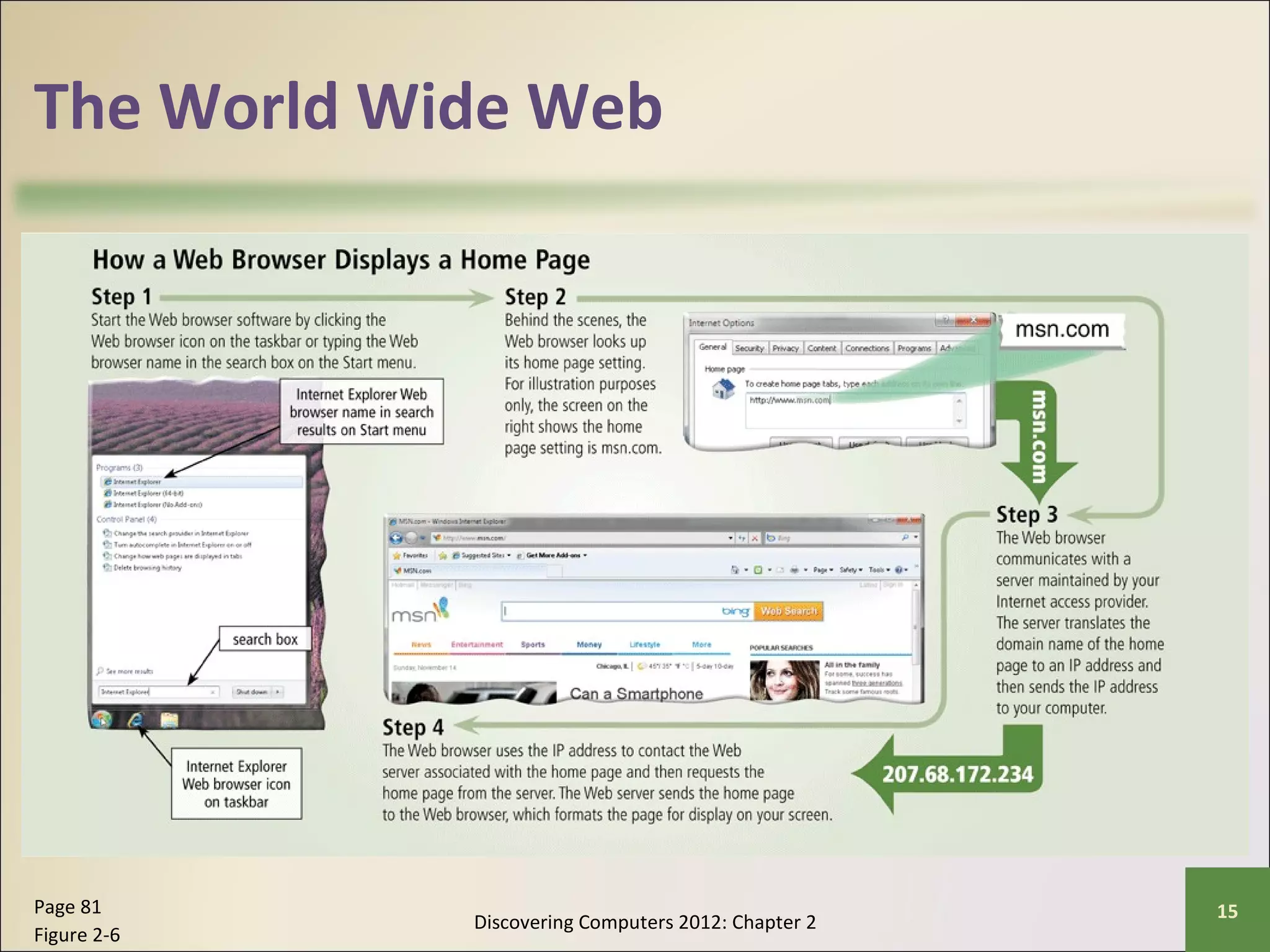
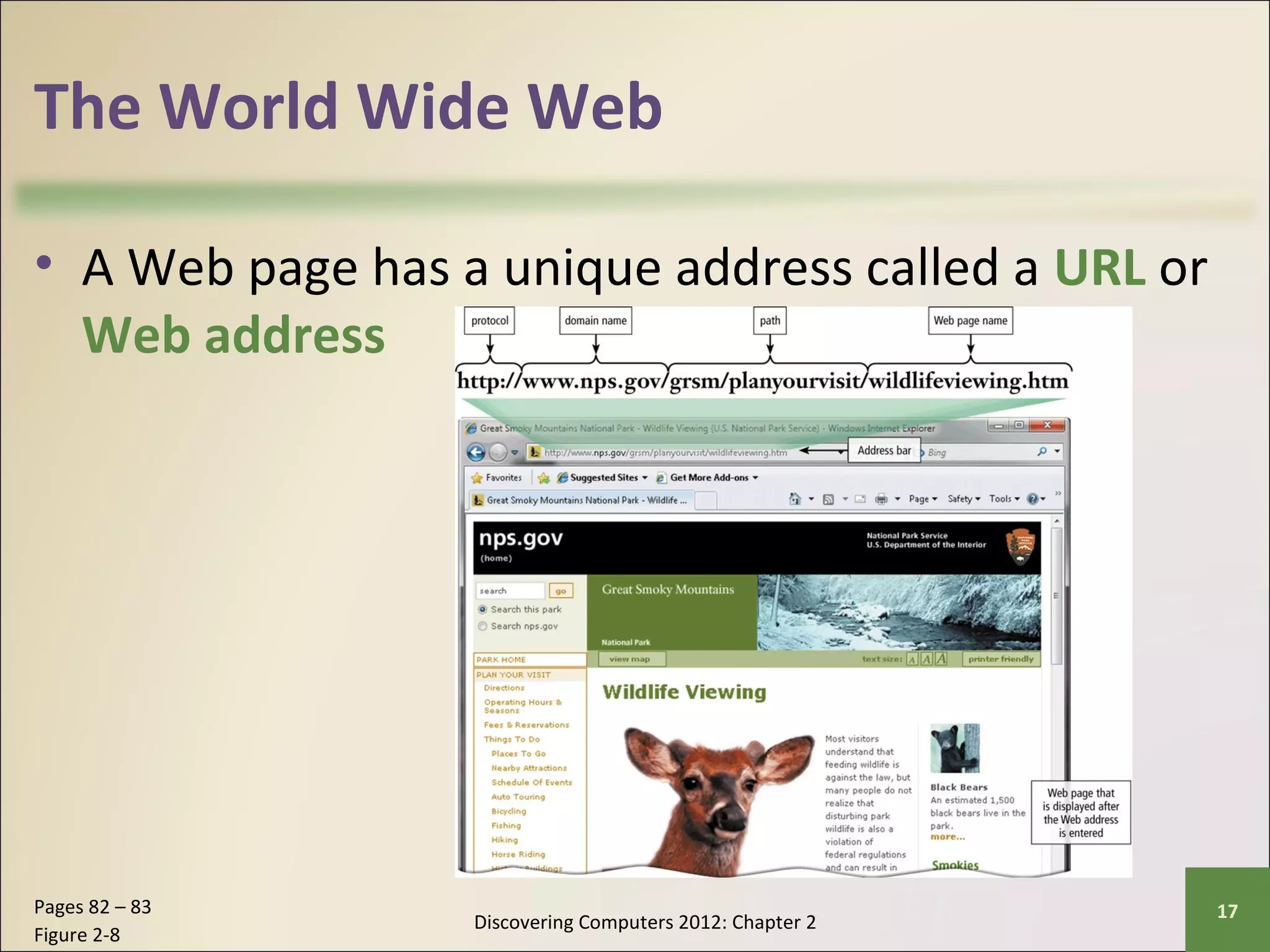
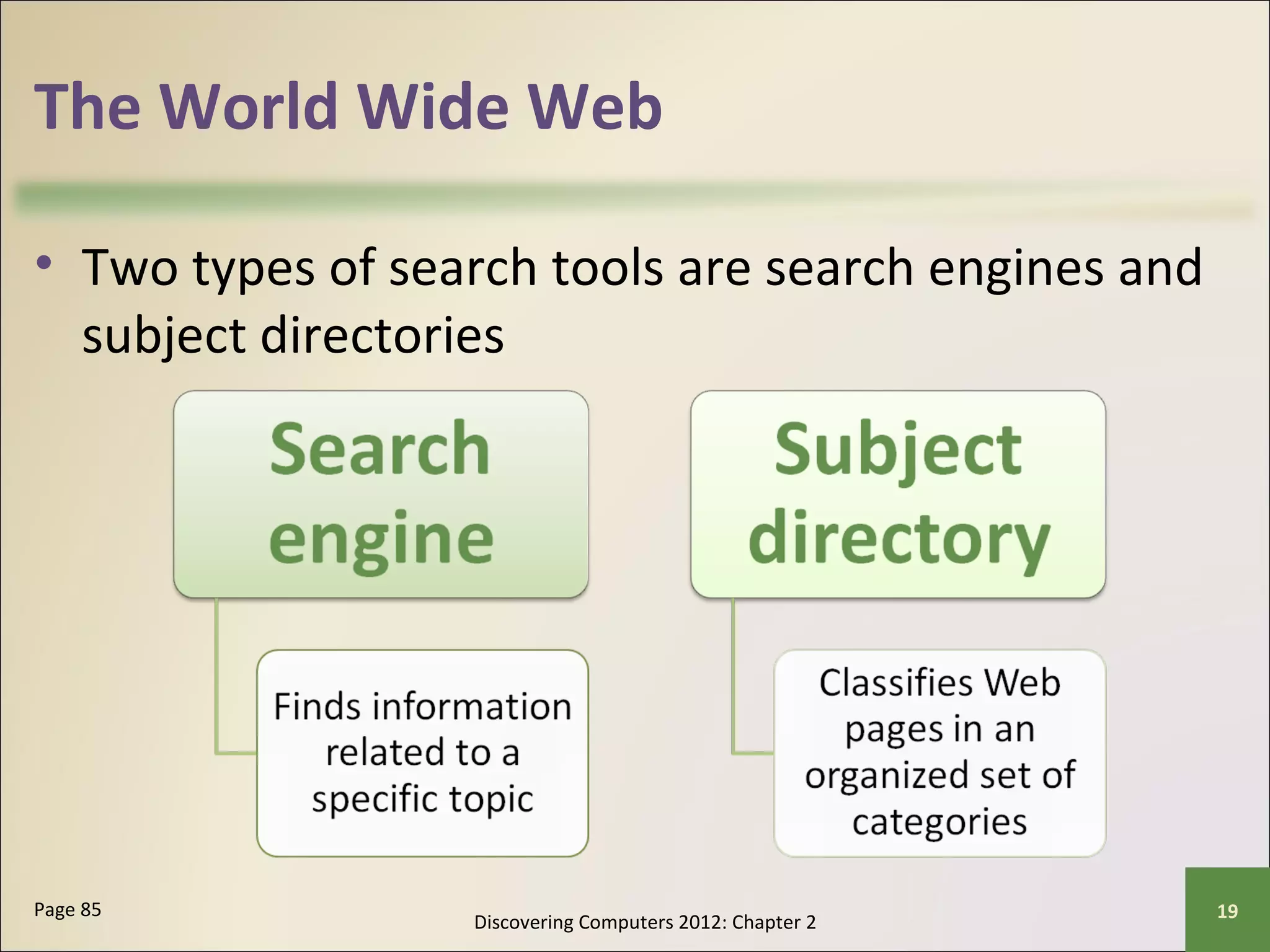
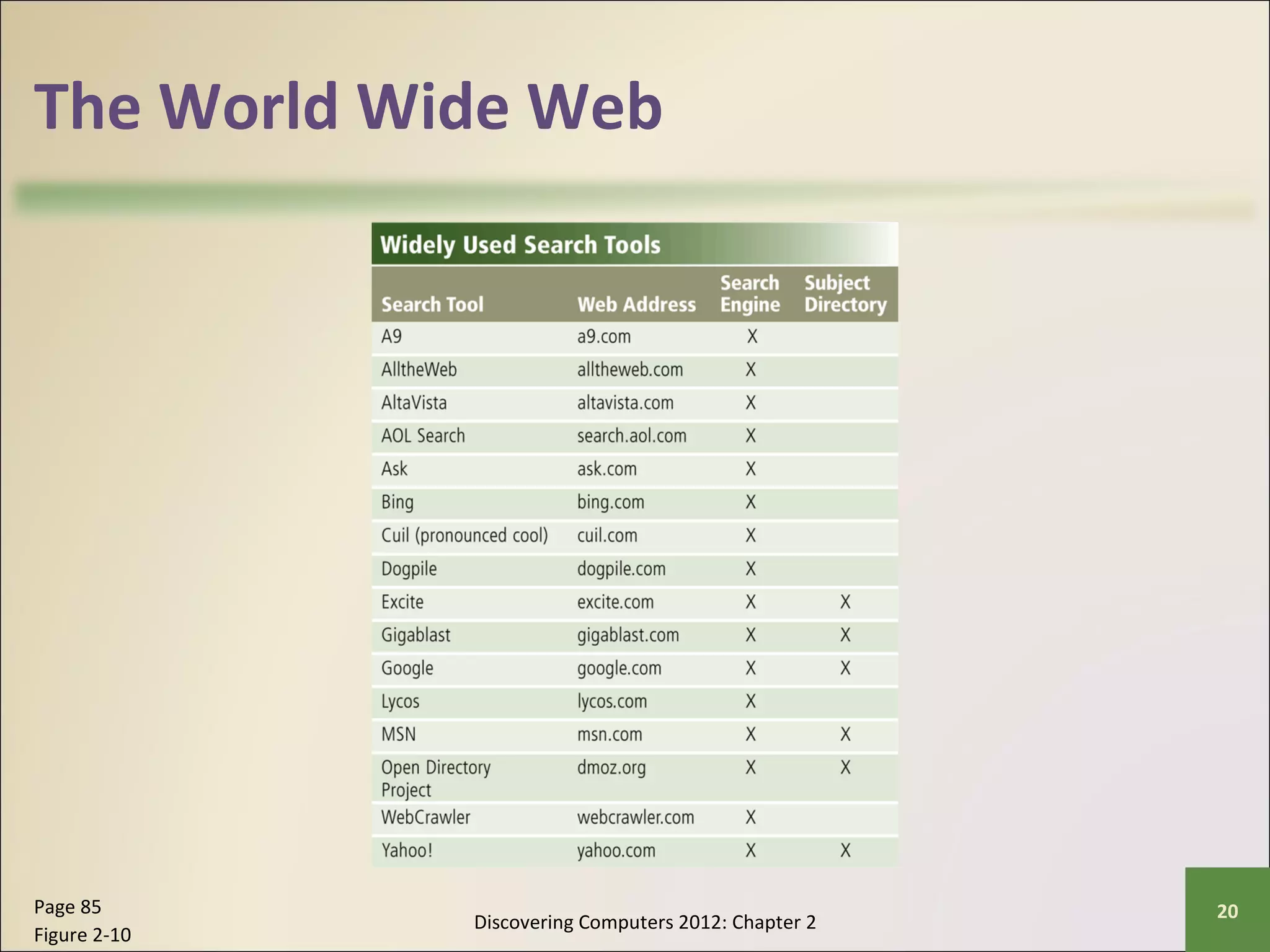
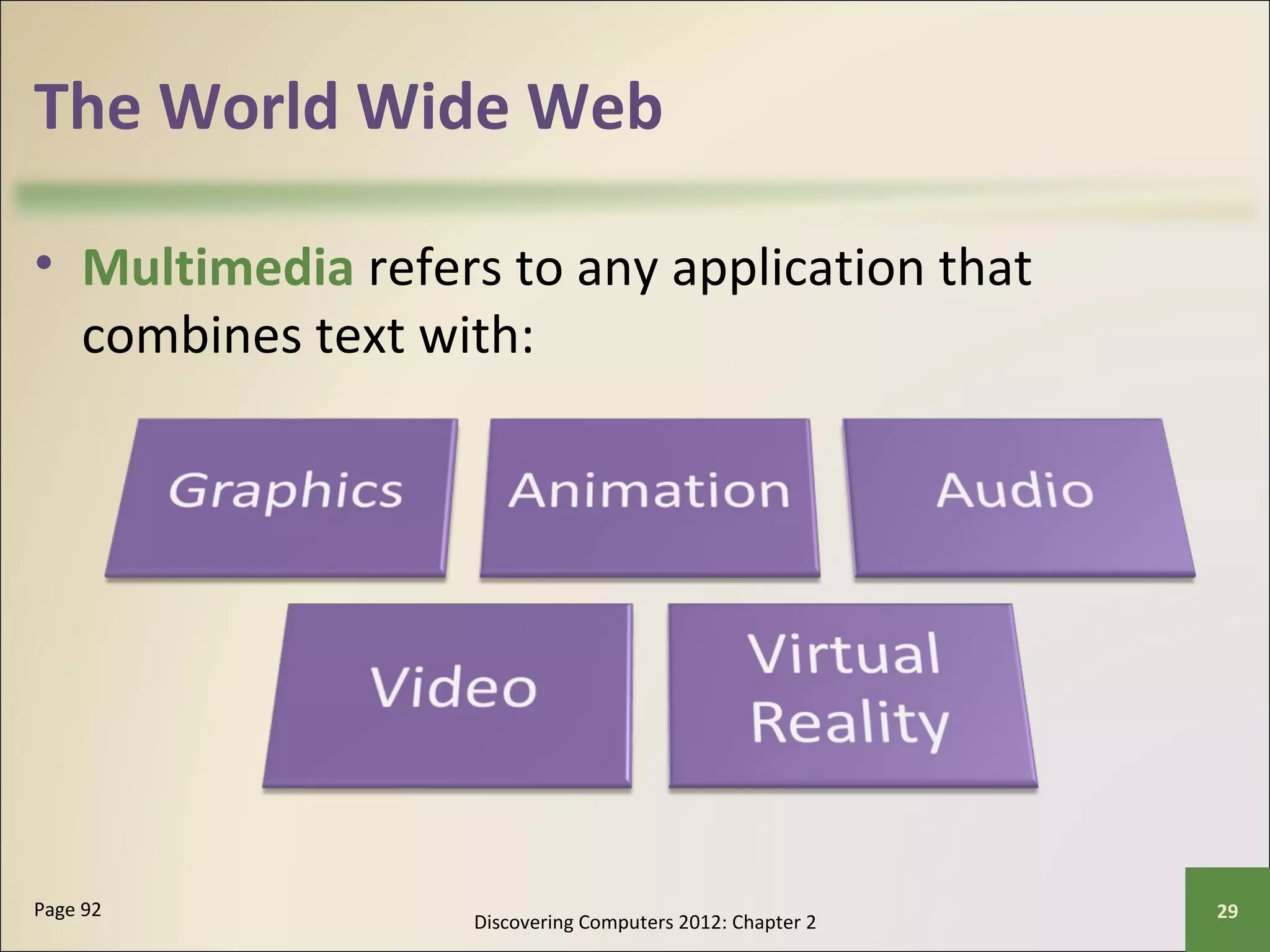
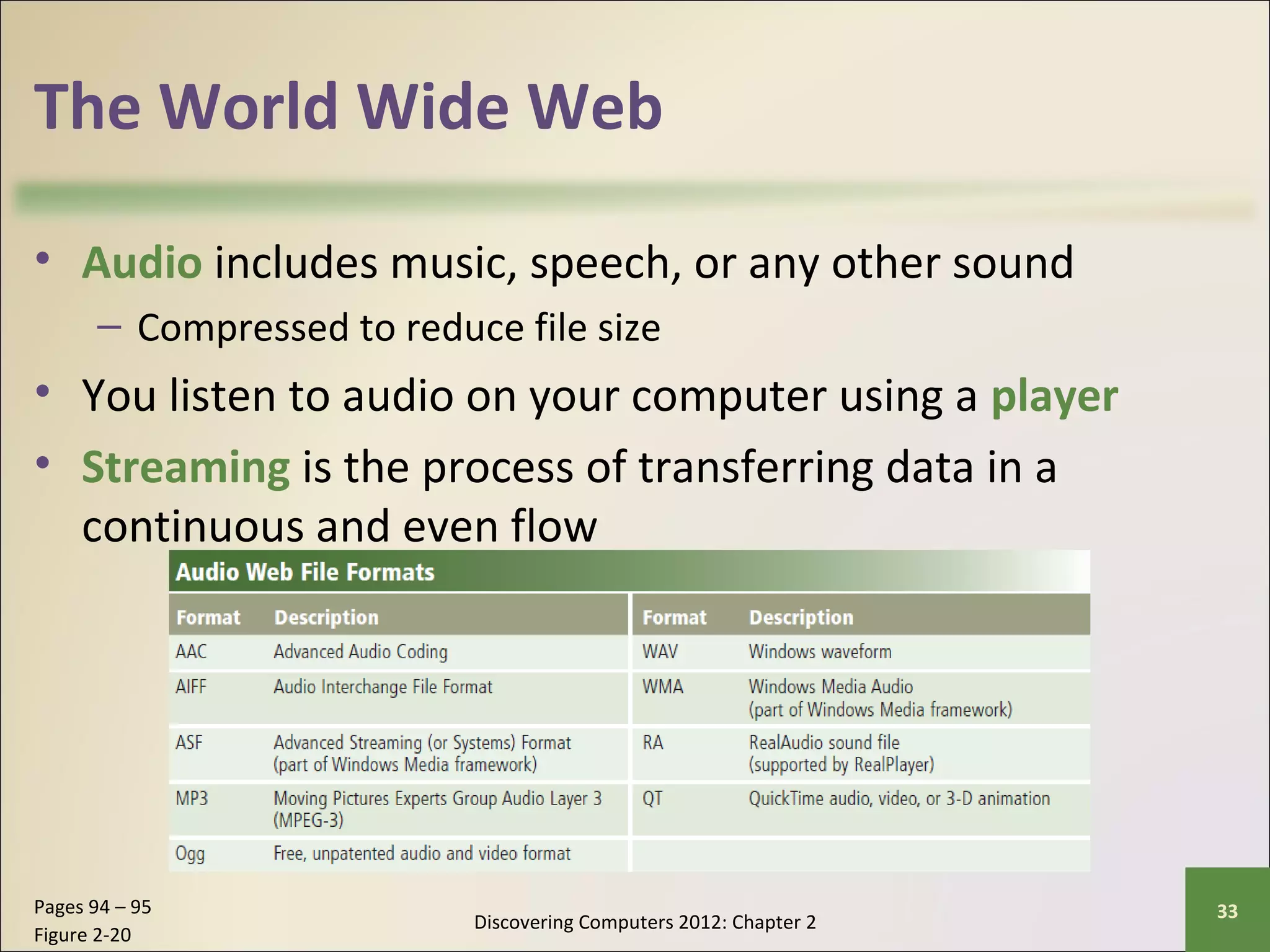
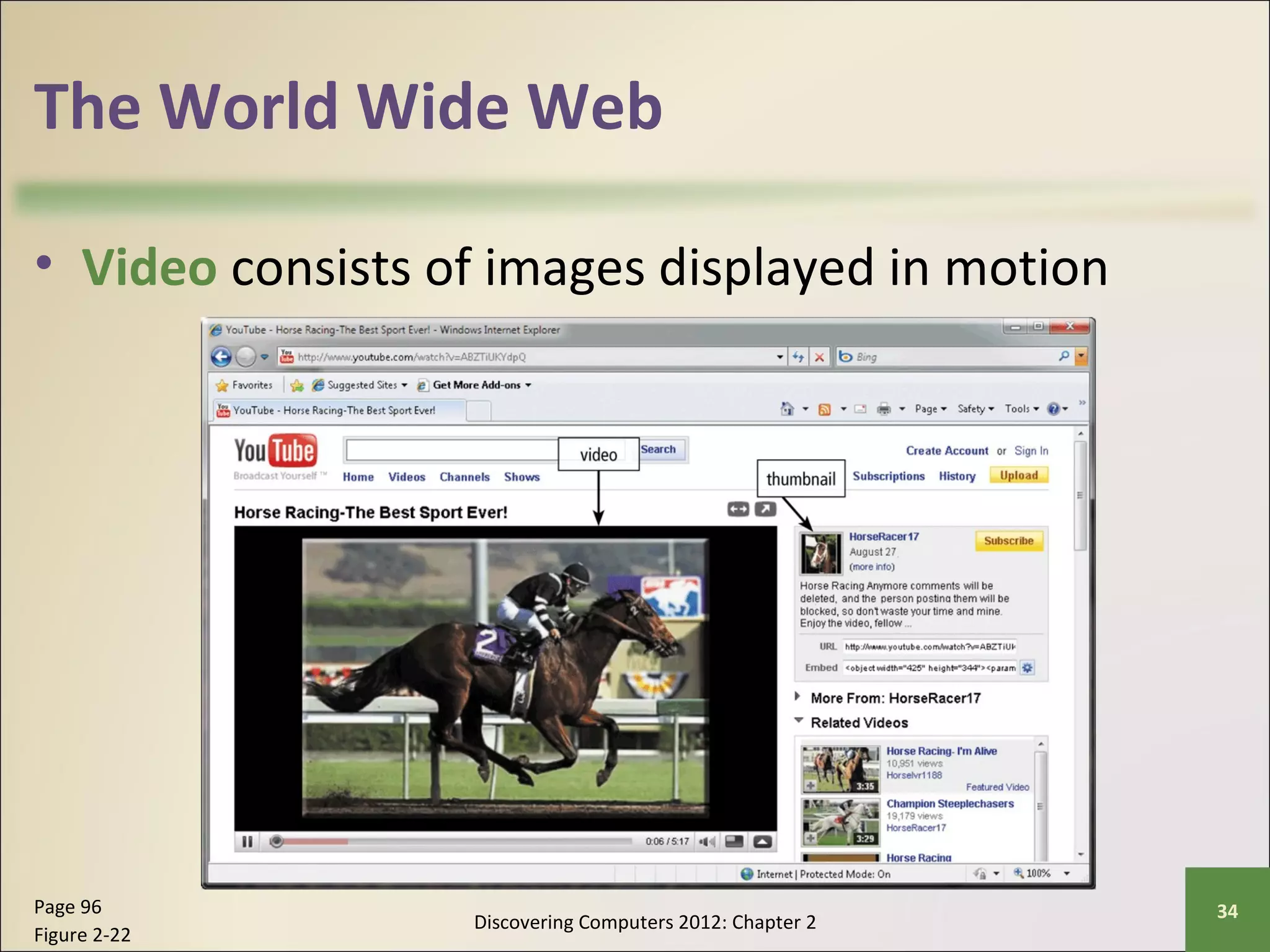
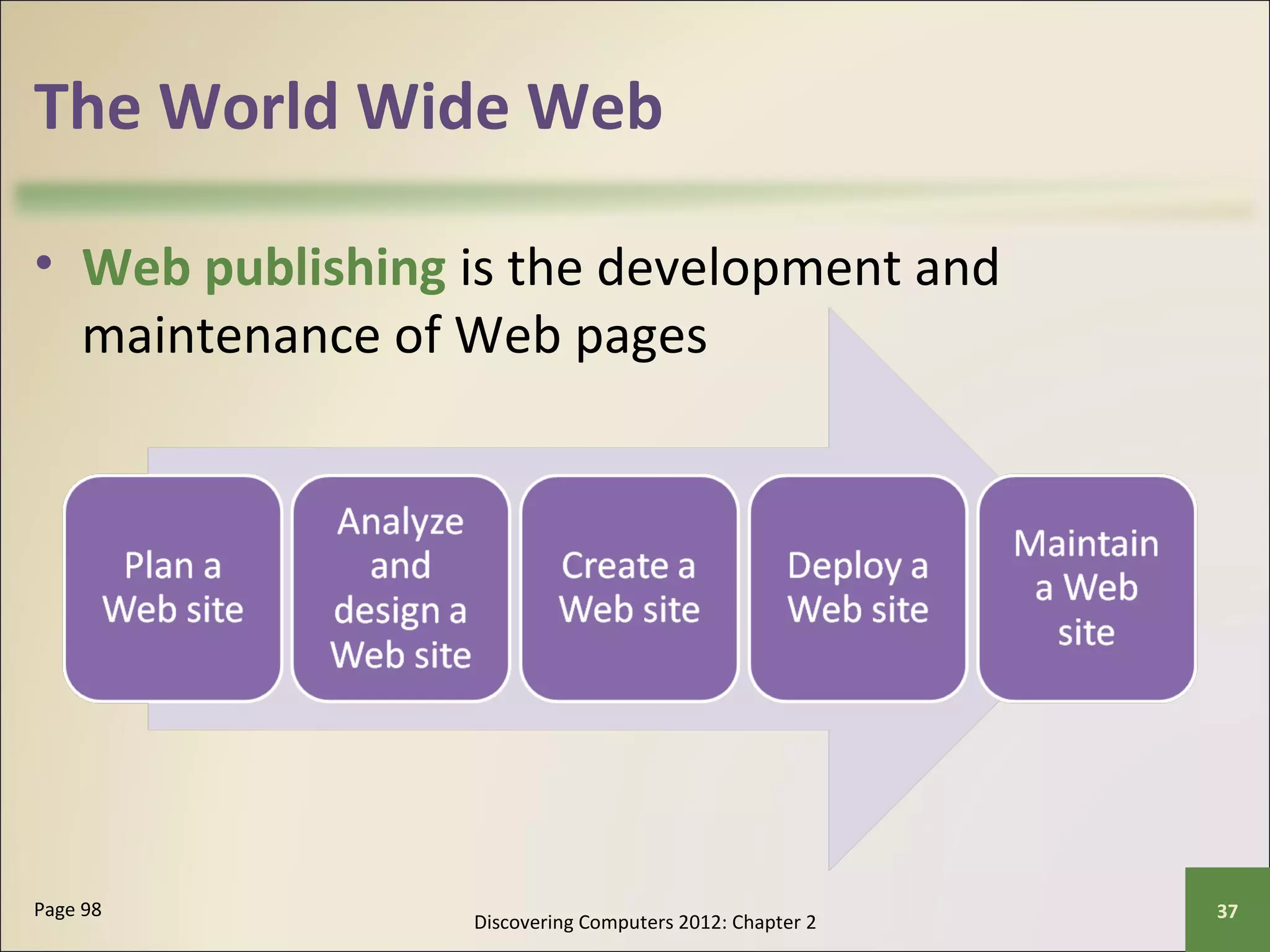
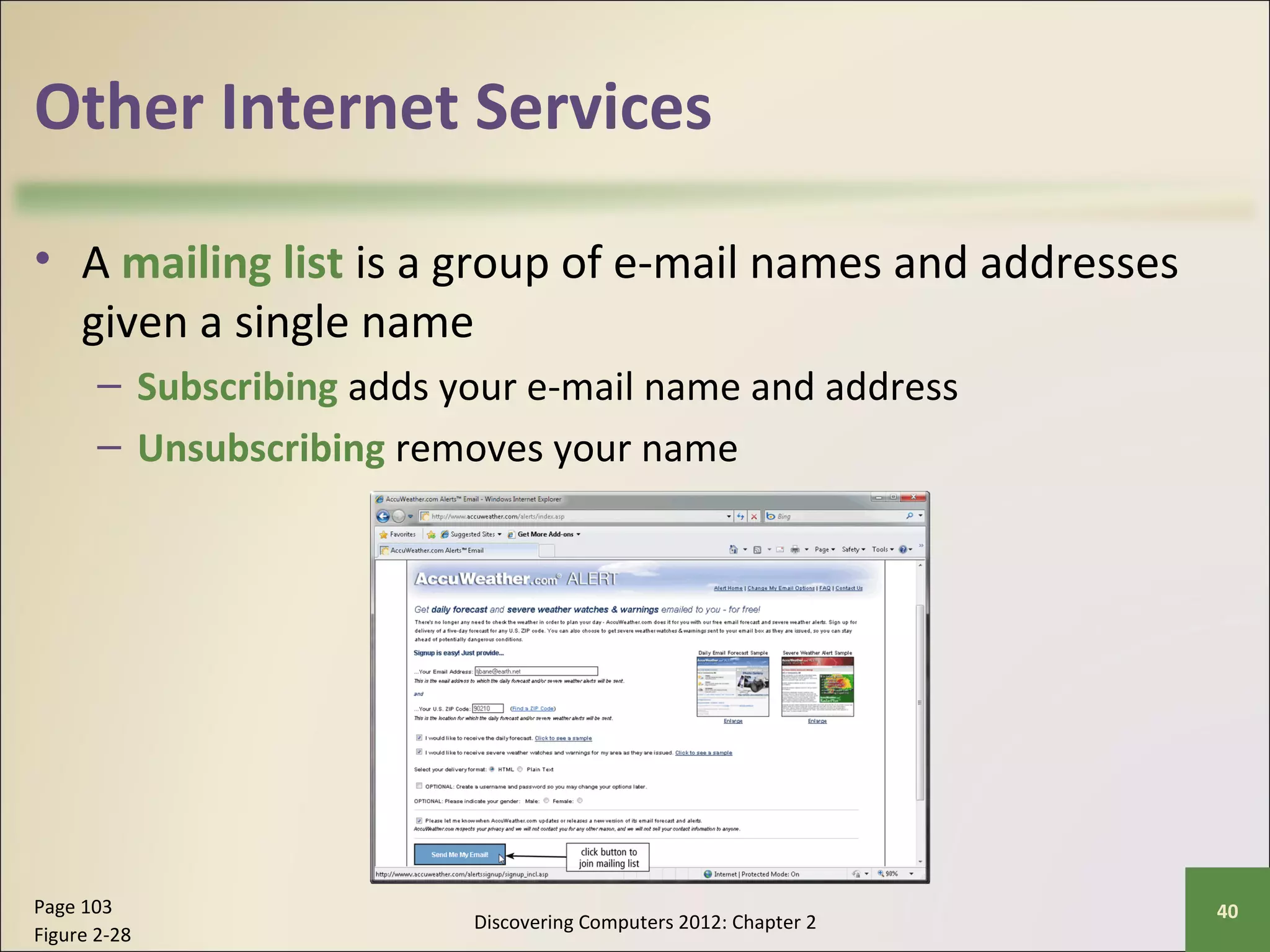
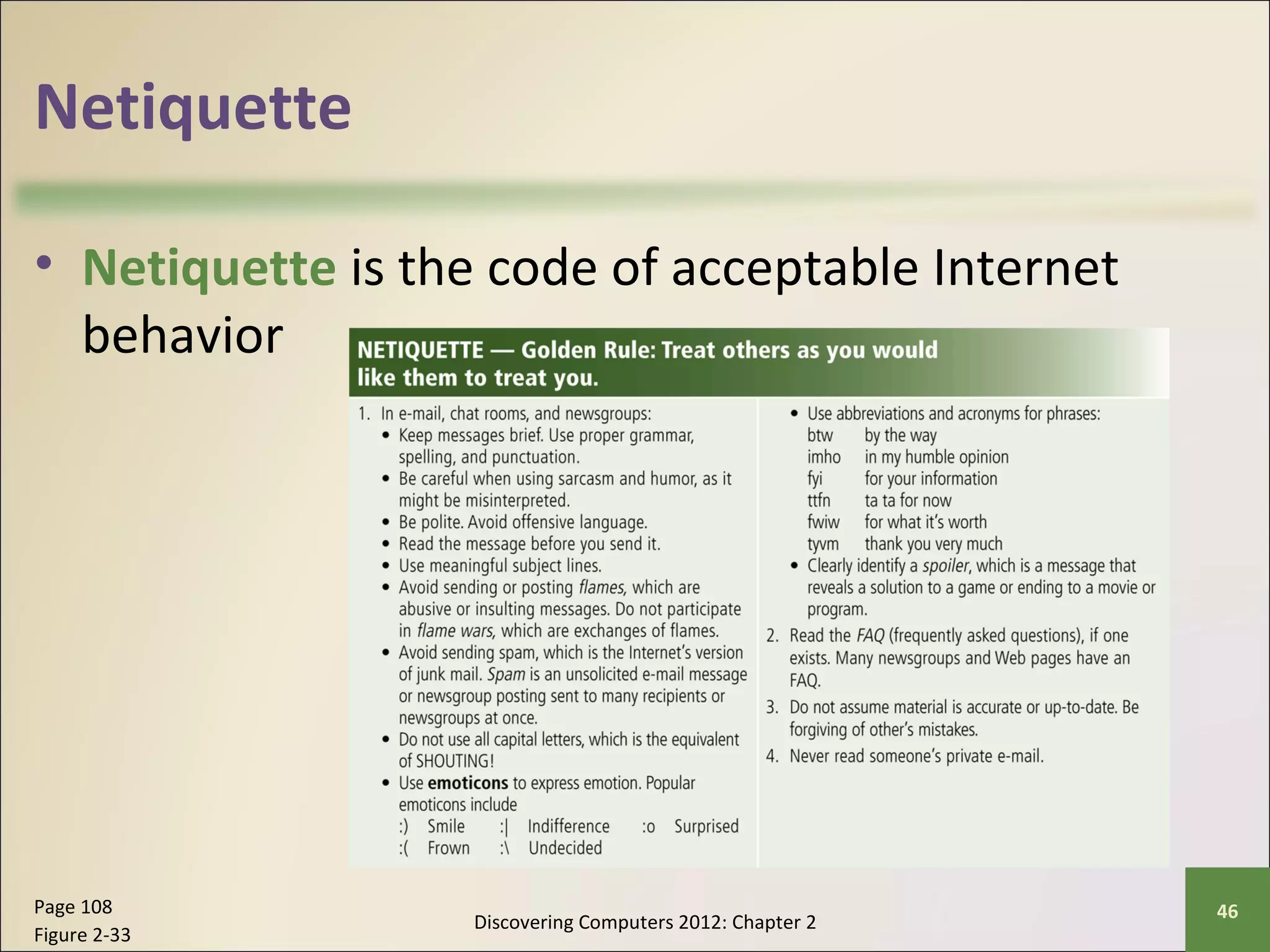
This chapter discusses the fundamentals of the Internet and World Wide Web. It describes how the Internet originated as ARPANET in 1969 and has evolved into a worldwide collection of interconnected networks. The World Wide Web is a collection of electronic documents that can be accessed via the Internet using browsers. The chapter also covers other Internet technologies and services such as email, instant messaging, file transfer, and netiquette.