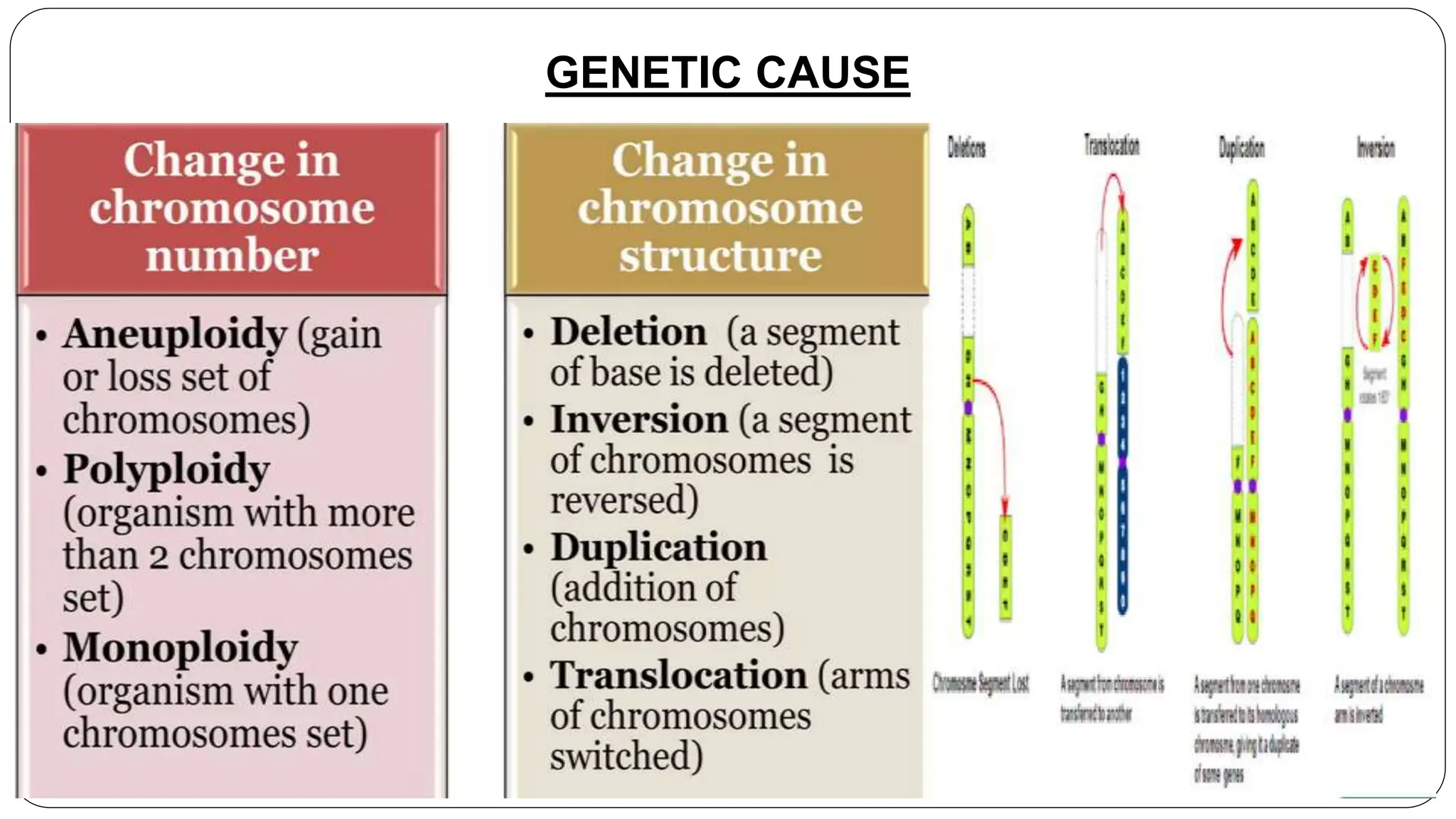
Somaclonal variation refers to genetic variability observed in plants regenerated from tissue culture, often leading to new phenotypes with desirable traits such as disease resistance, improved yield, and stress tolerance. The variation can arise from factors including chromosomal changes, spontaneous mutations, and alterations in nucleotide pools during culture conditions. Techniques for inducing and selecting somaclonal variants involve both in-vitro and non-in-vitro methods, with applications in creating agriculturally beneficial crops.