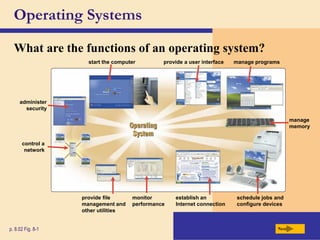
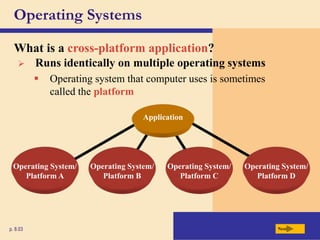
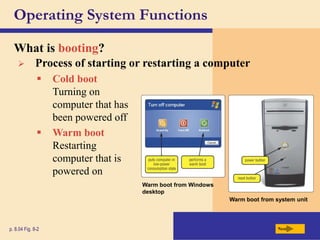
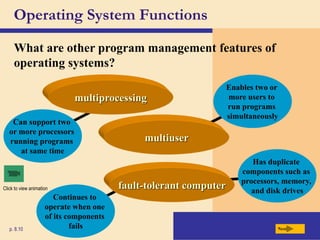
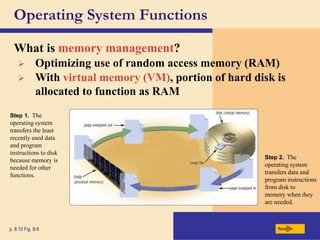
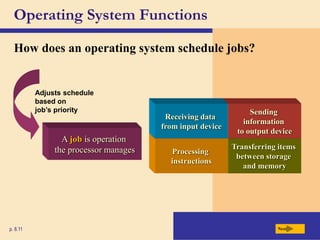
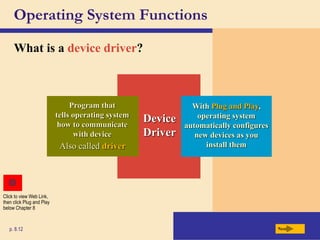
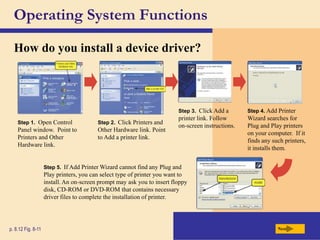
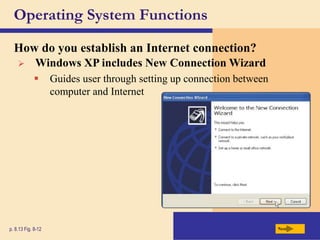
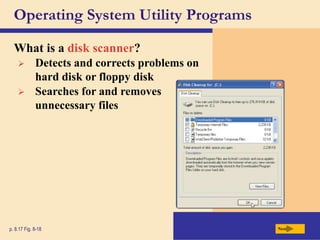
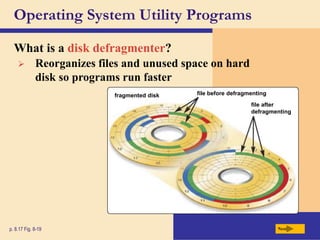
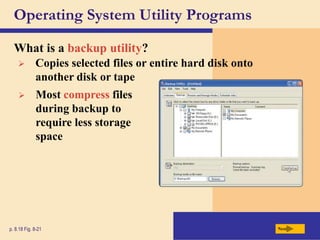
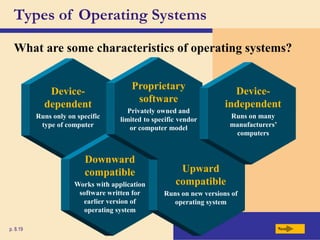
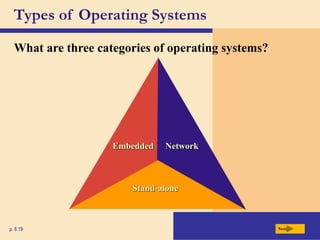
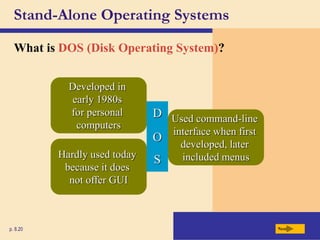
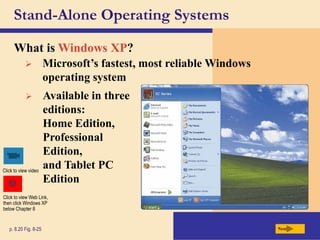
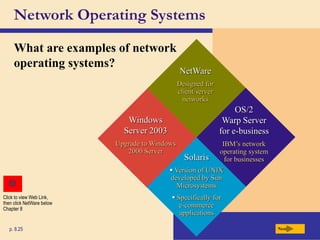
The chapter discusses system software, operating systems, and utility programs. An operating system coordinates computer hardware and software resources, provides a user interface and file management, establishes internet connections, and more. Common operating systems include Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. Utility programs perform maintenance tasks like file management, uninstalling programs, scanning disks for errors, and backing up files. The chapter also covers embedded, stand-alone, and network operating systems.