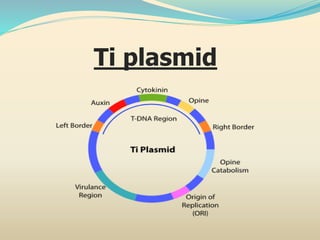
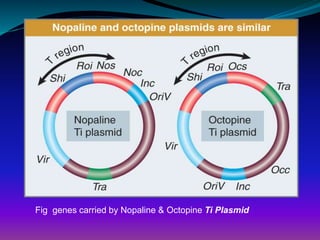
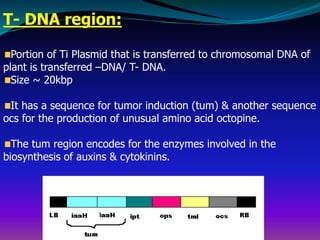
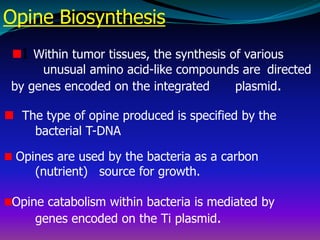
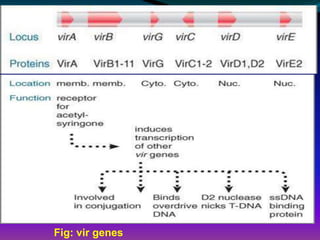
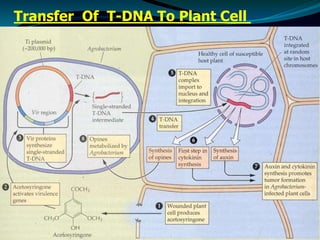
The document discusses the properties, classification, and mechanisms of Agrobacterium tumefaciens and its Ti plasmid, which is crucial for genetic engineering in plants. It highlights the structure and function of T-DNA in tumor induction and opine synthesis, as well as the limitations of using wild-type Ti plasmids as vectors due to size and other factors. The document emphasizes Agrobacterium's role as a natural genetic engineer with the ability to integrate DNA into plant chromosomes.