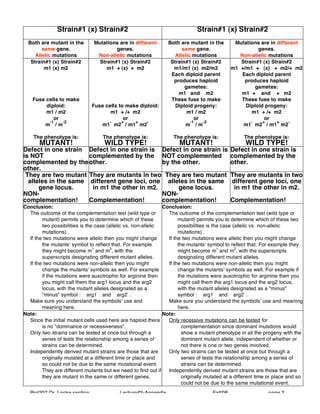
1. The document discusses complementation testing in genetics, which involves crossing two mutant strains to determine if their mutations occurred in the same or different genes.
2. If the mutations are in the same gene, the hybrid will be mutant, but if in different genes, the hybrid will have a wild type phenotype due to complementation.
3. The results of complementation tests allow researchers to classify mutations into complementation groups based on whether they fail to complement (allelic) or complement (non-allelic).