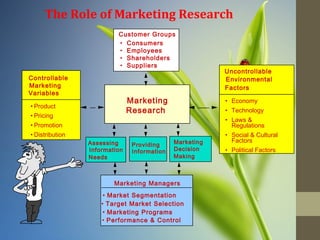
Marketing research involves the systematic collection, analysis, and reporting of data to help companies solve marketing problems and make better business decisions. It is a multi-step process that includes establishing research objectives, designing the research, collecting and analyzing data, and reporting findings. The goal is to gather accurate and up-to-date information to help with marketing effectively in areas like product development, pricing, advertising, and distribution in response to changes in customer needs and the business environment.