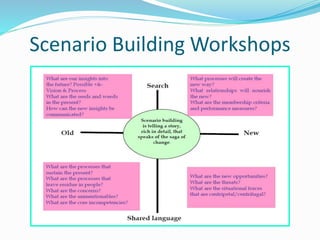
Organizational Development (OD) is a planned, organization-wide effort aimed at increasing effectiveness and health through behavioral science interventions. Key techniques include survey feedback, team building, sensitivity training, and management by objectives, among others, which aim to enhance problem-solving and adapt to changes. A case study on Tata Consultancy Services illustrates OD’s implementation, showcasing a shift from individual effort to teamwork, fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.