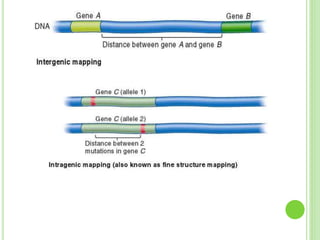
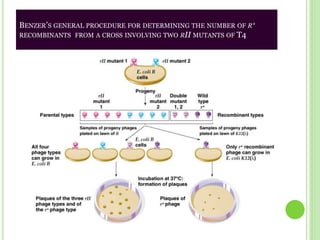
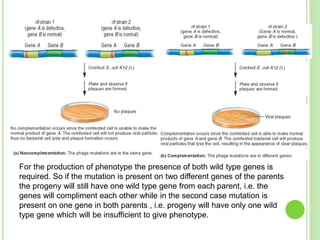
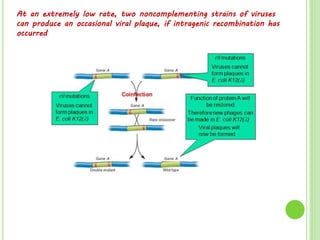
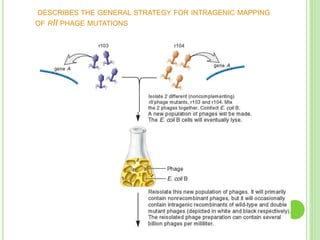
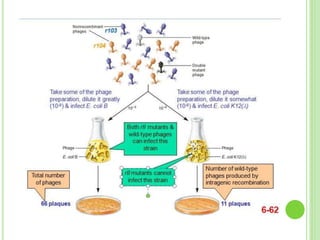
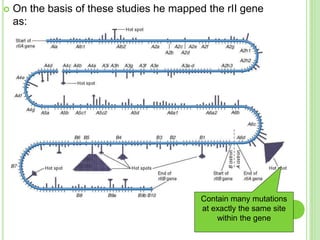
Benzer conducted experiments to study intragenic recombination within the rII gene of bacteriophage T4. He isolated rare recombinants that arose from exchanges between DNA of co-infecting phages. This allowed him to map mutations within the rII gene at high resolution. He determined that rII mutations occurred in two complementation groups, rIIA and rIIB, representing two different genes. Through deletion mapping, Benzer was able to localize many rII mutations to a short region within gene A or B. His work established the concept of the cistron as the smallest genetic unit.