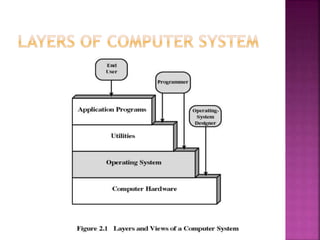
The operating system is essential software that enables computer hardware and programs to work together. It performs basic tasks like managing memory, prioritizing tasks, controlling input/output devices, and facilitating networking. The OS acts as an interface between application programs and hardware. It has four main layers: hardware, the OS software, system programs, and application programs. Operating systems provide interfaces, run programs, manage devices, organize storage, and support many applications and system functions through system calls.