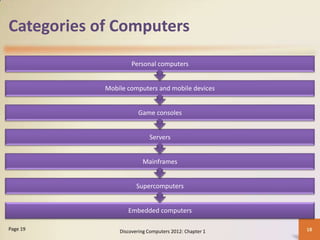
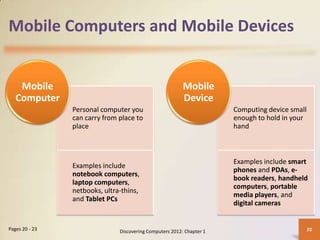
The document provides an overview of computers, their components, and their applications in various fields such as education, finance, and healthcare. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of using computers, along with the roles of different users and types of software. Additionally, it covers networks and the internet and how they connect a vast range of users and devices.