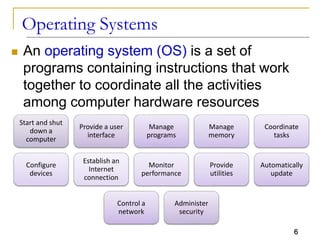
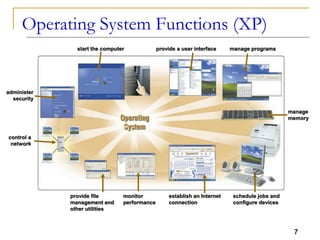
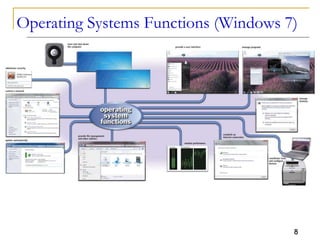
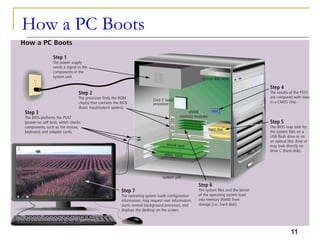
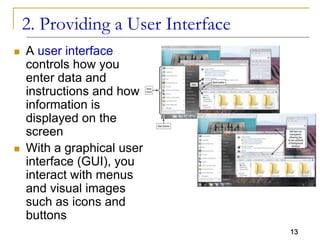
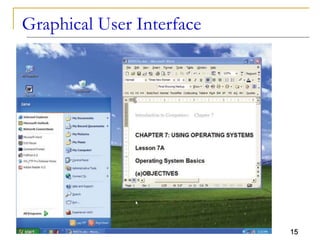
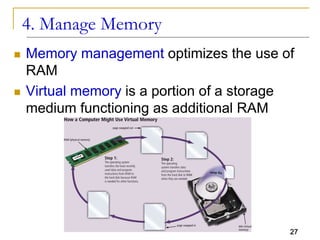
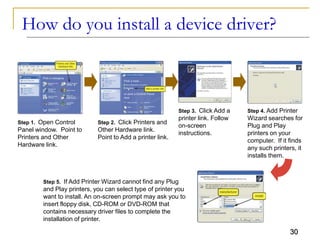
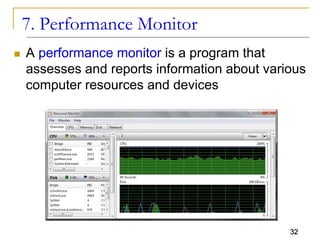
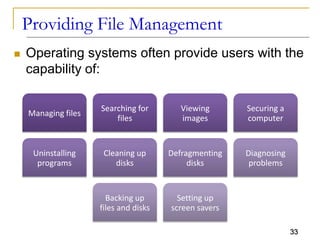
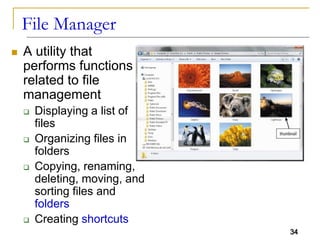
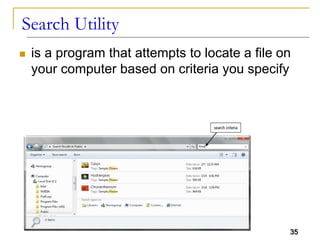
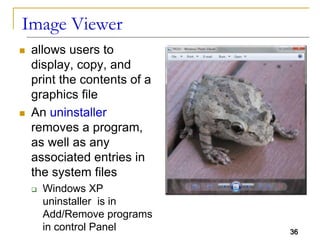
The document provides an overview of system software, focusing on operating systems and their essential functions, such as managing hardware, providing user interfaces, and controlling tasks. It describes the startup process, various types of operating systems, and features like memory management, task coordination, and file management utilities. Additionally, it explains how operating systems enable connectivity and maintain system performance.