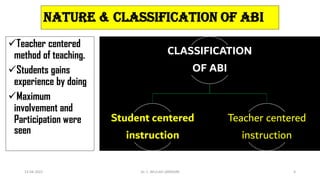
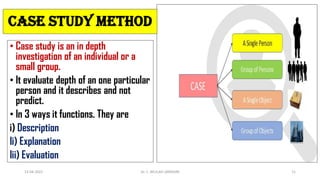
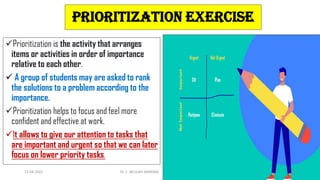
Activity-based instruction (ABI) is an interactive teaching method that allows students to learn at their own pace through participation in various activities, promoting engagement and skill development. It has roots in World War II, with David Horsburgh being a pioneer through his Neel Bagh school in India, where diverse curricula were implemented. ABI encourages collaboration and communication among students, fostering a more hands-on learning experience.