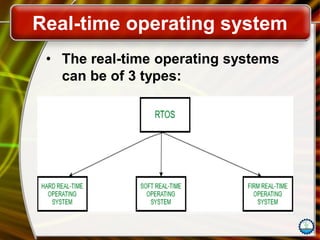
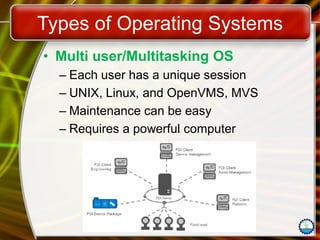
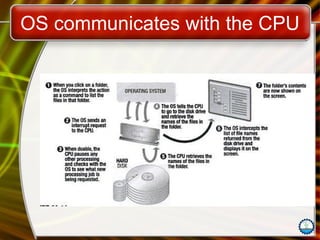
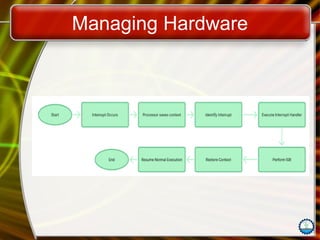
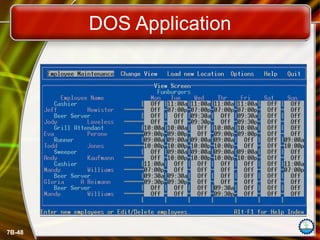
The document discusses the fundamentals of operating systems (OS), including their functions, types, and user interfaces. It categorizes OS into real-time, single user/single tasking, single user/multitasking, and multi-user/multitasking. Additionally, it covers various PC and network operating systems, focusing on their features, stability, and user accessibility.