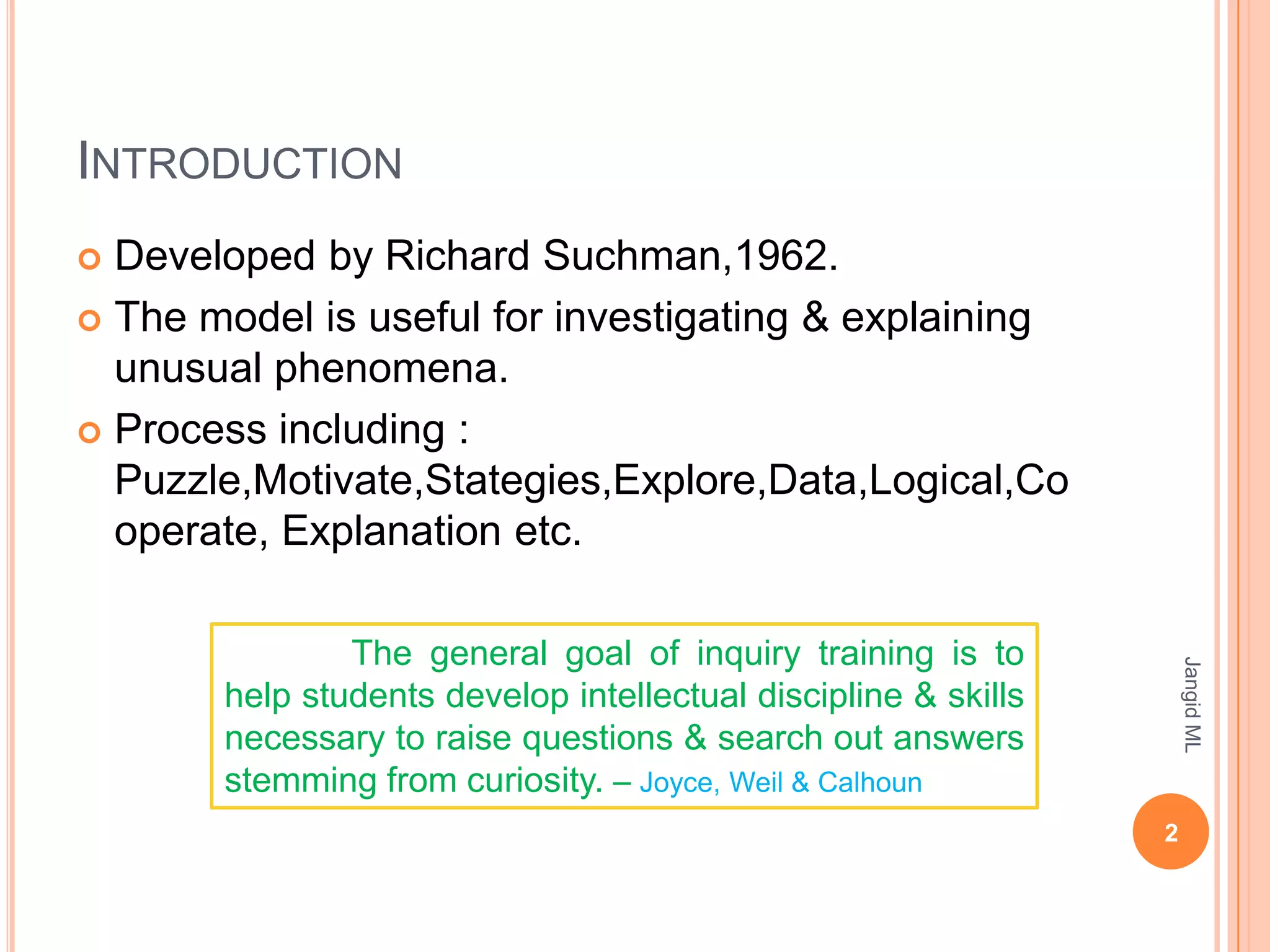
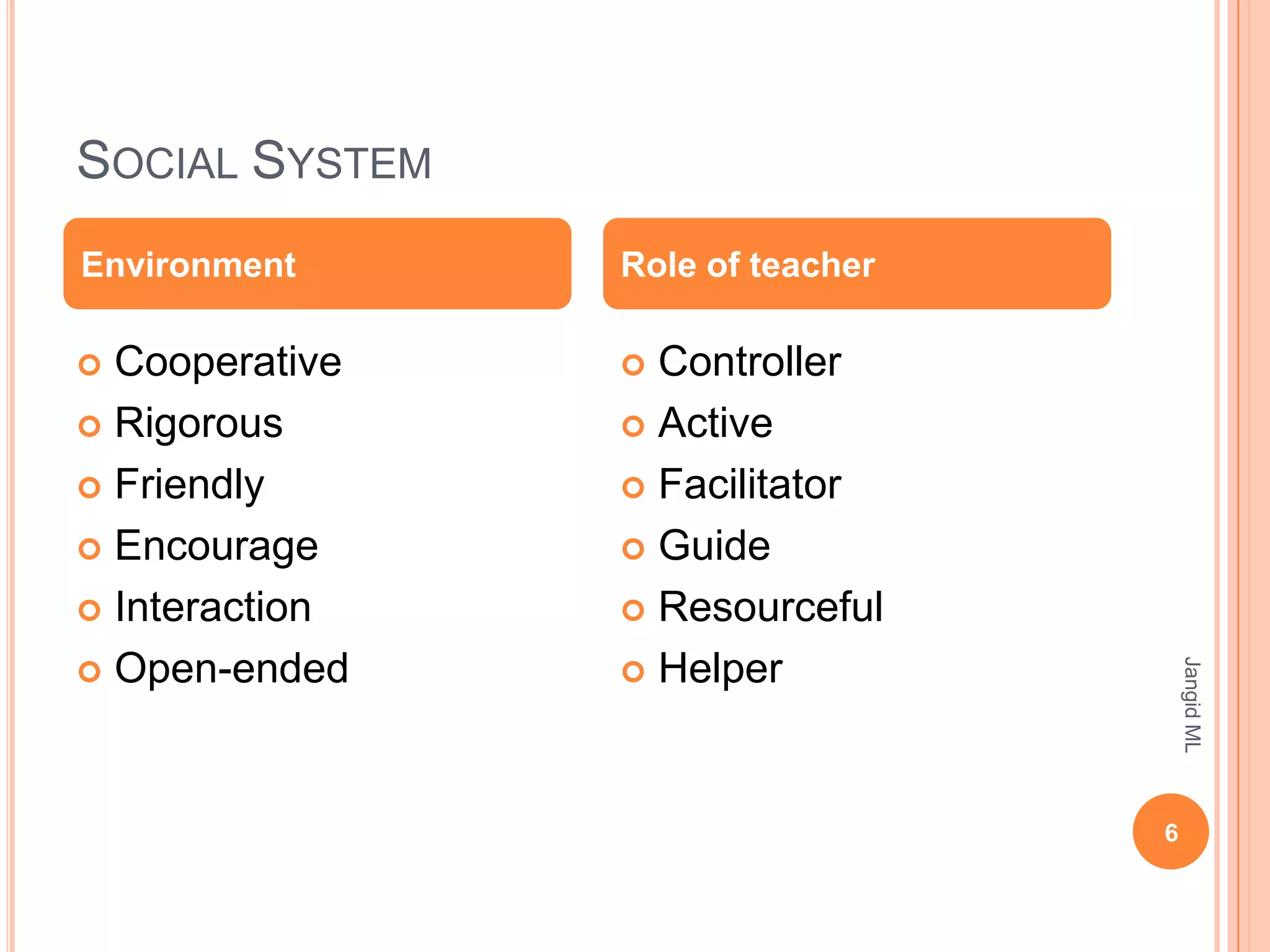
The Inquiry Training Model was developed by Richard Suchman in 1962 to help students develop intellectual discipline and skills for investigating unusual phenomena. It involves raising questions and searching for answers driven by curiosity. The model expects students to be curious, active, creative, conduct experiments, understand problems and puzzles, and solve problems with guidance. It follows five phases: confronting the problem, gathering data through verification, gathering data through experimentation, organizing and formulating, and analyzing the inquiry process. The goal is to help students learn through an interactive, cooperative environment with optimal teacher support focused on intellectual processes and strategies of inquiry.