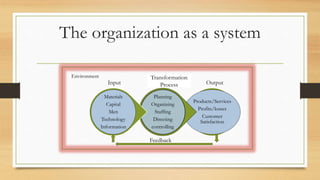
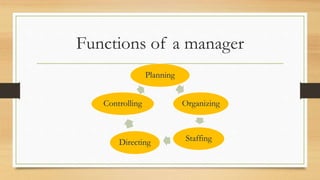
Organizational behavior (OB) focuses on understanding, predicting, and managing human behavior within organizations, contributing to better relationships and improved efficiency. It draws from various disciplines such as psychology, sociology, social psychology, anthropology, and political science to enhance insights into group dynamics and organizational culture. While OB presents opportunities for improving skills and productivity, it faces challenges, including ethical concerns and the potential for manipulation of individuals.