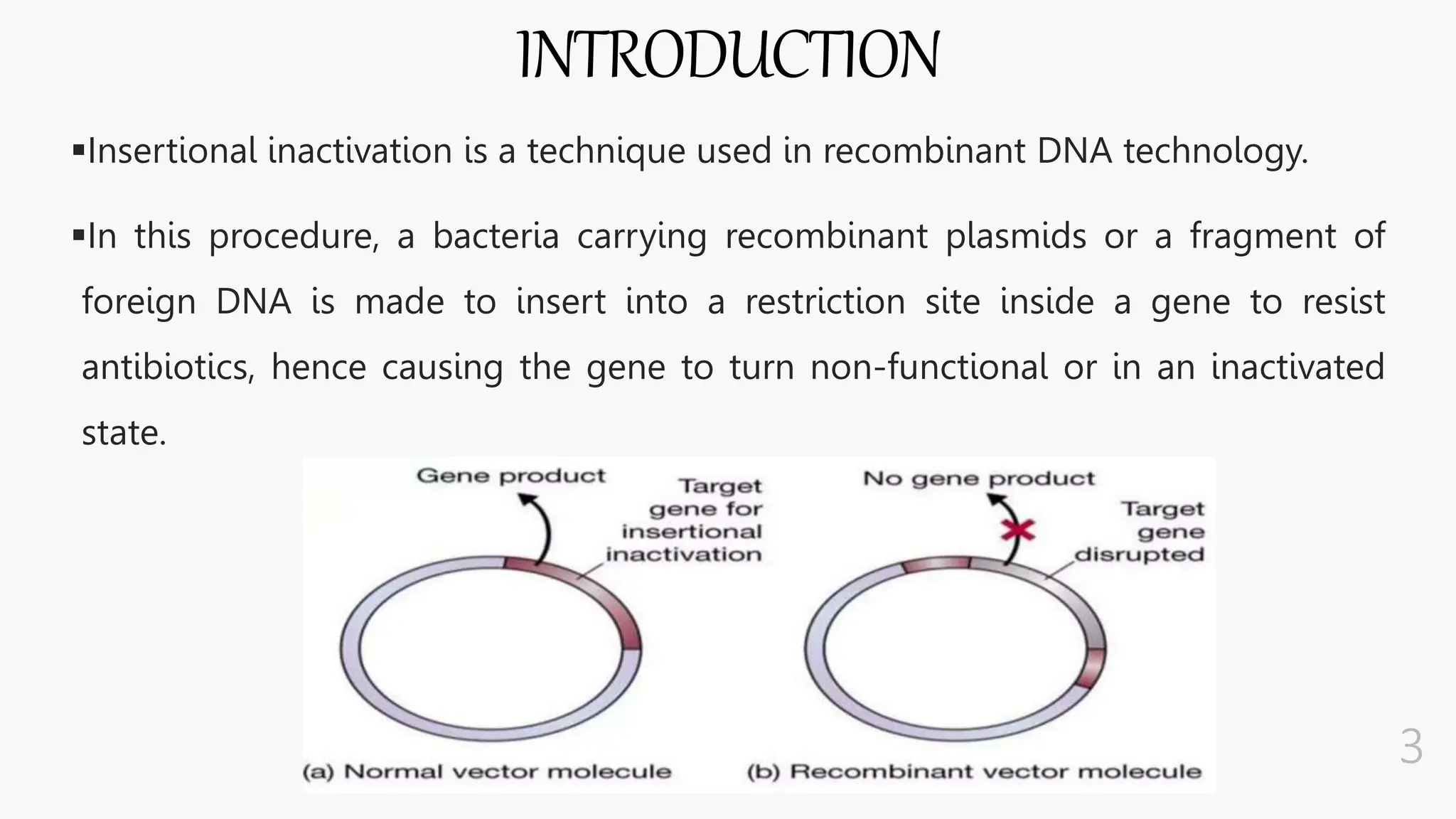
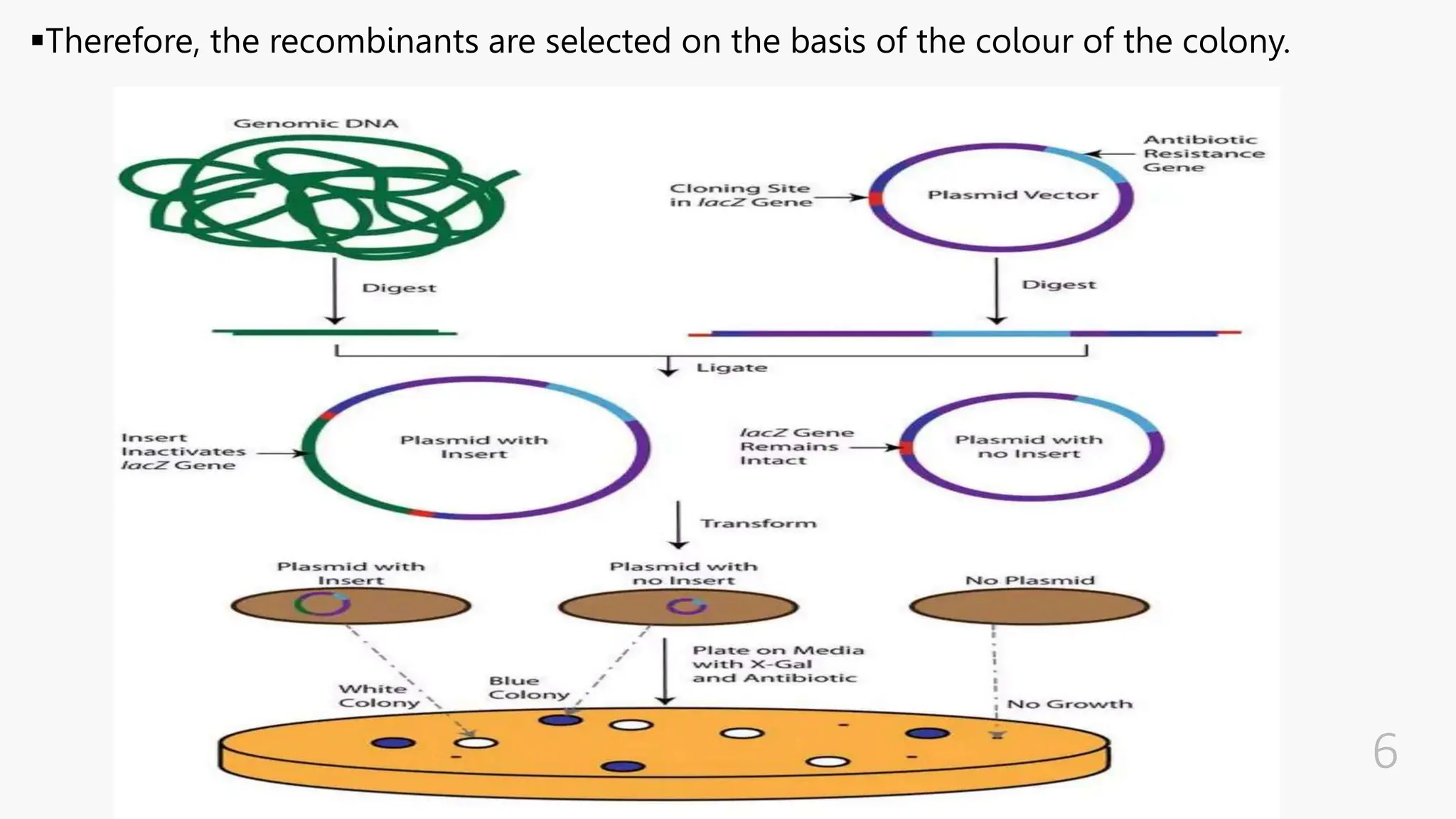
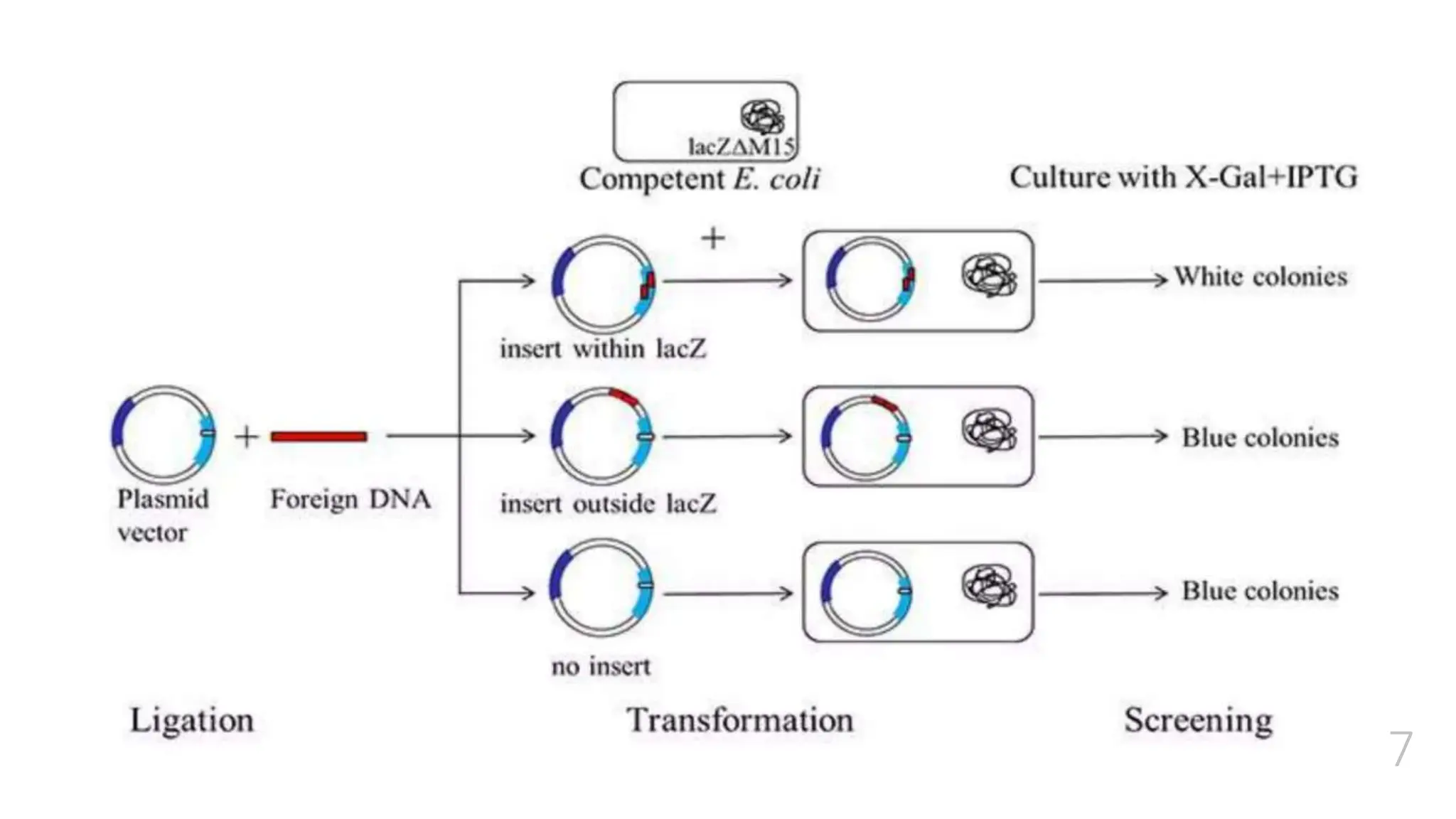
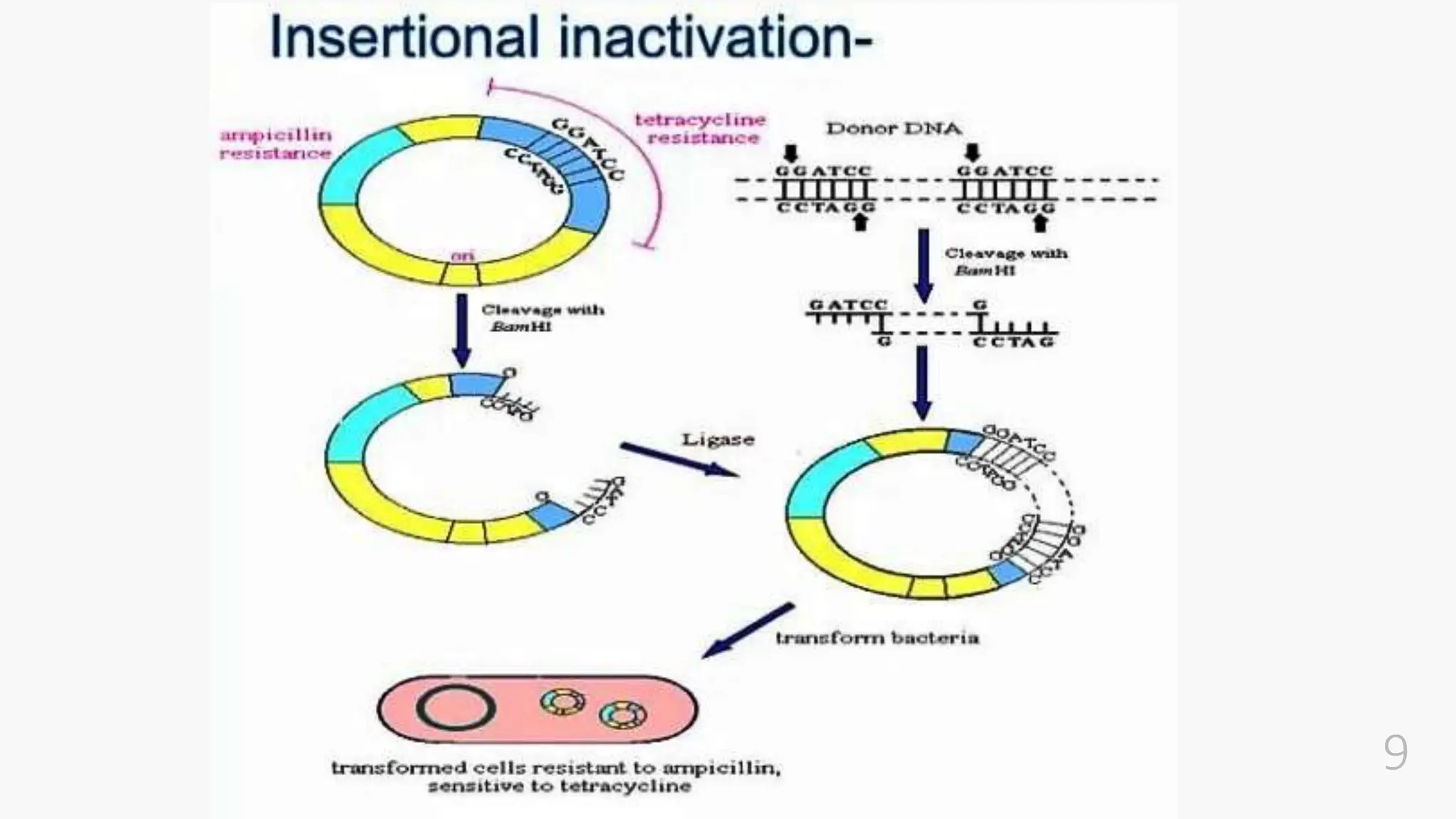
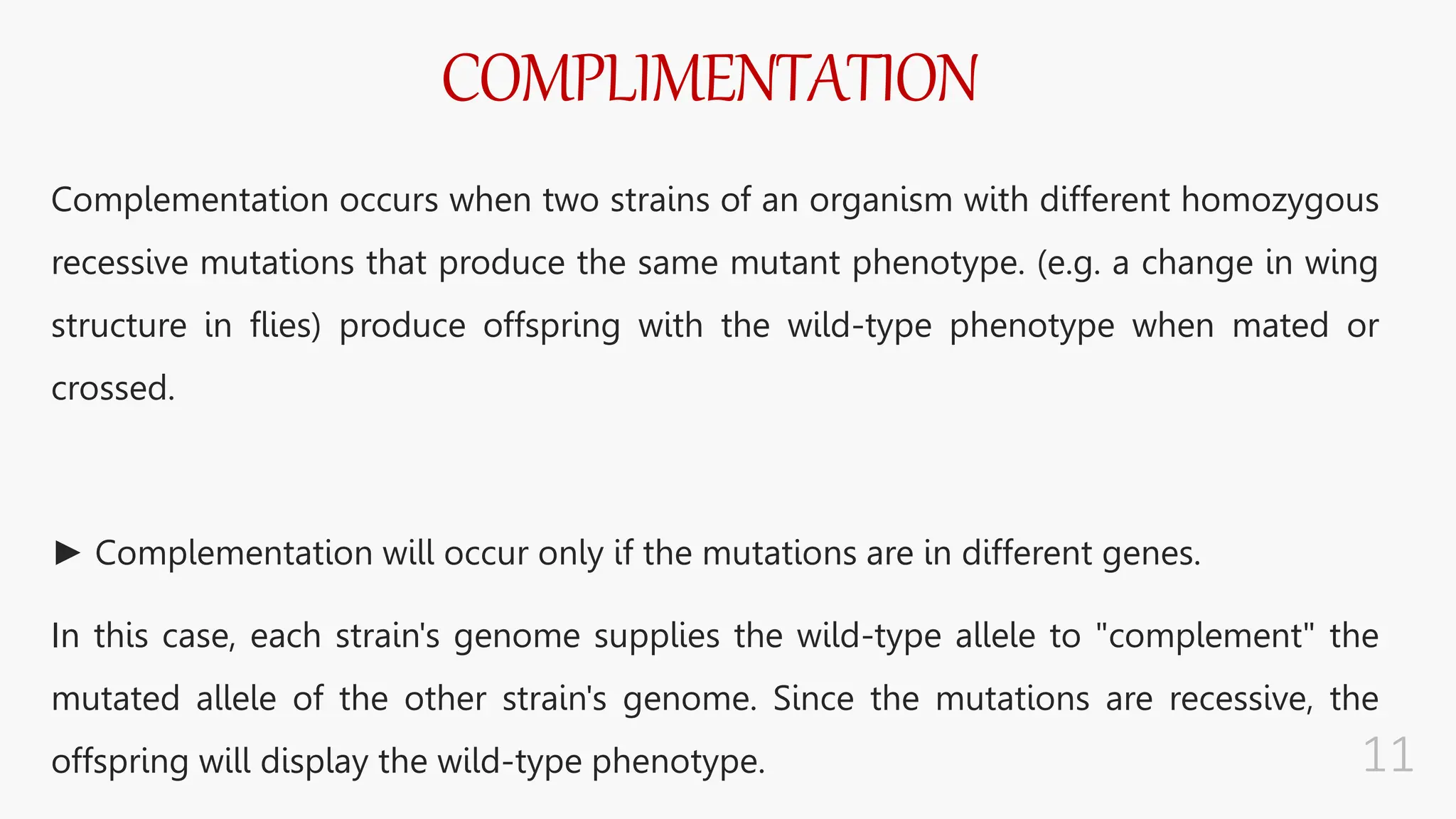
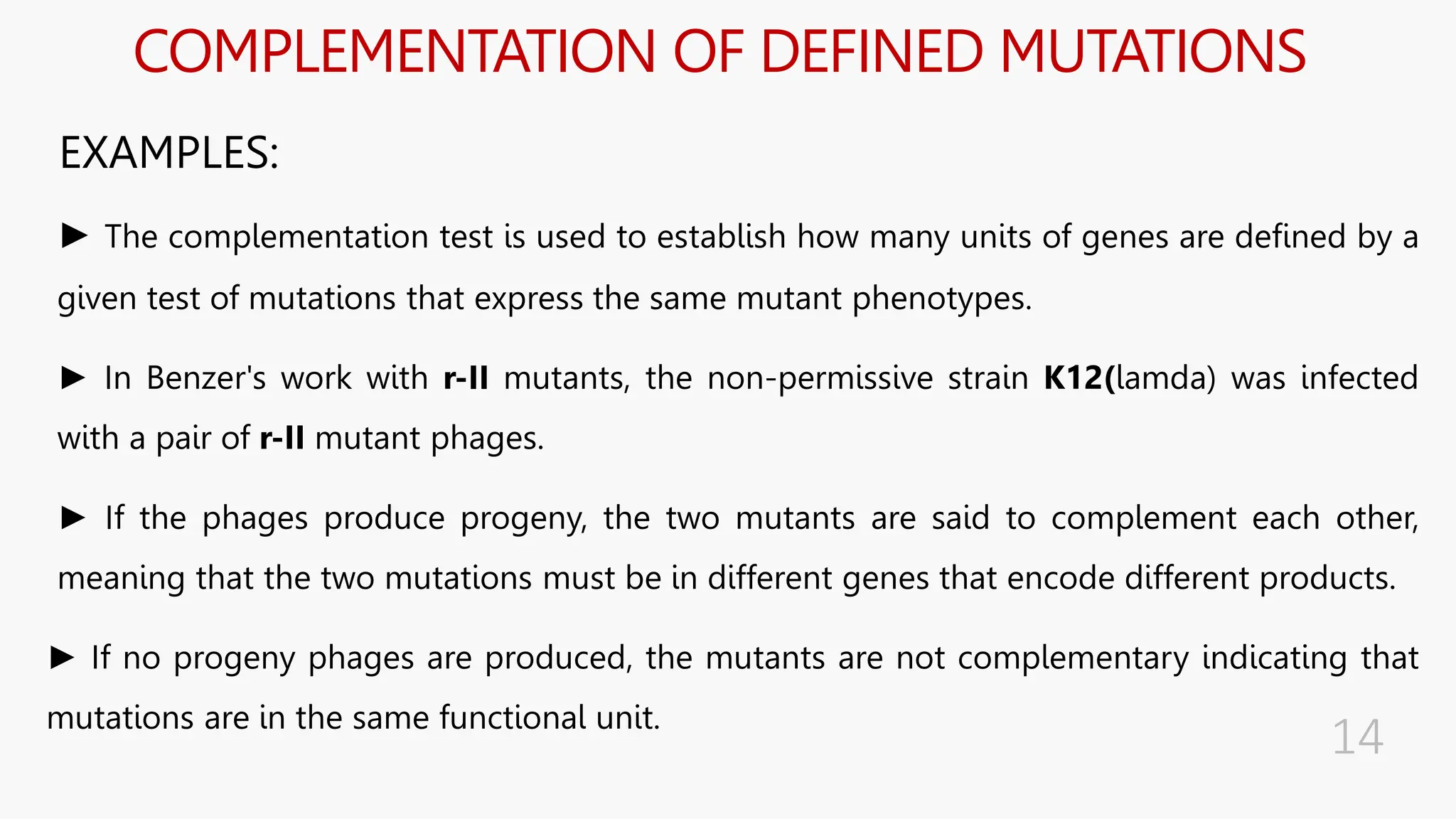
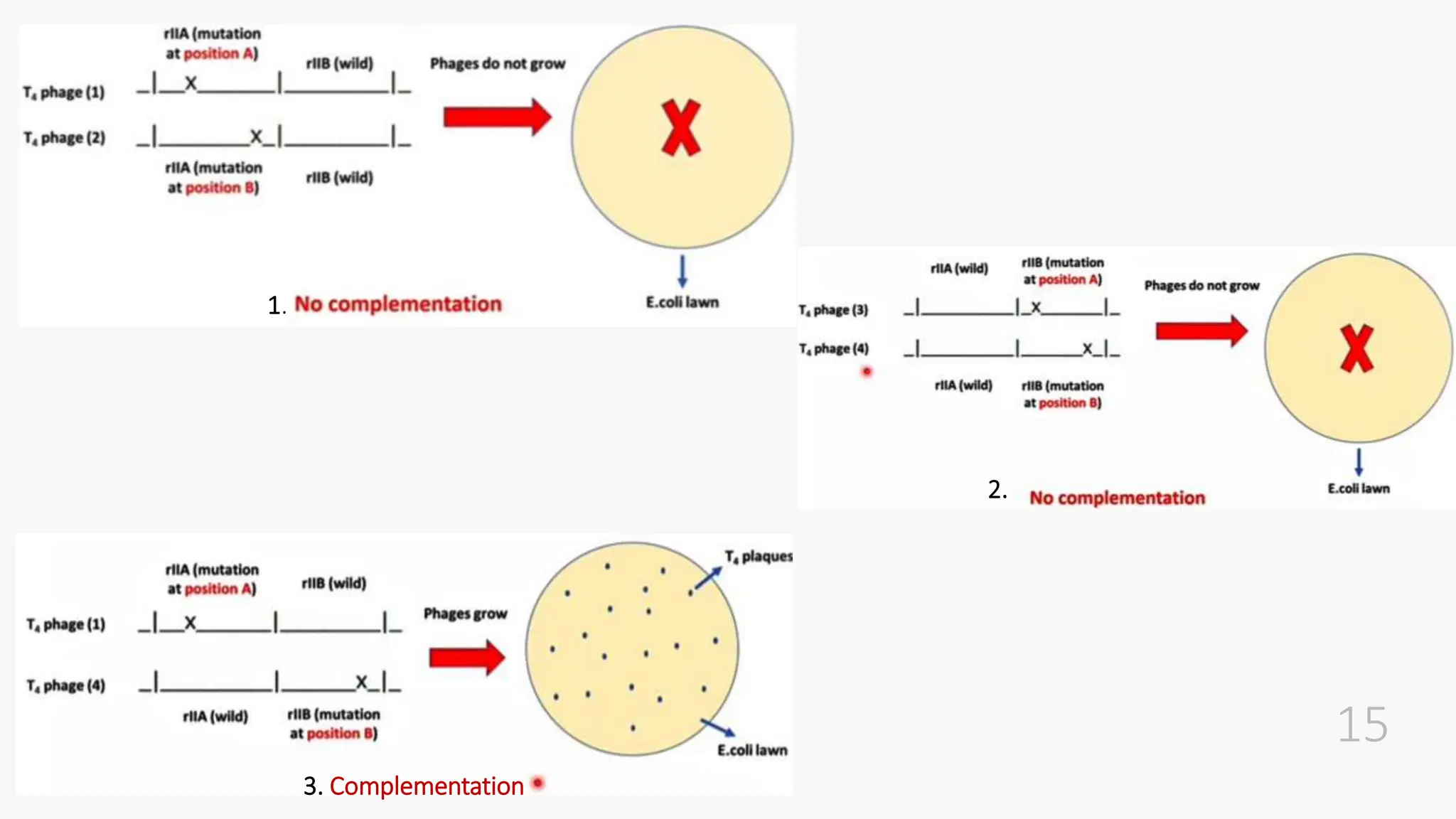
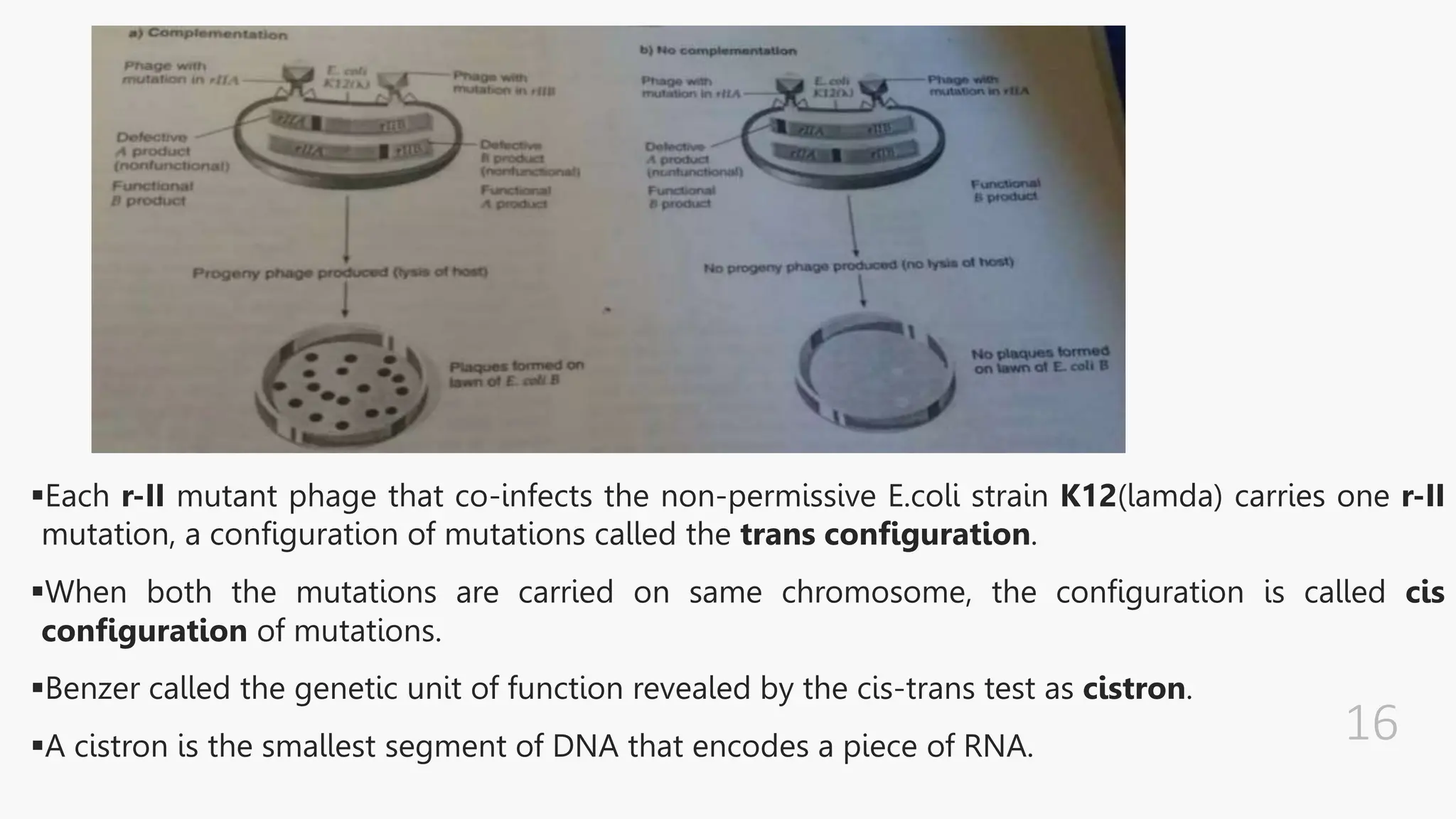
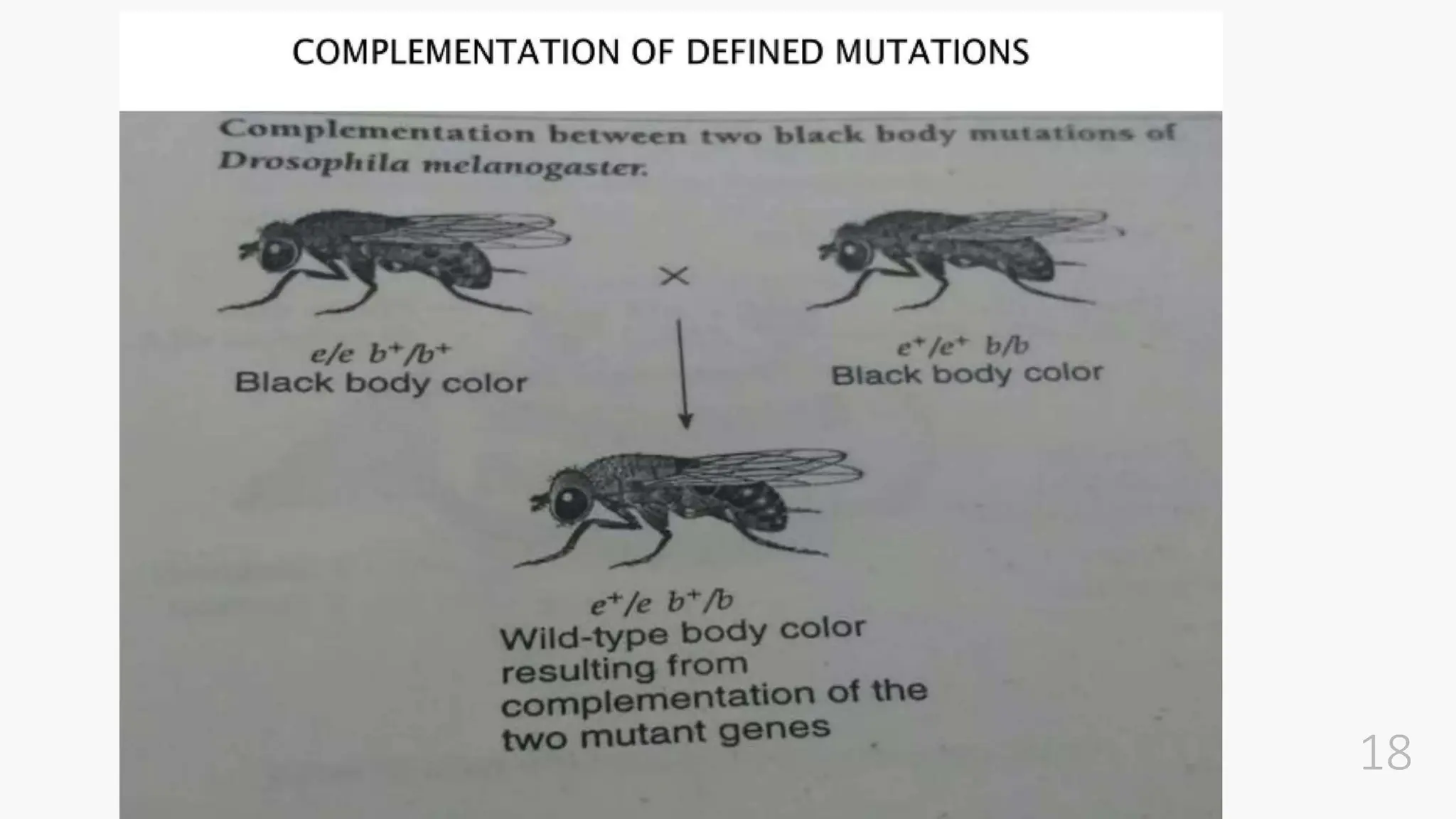
The document discusses insertional inactivation, a technique in recombinant DNA technology where foreign DNA is inserted into a gene to disrupt its function, used for screening cells with recombinant plasmids. It explains blue-white screening and antibiotic resistance, highlighting the selection of recombinant colonies based on colony color and antibiotic media. Additionally, it covers complementation tests to determine if mutations are in different genes and provides examples, including studies with Drosophila and phage mutants.