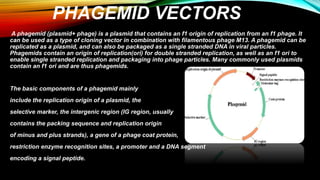
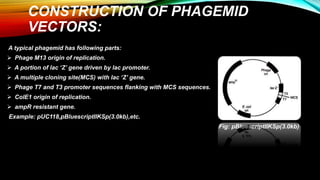
Phagemids are cloning vectors that have properties of both plasmids and bacteriophages. They contain an origin of replication for double-stranded DNA replication as plasmids do, as well as an f1 origin that allows for single-stranded replication and packaging into phage particles. Phagemids are used for cloning, expression, sequencing, and generating RNA probes. They offer advantages over other phage vectors such as larger cloning capacity and stability. A typical phagemid contains origins of replication from phage M13 and a plasmid, antibiotic resistance, a multiple cloning site, and phage promoters.