This document discusses David Ausubel's theory of meaningful verbal learning and advance organizers. It provides three key points:
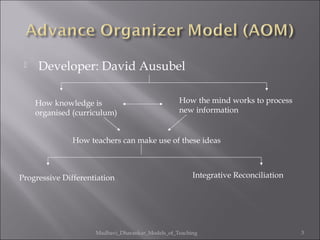
1. David Ausubel developed the theory of meaningful verbal learning and advance organizers, which focuses on how knowledge is organized and how the mind processes new information.
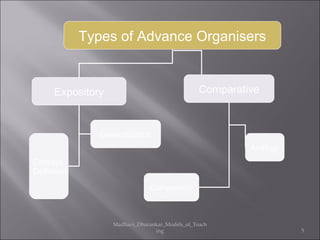
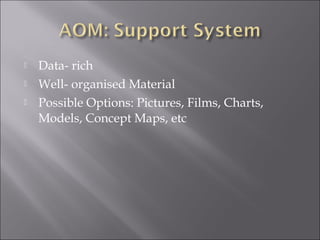
2. An advance organizer presents abstract and general information before a learning task to facilitate the assimilation of new knowledge. It establishes a cognitive framework to anchor and clarify new concepts.
3. Using advance organizers can improve conceptual structures and meaningful assimilation of ideas. It also nurtures interests in inquiry and habits of precise thinking.