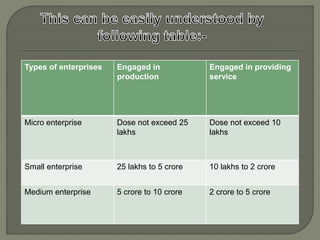
Small scale industries play a key role in India's economic development and industrialization due to their ability to generate large scale employment, require lower investment, and have shorter gestation periods. They account for 54% of India's exports and are important for utilizing India's abundant labor supply. However, they face challenges from globalization and trade agreements that liberalize markets. The document goes on to define micro, small, and medium enterprises based on investment levels and classify them as either manufacturing or service. It discusses the advantages small businesses provide like decentralized development and flexibility, as well as some disadvantages like financial and branding challenges.