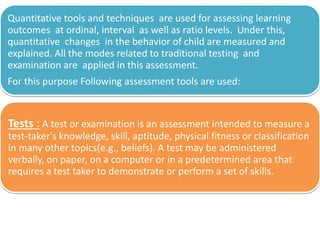
This document discusses and compares quantitative and qualitative assessment tools used to evaluate learning outcomes. Quantitative tools like tests, surveys, checklists and questionnaires focus on measurable data presented numerically. They are more objective but require statistical analysis expertise. Qualitative tools like interviews, observations, and focus groups provide descriptive data to understand experiences and meanings at a nominal level. They require skilled administration but provide depth, context, and insight not obtainable through quantitative methods alone. Both approaches have advantages and limitations depending on the assessment needs.