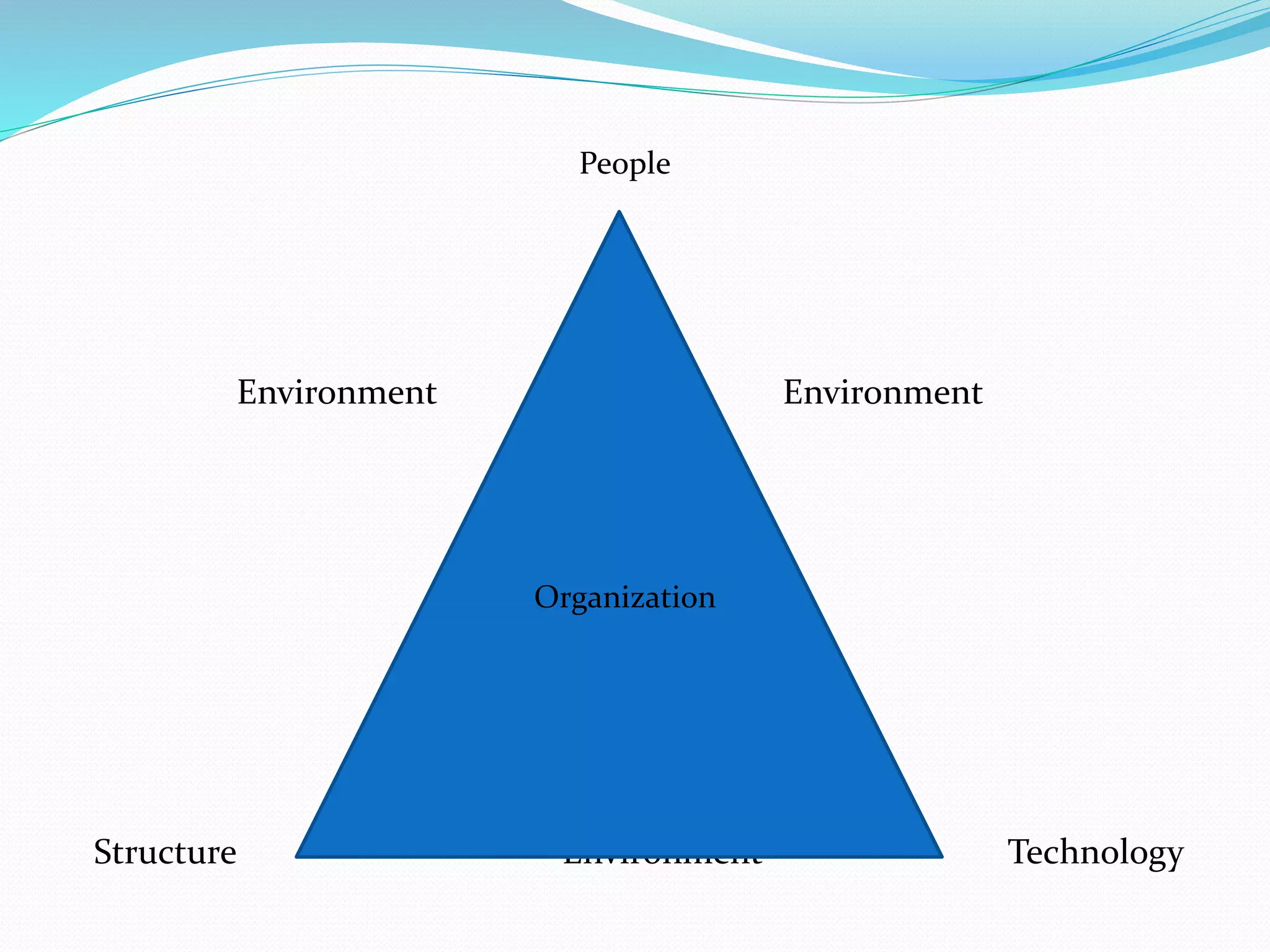
Organizational Behavior (OB) studies human behavior within organizations, focusing on individuals, groups, and structure to improve organizational performance. It incorporates insights from psychology, sociology, and other disciplines to understand and predict behavior, ultimately aiding management in motivating employees towards organizational goals. Key components of OB include environment, structure, technology, and the dynamic interactions among people.