This document discusses key concepts in interpersonal behavior and group dynamics. It covers psychological contracts, trust, prosocial behavior, organizational citizenship behavior, cooperation vs competition, and personal orientations. The main points are:
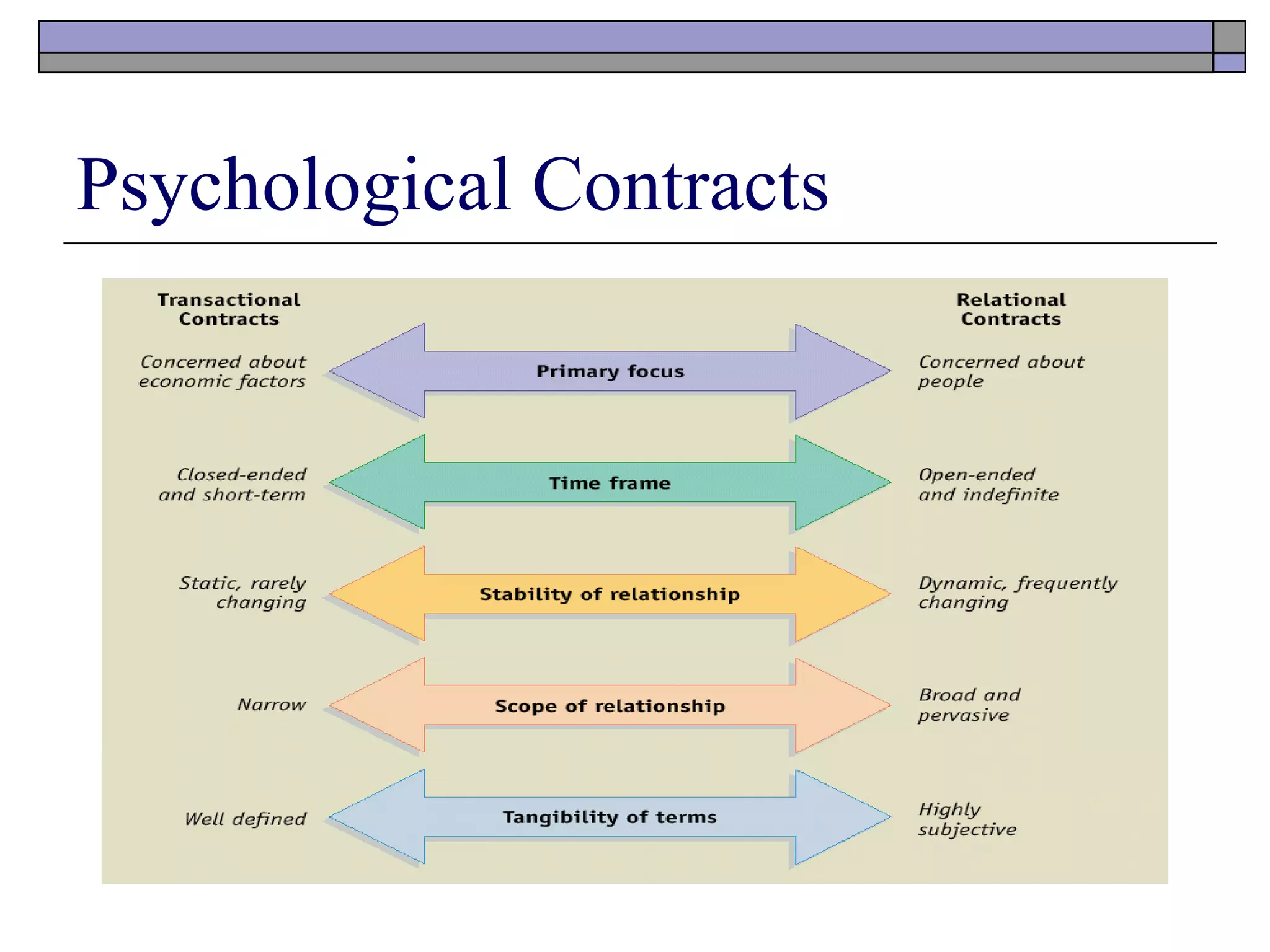
- Psychological contracts can be transactional, focusing on short-term economic exchanges, or relational, involving long-term, widely defined relationships.
- Trust can develop through calculus-based deterrence or identification-based acceptance. Meeting commitments and sharing values/goals promotes trust.
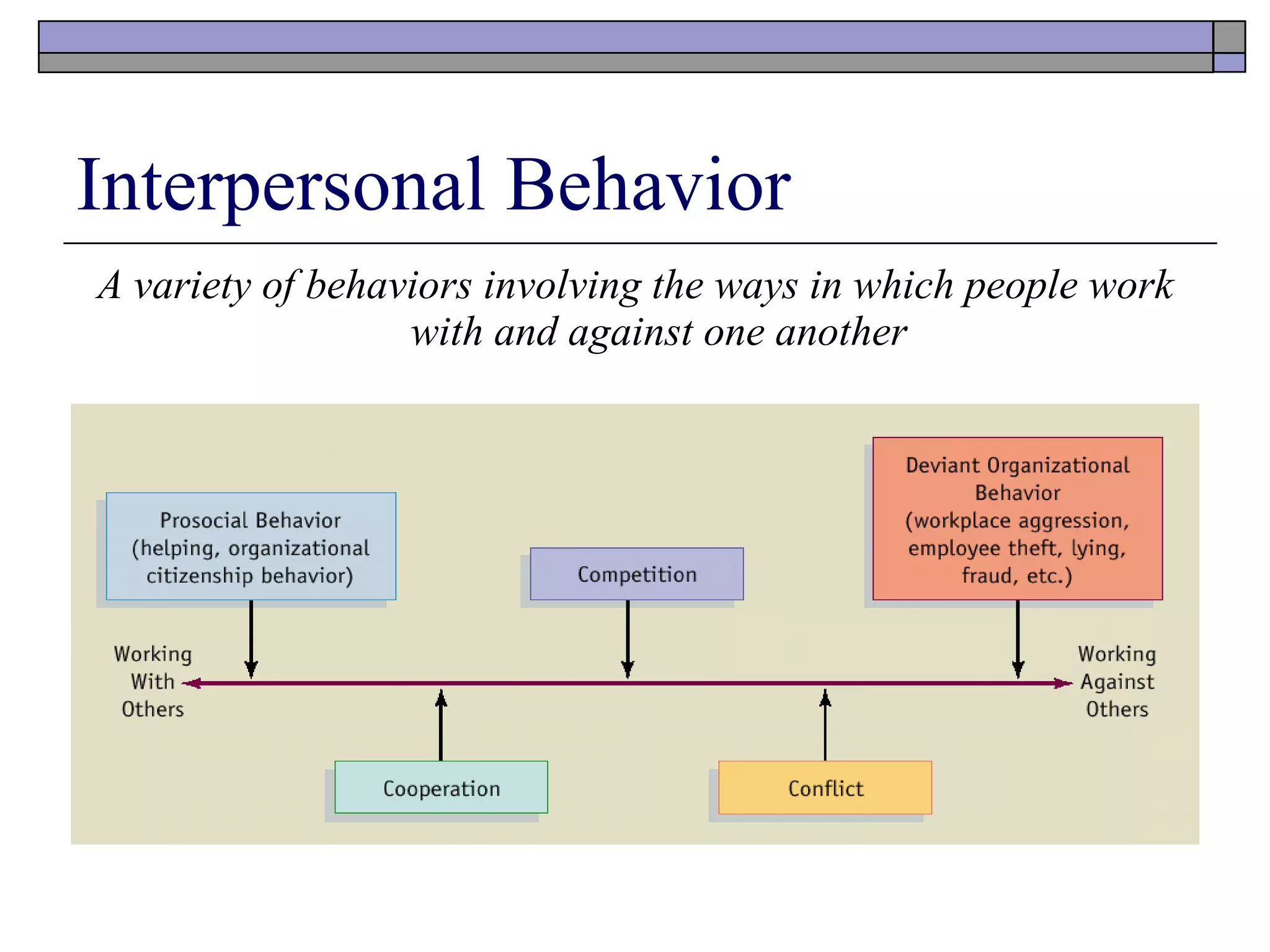
- Prosocial behaviors like organizational citizenship and whistleblowing benefit others in an organization. Fair treatment encourages these behaviors.
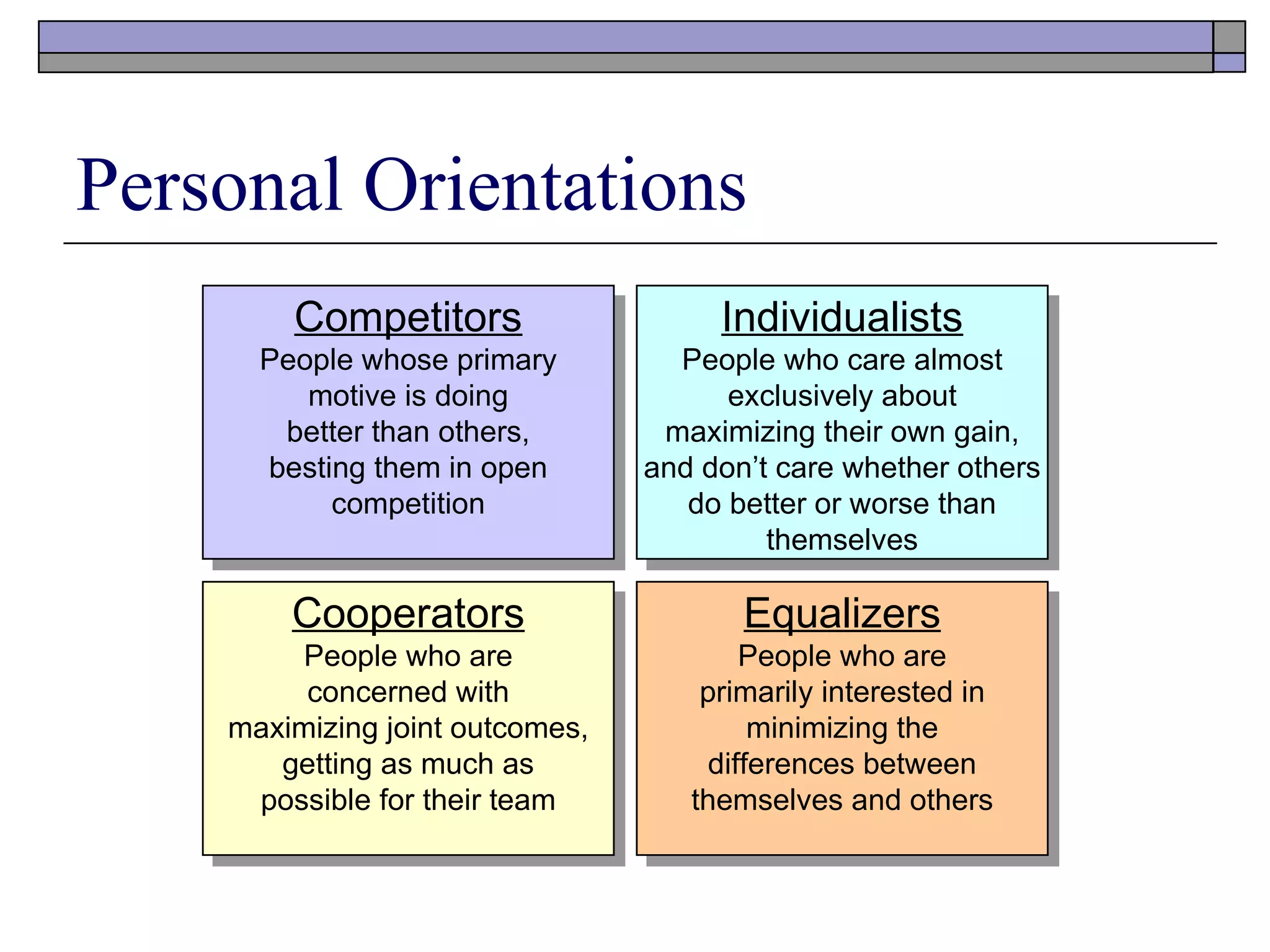
- Cooperation involves working together towards common goals, while competition aims to maximize personal gains at others' expense