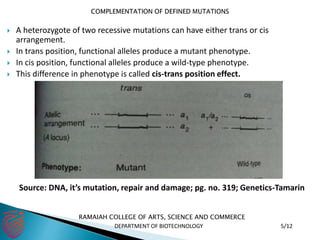
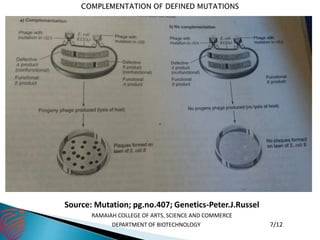
The document discusses complementation in genetics, where two strains with different homozygous recessive mutations can produce wild-type offspring if the mutations are in different genes. It also describes the complementation test, a method to determine if mutations are in the same or different genes, and introduces the concept of cis and trans configurations in heterozygotes. Additionally, examples from Drosophila melanogaster highlight how complementation can occur, allowing for the analysis of gene function.