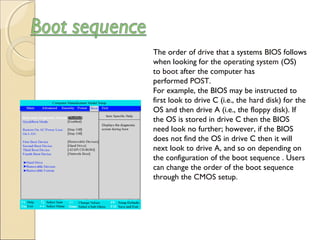
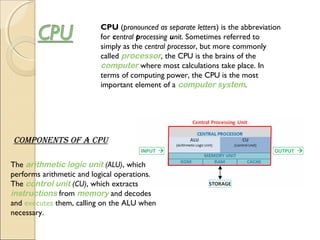
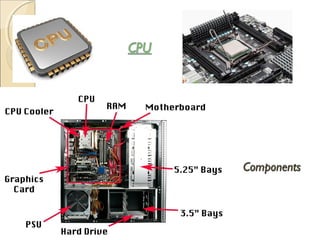
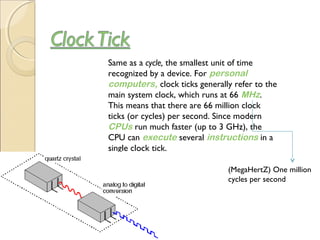
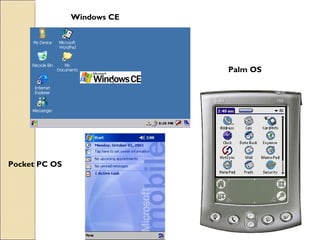
The document describes different types of software, including operating systems and utility programs. It discusses the startup process for personal computers and defines key terms like user interface. Common features of most operating systems are explained, such as supporting single or multiple users and tasks. The differences between stand-alone and network operating systems are outlined. Examples of specific operating systems are provided.